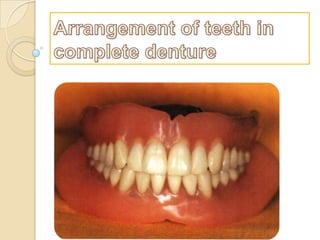
Arrangement of teeth in complete denture
- 2. HISTORY Skillfully designed dentures were made as early as 700 BC.and Talmud a collection of books of hebrews in 352-407 AD mentioned that teeth were made of gold ,silver,and wood. Egypt was the medical center of ancient world, the first dental prosthesis is believed to have been constructed in egypt about 2500 BC. Hesi-Re Egyptian dentist of about 3000 BC 2Dr Abhilash
- 3. Front and back views of mandibular fixed bridge, four natural incisor teeth and two carved ivory teeth Bound With gold wire found in Sidon-ancient Phoenicia about fifth and fourth century BC. 3Dr Abhilash
- 4. WOOD For years, dentures were fashioned from wood . Wood was chosen -readily available -relatively inexpensive -can be carved to desired shape Disadvantages -warped and cracked in moisture -esthetic and hygienic challenges -degradation in oral environment 4Dr Abhilash
- 5. Wooden denture believed to be carved out of box wood in 1538 by Nakoka Tei a Buddist priestess Wooden dentures 5Dr Abhilash
- 6. Bone Bone was chosen due to its availability, reasonable cost and carvability . It is reported that Fauchard fabricated dentures by measuring individual arches with a compass and cutting bone to fit the arches . It had better dimensional stability than wood, esthetic and hygienic concerns remained. 6Dr Abhilash
- 7. IVORY Denture bases and prosthetic teeth were fashioned by carving this material to desired shape Ivory was not available readily and was relatively expensive. Denture bases fashioned from ivory were relatively stable in the oral environment They offered esthetic and hygienic advantage in comparison with denture bases carved from wood or bone. Carved ivory upper denture retained in the mouth by springs with natural human teeth cut off at the Neck and riveted at the base. 7Dr Abhilash
- 8. Since ancient times the most common material for false teeth were animal bone or ivory,especially from elephants or hippopotomus. Human teeth were also used,pulled from the deceased or sold by poor people from their own mouths. Waterloo dentures 1788 A.D. Improvement and development of porcelain dentures by DeChemant. G.Fonzi an italian dentist in Paris invented the Porcelain teeth that revolutionized the construction Of dentures.Picture shows partial denture of about 1830,porcelain teeth of fonzi’s design have been Soldered to a gold backing.8Dr Abhilash
- 9. One piece porcelain upper denture crafted by Dr John Scarborough,Lambertville,New Jersey 1868. 9Dr Abhilash
- 10. In 1794 John Greenwood began to swage gold bases for dentures. Made George Washington's dentures. George washington’s last dental prosthesis. The palate was swaged from a sheet of gold and ivory teeth riveted To it.The lower denture consists of a single carved block of ivory. The two dentures were held togther by steel Springs. 10Dr Abhilash
- 11. In 1839 an important development took place CHARLES GOODYEAR discovered VULCANIZATION of natural rubber with sulphur(30%) and was patented by Hancock in england in 1843. NELSON GOODYEAR (brother of charles goodyear) got the patent for vulcanite dentures in 1864. . They proceeded to license dentists who used their material, and charged a royalty for all dentures made. Dentists who would not comply were sued. The Goodyear patents expired in 1881, and the company did not again seek to license dentists or dental products. Vulcanite dentures were very popular until the 1940s, when acrylic denture bases replaced them. 11Dr Abhilash
- 12. A set of vulcanite dentures worn by Gen. John J. (Blackjack) Pershing, commander of the American Expeditionary Forces in France during the First World War Set of complete dentures having palate of swaged Gold and porcelain teeth set in vulcanite. 12Dr Abhilash
- 13. In 1937 Dr. Walter Wright gave dentistry its very useful resin. It was polymethyl methacrylate which proved to be much satisfactory material tested until now. Dentures made of polymethyl methacrylate 13Dr Abhilash
- 14. DEFINITIONS Occlusion - It is the static relationship between the incising or masticating surfaces of the maxillary or mandibular teeth or tooth analogues [ GPT 7 ] Articulation - The static and dynamic contact relationship between the occlusal surfaces of the teeth during function is called as articulation 14Dr Abhilash
