Design Thinking Method Sticker 2014
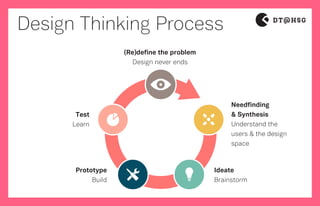
- 1. Design Thinking Process (Re)define the problem Design never ends Needfinding & Synthesis Understand the users & the design space Ideate Brainstorm Prototype Build Test Learn
- 2. Design space exploration Final prototype Critical function prototype Dark horse prototype D I V E R G I N G C O N V E R G I N G Funky prototype Functional prototype X-is finished prototype Design Thinking Phases
- 3. (Re)Define (Re)defining the problem asks you to simplify the visionary challenge into a more differentiated problem statement. By (re) defining the problem statement from the users perspective, you are able to focus on unanswered and specific areas during the needfinding phase. Framing what your team seeks to ‘un- derstand’ enables you to generate interview questions and to come up with places for observations that seem promising to understand the problem statement. Through constant and crit- ical reflection, the problem statement needs to be redefined as insights that provide new directions.
- 4. Design Space Map »» Establish a common understanding of your challenge »» Formulate key questions and discuss important aspects »» Keep modifying and expanding your map throughout your project »» Treat your map as a visual record of how your project evolves »» Revisit this map from time to time, so your team stays aligned Challenge (RE)D EFIN E
- 5. Stakeholder Map THINK OF Experts | Skeptics | Fans | Extreme Users | Lead Users | Non-Users | Mis-Users | Early Adopters | Innovators | Followers | Laggards | Customers | Partner Organizations | Competitors | Suppliers Who should we talk to? Who can we learn from? Where can we find them? (RE)D EFIN E/ N EED FIN D IN G
- 6. Needfinding Ask, listen, observe and engage! Understanding the people you are designing for is the foundation of human-centered innovation. By observing and directly engaging with users, your team learns about the way people think and the values they hold. Gaining empathy enables you to discover the emotions that guide peoples’ behavior and helps to capture physical manifestations of experiences. This allows to sense intangible meanings of user experiences and define latent needs. These insights evoke user-centered inspiration for ideation and prototyping.
- 7. »» Do desk research to get a first deep dive into your challenge (read articles, blogs, forums regarding your topic and look at your company’s website, …) »» Identify sources of inspiration »» Explore emerging trends and market opportunities »» Constantly share your research with the team (Diigo.com) »» Print out important numbers, quotes, and findings to share your desk research within the team »» Update your Design Space Map accordingly How To Become An Expert Instantly IN STAN T EXPERTISIN G
- 8. How To Interview Shortly introduce yourself. Tell the interviewee that you are interested in their experiences regarding your topic. What do you like about coffee (example topic)? Have you had coffee today? How was your experience? How did you buy it? How was the provided service? Can you describe your most memorable coffee experience? What happened? If you would design the ultimate coffee experience, what would that be like? INTRO KICK-OFF BUILD RAPPORT GRAND TOUR REFLECTION N EED FIN D IN G Intro Kick-Off Build rapport Grand tour Explore emotions Reflections Wrap up
- 9. Choose one who is leading the interview while the other is documenting Encourage storytelling: use open-ended questions like “Tell me about…” Always ask why! (“5 Whys”) Do not skip to a new topic before you’ve exhausted the current one Capture memorable quotes to illustrate your findings Look for inconsistencies and non-verbal clues (body-language, tone) Expand your notes as soon as possible after each interview Keep in mind: there might be a gap between what people say and what they do! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Interview Tips N EED FIN D IN G
- 10. How To Engage Self Test and Self Documentation »» make first-hand experiences and walk in the shoes of your customers »» engage in things and activities that people normally do »» do typical activities of your stakeholders »» use empathy tools Tips Don’t lose the balance between objectivity and subjectivity. You are still the design team and not the target group Empathize without judgment! 1. 2. N EED FIN D IN G
- 11. What To Observe I What do people do? What are the specific activ- ities they go through? Activities Environment Interactions Objects User What is the character and function of the space? What is the nature of inter- actions be- tween people, objects, and across distanc- es? What are the objects and devices people have in their environments? Who is there? What is their role and behavior? N EED FIN D IN G A E I O U
- 12. Distinguish interpretation from observation Don’t let your expectations affect your observations Look for anything that surprises you, that you may find irrational, that makes you question your assumptions, that prompts shifts in (routine) behaviors Take field notes, photos, videos, audio recordings Try to picture the scene from different perspectives Capture everything (notes) you experience, see, hear, feel, and taste After the observation - print pictures and put quotes on post-its Share the observations with your team 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Observation Tips N EED FIN D IN G
- 13. What To Observe II CONFUSION. Watch the users’ facial expressions. A confused look signals an opportunity to make the experience more intuitive. EXHAUSTION. Notice moments when people must work too hard (even if they don’t realize it) as they seek to solve their problem. PAIN POINTS. Look for moments that are actualy unpleasant or annoying. You will see it in the users’ facial expressions and body language. APPROPRIATION + WORKAROUNDS. Pay attention to adaptations and the use of a product for a new/different purpose. SKIPPED STEPS. If users skip a step, it might signal that they don’t need, want, or understand the value of that step. 1. 2. 4. 5. 6. N EED FIN D IN G What to lookfor duringobservations
- 14. Synthesize Synthesis is orientation and is therefore giving direction. After engaging with users it’s time to transform your data into in- sights. This is a difficult mental task to work out what connects to what, which ideas are more outliers on their own, and which concepts tie to the core of the design challenge. By looking at your findings, try to link similarities, contradictions, exceptions or patterns. Common themes provide inspiration for new, improved prototypes which solve uncovered user needs. The process of focusing your needfinding and testing data enables you to create a shared understanding and team knowledge.