- 15. Development of occlusion in complete dentures differs from that present in natural dentition due to the difference in the support system 15Dr Abhilash
- 16. Differences between natural and artificial occlusion • Presence of periodontium in natural dentition • Teeth act individually in natural dentition and as a single unit on an unyielding base in a complete denture • Bilateral balance is deemed necessary in artificial occlusion but not in natural dentition 16Dr Abhilash
- 17. • Malocclusion in natural dentition may remain uneventful but evokes severe response in artificial occlusion • Non vertical forces are well tolerated in natural dentition but traumatic in artificial dentition • Incising with natural teeth is uneventful but in complete dentures affects all teeth and the base 17Dr Abhilash
- 18. • In natural dentition second molar is favoured for mastication but in a complete denture it is the first molar and second premolar which are favoured for mastication • Proprioception present in natural dentition but absent in artificial occlusion 18Dr Abhilash
- 19. Preliminary selection of Artificial Teeth Anterior teeth – Esthetic requirement Posterior teeth – Masticatory functional requirement Compatibility with surrounding oral environment Preliminary selection is based on: Size Form Color 19Dr Abhilash
- 20. SIZE Selection of Anterior teeth Size of the face Size of Maxillary arch Incisal papilla and the cuspid eminence Maxillomandibular relations Vertical distance between ridges 20Dr Abhilash
- 21. Selection of Posterior teeth Functional harmony with musculature Less buccolingual dimension Anteroposterior dimension 21Dr Abhilash
- 22. FORM Conform to the general outline of face Facial forms Square Square tapering Tapering Ovoid Sex Ageing 22Dr Abhilash
- 23. Form of Posterior teeth Occlusal surface – primary concern Balanced in centric and eccentric positions – cusp form Disocclusion in eccentric position – Cusp or monoplane Balanced in centric position only – Monoplane Arrangement of artificial posterior teeth for functional harmony depends on a thorough understanding of 23Dr Abhilash
- 24. SHADE Harmony with color of skin, eyes and hair Shade of posterior teeth should harmonize with shade of anterior teeth Bulk influences the shade . . . . 24Dr Abhilash
- 25. Horizontal orientation of Anterior teeth Insufficient support of lips Drooping of corner of mouth Deepening of nasolabial groove Deepening of sulci Reduction in prominence in philtrum Reduction in visible part of vermilion border 25Dr Abhilash
- 26. Excessive support of lips Stretched appearance of lips Elimination of contour of lips Distortion of lip and sulci Tendency of lip to dislodge the denture 26Dr Abhilash
- 27. Incisive papillae Midline of upper denture 27Dr Abhilash
- 28. Buccolingual position of posterior teeth Mainly determined by Neutral zone 28Dr Abhilash
- 29. If teeth located lingually . . . If teeth located buccally . . . 29Dr Abhilash
- 30. Vertical orientation If the upper lip is relatively long . . . Anterior teeth . Length and movement of upper lip 30Dr Abhilash
- 31. Lower lip is a better guide Cusp tips of canine and I premolar are even with lower lip - If lower anterior - above this level - If lower anterior 31Dr Abhilash
- 32. Maxillary anterior teeth are arranged according to phonetics 32Dr Abhilash
- 33. Posterior teeth Two basic anatomic guide - Orifice of Stenson’s Duct - Retromolar pad If occlusal level is too low If occlusal level too high Character of residual ridge 33Dr Abhilash
- 34. Inclination of teeth Labial surface of bone Profile form of the patient 34Dr Abhilash
- 36. ARRANGMENT OF TEETH The four principal factors that govern the positions of the teeth for complete dentures are (1) the horizontal relations to the residual ridges, (2) the vertical positions of the occlusal surfaces and incisal edges between the residual ridges, (3) the esthetic requirements, and (4) the inclinations for occlusion 36Dr Abhilash
- 37. Dr Abhilash 37 Guidelines for horizontal Placement of Anterior Teeth
- 38. Dr Abhilash 38 Role of incisive papilla & mid palatal suture It is found in Lingual embrasure b/t Maxi.C.I. Labial surface of maxillary incisors is approx. 8 to 10 mm anterior to incisive papilla. A transverse line bisecting the middle of I.P. passes through the tip of canine.
- 39. Dr Abhilash 39 Cuspid eminences When cuspid eminences are visible on cast, a line marking the distal of eminences co- incide with distal margin of cuspids. Relation to residual alveolar ridge Max. Anterior teeth are placed anterior to residual ridge, depending upon amount of resorption.
- 40. Dr Abhilash 40 Arch Form And Shape Square arch – C.I. in line with the canine Tapering arch – C.I. at a greater distance forward than canine Ovoid arch - in between
- 41. Dr Abhilash 41 Esthetics Vermilion border of upper lip. Mento-Labial & Naso-Labial groove. Everted upper lip. Corner of mouth (no drooping appearance)
- 42. Dr Abhilash 42 RELATION WITH THE UPPER LIP ◦ If set too far posteriorly Lip looks unsupported. Vermilion border would not be visible. ◦ If set too far anteriorly Lip would taut & stretch. Nasolabial fold may fill out. Incisal two-thirds of labial surface of teeth supports the lips.
- 43. Dr Abhilash 43 MEDIO- LATERAL POSITION Midline – midline of face passes between 2 upper & lower central incisors. Ala of nose – line dropped from the Ala passes through tip of canine.
- 44. Dr Abhilash 44 Guidelines for vertical Orientation of Anterior Teeth
- 45. Dr Abhilash 45 Role of upper lip Visibility of upper anterior teeth Incisal edges are visible by 1 to 2 mm below the upper lip at rest. Short or long or incompetent lip influences the amount of teeth visibility. Some racial types have fuller lips, others have thinner.
- 46. Dr Abhilash 46 Effect of aging In young pt, Incisal edges are visible by 1 to 2 mm below the upper lip at rest. While smiling or during speech,incisal & middle 1/3 are visible in normal person. With aging, tone of upper lip decreases, lesser amount of maxillary teeth visible and more of mandibular teeth become visible.
- 47. Dr Abhilash 47 Relationship of lower lip to anterior teeth Lower canine & Ist premolar should be even with lower lip at the corner of mouth. If lower teeth are high -Anterior plane of occlusion may be too high -excessive VDO -Excessive vertical overlap reverse is true if mandibular teeth are below lower lip at corner of mouth.
- 48. Dr Abhilash 48 Guides to position of posterior teeth
- 49. Dr Abhilash 49 Retromolar pad The maximum extension posteriorly of any artificial tooth is anterior border of Retromolar pad. to avoid having a tooth over an incline which results in denture sliding. Sometimes space is available for only 3 mandibular posterior teeth, then drop Ist premolar.
- 50. Dr Abhilash 50 Retromolar pad
- 51. Dr Abhilash 51 Maxillary Tuberosity Teeth should not be set on the Tuberosity as it can lead to lever imbalance and might lead to cheek bite in posterior region. When space permits,4 maxillary posterior teeth can be placed opposing 3 mandibular posterior teeth, to provide support to cheeks
- 52. Dr Abhilash 52 OCCLUSAL PLANE Anterior occlusal plane parallel to interpupillary line & at the level of commissure. - posterior occlusal plane should be at the level of 2/3 the height of retromolar pad
- 53. Dr Abhilash 53 Stenson’s duct –it exits at Bu mucosa in the region of 2nd Molar. Occlusal plane is located of 1/8 of an inch below this. With these anterio-posterior guidelines,occlusal plane is made parallel to lower mean foundation plane and Ala-Tragus plane. Height of occlusal plane is also influenced by- -length of lips -Ridge height -Amount of maxillomandibular space available
- 54. Dr Abhilash 54 Relationship with tongue Occlusal plane should be located in relation to lateral surface of tongue near demarcation zone b/w Dorsal keratinized mucosa & ventral nonkeratinized mucosa.
- 55. Dr Abhilash 55 Buccal Limit Teeth should not be set too far off the ridge. Placing too far Buccally can cause: - Cheek Biting - Esthetic problems due to obliteration of Buccal corridor. - Denture instability due to lever imbalance & muscle function.
- 56. Dr Abhilash 56 Lingual Limit Lingual cusps of molars are in alignment with Mylohyoid ridge. Placing too far lingually can cause ◦ Crowding of tongue. ◦ Tongue biting. ◦ Imbalance due to tongue function.
- 57. Dr Abhilash 57 Overjet & Overbite Class I – Normal , Class II – Retruded , Class III - Protruded
- 58. Dr Abhilash 58 Canine & Molar Relationship Mesial slope of cusp of upper canine opposes the distal slope of Lower canine cusp. OR Distal surface of lower canine is in line with tip of upper canine. M.B cusp of upper 1st molar opposes the Buccal groove of lower 1st molar.
- 59. Dr Abhilash 59 Buccal Corridor Space b/w buccal surface of posterior teeth & inner surface of cheeks. Excessive buccal corridor results when posterior teeth are set too far ligually. Resulting dark space appears excessive & unaesthetic. Inadequate buccal corridor occurs when posterior teeth are placed too far buccally, causing obliteration of buccal corridor.
- 60. Dr Abhilash 60 Canine-retromolar Pad Reference Line From tip of Canine to center of Retromolar pad. This designates centre of mandibular Ridge. Central fossae of mandibular Posterior teeth should coincide with this line OR This in turn corresponds to maxillary palatal cusps .
- 61. INDIVIDUAL ORIENTATION OF MAXILLARY TEETH 61Dr Abhilash
- 62. ARRANGING TEETH FOR COMPLETE DENTURE OCCLUSION Maxillary Central Incisor: The long axis of the tooth is perpendicular to the horizontal (labiolingual inclination) Its long axis slopes towards the vertical axis ( mesiodistal inclination) Slopes labially about 15 degrees when viewed from the side. Incisal edge is in contact with the 62Dr Abhilash
- 63. Teeth is set on the occlusal rim 63Dr Abhilash
- 64. Maxillary Lateral Incisor: Long axis slopes rather more towards the midline Inclined labially about 20 degrees when viewed from the side The neck is slightly depressed The incisal edge is about 1mm short of the occlusal plane. 64Dr Abhilash
- 65. 65Dr Abhilash
- 66. Maxillary Canine : Its long axis is parallel to the vertical axis when viewed from both the front and side or it may be slightly to the distal. The bulbous cervical half of the tooth provides its prominence. Its cusp is in contact with the horizontal plane. . The neck of the tooth must be prominent 66Dr Abhilash
- 67. 67Dr Abhilash
- 68. Dr Abhilash 68
- 69. Remaining maxillary teeth are arranged on the other side of the arch to complete the anterior set up. To maintain the set teeth in position, the wax supporting the teeth must be heated and sealed both to the teeth and to the record base. 69Dr Abhilash
- 70. 70Dr Abhilash
- 71. Dr Abhilash 71
- 72. First premolar: Long axis is parallel to the vertical axis when viewed from the front or the side. Its palatal cusp is about 1mm short of, and its buccal cusp in contact with, the occlusal plane. 72Dr Abhilash
- 73. Second premolar: Its long axis is parallel with the vertical axis when viewed from the front or the side. Both buccal and palatal cusps are in contact with the occlusal plane. 73Dr Abhilash
- 74. First molar: Long axis slopes buccally when viewed from the front, and distally when viewed from the side. Only mesiopalatal cusp is in contact with the occlusal plane. 74Dr Abhilash
- 75. Second molar: Long axis slopes buccally more steeply than the first molar when viewed from the front, and distally more steeply when viewed from the side. All four cusps are clear of the occlusal plane, but the mesiopalatal cusp is 75Dr Abhilash
- 76. Maxillary teeth set checked on occlusal plane 76Dr Abhilash
- 77. 77Dr Abhilash
- 78. Dr Abhilash 78
- 79. Dr Abhilash 79
- 80. ORIENTATION AND ARRANGEMENT OF MANDIBULAR TEETH 80Dr Abhilash
- 81. Arranging the Mandibular Teeth Mandibular central incisor: Long axis slopes slightly towards the vertical axis when viewed from the front. Slopes labially when viewed from the side. Incisal edge is about 2mm above occlusal plane 81Dr Abhilash
- 82. Mandibular lateral incisor: Long axis inclines to vertical axis when viewed from the front Slopes labially when viewed from side but not so steeply as the central incisor. Incisal edge is about 2mm above occlusal plane 82Dr Abhilash
- 83. Mandibular canine: Long axis leans very slightly towards the midline when viewed from the front. Leans very slightly lingually when viewed from the side Neck is slightly prominent and the tooth is tilted to the distal Tip at same level as incisors. 83Dr Abhilash
- 84. Dr Abhilash 84
- 85. Dr Abhilash 85
- 86. Teeth arrangement checked in patient mouth 86Dr Abhilash
- 87. The retromolar pad is exposed and points are marked on pounds li joining the cannine to retromolar pad. 87Dr Abhilash
- 88. First molar: Long axis leans lingually when viewed from the front and mesially when viewed from the side. All cusps are at a higher level above the occlusal plane than those of the second premolar. The buccal and distal cusps are higher than the mesial and lingual. The mesiobuccal cusp occludes in the fossa between upper second premolar and first molar. 88Dr Abhilash
- 89. Dr Abhilash 89 Mandibular 1st Molar Facial: Long axis leans mesially, when viewed from side. Proximal : Long axis inclines Lingually, when viewed from front. Occlusal: Buccal cusps are higher than Lingual cusps.Distal cusps are higher than Mesial cusps.
- 90. 90Dr Abhilash
- 91. Second premolar: Long axis is parallel to the vertical plane when viewed from both the front and the side. Both cusps are about 2mm above the occlusal plane. The buccal cusp contacts the fossa between the two upper premolars. 91Dr Abhilash
- 92. Dr Abhilash 92 Mandibular 2ed Premolar Facial & Proximal : Long axis is vertical from both views. Occlusal : Both cusps are about 1-2mm above Occlusal plane
- 93. 93Dr Abhilash
- 94. First premolar: Long axis is parallel to the vertical plane when viewed from the front and the side. Its lingual cusp is below the horizontal plane Its buccal cusp about 2mm above it as it contacts the mesial marginal ridge of the upper first premolar. 94Dr Abhilash
- 95. Dr Abhilash 95 Mandibular Ist Premolar Facial : Long axis is parallel to vertical plane. Proximal : Long axis is parallel to vertical plane. Occlusal : Bu cusp is above the occlusal plane, whereas Li cusp is below occlusal plane.
- 96. 96Dr Abhilash
- 97. Second molar: Lingual and mesial inclination of the long axis is more pronounced than in the case of the first molar. All the cusps are at a higher level above the occlusal plane than those of the first molar, the distal and buccal cusps more so than the mesial and lingual. The mesiobuccal cusp contacts the fossa between the two upper molars. 97Dr Abhilash
- 98. Dr Abhilash 98 Mandibular 2nd Molar Facial : Mesial inclination is more than 1st molar. Proximal : Lingual inclination is slightly more than 1st molar. Occlusal : Buccal cusps are higher than Lingual. Distal cusps are higher than Mesial.
- 99. 99Dr Abhilash
- 100. 100Dr Abhilash
- 101. Key of occlusion Cannine key of occlusion ◦ The distal arm of the lower cannine should align with the mesial arm of the upper cannine. 101Dr Abhilash
- 102. Molar key of occlusion ◦ The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary permanent molars should coincide with the mesiobuccal groove of the mandibular permanent molar 102Dr Abhilash
- 103. Overjet & overbite Overjet denotes the distance between the upper & lower incisor measured in horizontal plane - 2mm Overbite denotes the vertical overlap of the maxillary and mandibular anterior – 2mm 103Dr Abhilash
- 105. Dr Abhilash 105
- 106. Dr Abhilash 106
- 107. Dr Abhilash 107