- 15. Pattern Recognition Share your findings with your team! Share them while they are fresh. Which stories/behaviors are most intruiging? Listen actively! This helps to identify first patterns and repeating themes. Look for patterns, repetitions, exceptions. Group notes together that form a theme. Find titles for each cluster and phrase insights. Insights extrapolate individual stories into overall “truths”. N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS Storytelling Themes
- 16. Generating Insights interviews, observations, articles life experience, intuition values, morals learning about your user that you wouldn’t have assumed before your observations N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS I saw I know Insight+ =
- 17. Frameworks cheap expensive organic conventional N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS Venn Diagram 2x2 Matrix Coffee Sugar Cream Heaven
- 18. THINK & FEEL What really counts, major preoccupations, worries and aspirations SAY & DO Attitude in public, appearance, behavior towards others HEAR What friends, boss, or influencers say SEE Environment, friends, what the market offers PAIN Fears, frustrations, obstacles GAIN Wants/needs, measures of success Empathy Map Who‘s your user... N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS
- 19. Need Classification N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS I need to... Common needs …feel respected Context needs …confirm the validity of my work Activity needs …get feedback at the end of a project Qualifier needs …talk to my project supervisor How? Why?
- 20. Persona demographics like age, education needs and tasks goals and aspirations behavior, bugs and likes N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS Name & Picture typical statements
- 21. Generating a Point of View (POV) N EED FIN D IN G / SYN TH ESIS User + Need + insight = Persona Problem POV
- 22. Ideate Ideation is the mode of generating a large quantity of diverse ideas. Mentally, it represents the process of “going wide” which enables to explore a broad solution space. Brainstorming is a renowned method to come up with a lot of ideas. It leverages collective thinking of your team by engaging with each other, listening, and building on each others ideas. Generating ideas based on specific user needs and insights provides the fuel and source material for building rapid prototypes in order to get relevant innovations into the hands of your users.
- 23. Brainstorming Tips ID EATE DEFINE GOALS & STATE THE PROBLEM. Start by defining a clear, concise statement that explains the purpose of the session. Make sure the problem statement isn’t too specific as this can limit creativity. IDEATE INDIVIDUALLY. Instead of immediately shouting out ideas in a group setting, allow to generate ideas individually for a fixed amount of time. Then come together, share and build on each others ideas. CATEGORIZE AND SYNTHESIZE. It’s crucial to move forward with the ideas that you generate. Categorize common themes and decide on evaluation criteria that allow you to identify the most promising ideas for prototyping and testing.
- 24. Go for quantity Defer judgement Encourage wild ideas Be visual Build on the ideas of others (Yes, AND...) Stay focused on topic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Brainstorming Rules ID EATE
- 25. Prototype Build to think! Prototypes are tools to have a conversation around. Prototyping gets ideas and explorations out of your head into the physical world. A prototype can be anything that takes an experienceable form – a role play activity, a paper wireframe or even a sketch or storyboard. Creating quick, low-resolution prototypes allows your team to test assump- tions early and learn without investing a lot of time and money. Rapid prototypes also enable to refine ideas together with the user and gain deeper empathy, by allowing people to interact with a tangible version of your vision.
- 26. Prototypes Prototyping is a tool to deepen your understanding of the design space and your user, even at a pre-solution phase of your project. Identifying a variable to explore encourages you to break a large problem down into smaller, testable pieces. »» Paper prototypes »» Customer Journey »» Storyboards »» Graphics and interface mock-ups »» Role Play »» Videos »» And many more PRO TO TYPE
- 27. Prototypes PRO TO TYPE »» RIGHT. Think about the goal that is to be reached with the respective prototype. Consider which aspect the prototype is to represent and what is an appropriate method for creating this prototype. »» RAPID. Turn your ideas quickly into low cost and effort prototypes. »» ROUGH. Get things built fast and cheap, a scribble or artefact not looking pretty, to see what people think by testing your idea. Principles Versions »» FORM - “looks like”. This relates to size, proportions, aesthetics or ergonomics of a product or service. »» ACTION - “works like”. This relates to the functionality or interplay of components. BEHAVIOR - “behaves like”. This embodies the interactivity with the user. »» CONTEXT - “has a relationship to”. This relates to the situation-dependent use (action + behavior).
- 28. Prototyping Tips PRO TO TYPE One question, one prototype Build fast, before overthinking your idea Stop before it’s perfect Cannibalize as much ideas as possible Don’t fall in love with your prototype Always build and share more than one prototype Create to provoke and persuade Break rules, laws and facts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
- 29. Test Testing is the chance to refine solutions together with the user. It is another opportunity to gain empathy through observa- tion and engagement and often yields unexpected insights. Testing is the mode in which the low-resolution artifacts are put into practice by placing the prototype in the appropriate user context. Handing over a prototype into the users’ hands, observing how they interact with it and listening to what they say, allows your team to discover new insights and gain deeper understanding of hidden user needs.
- 30. Testing Tips TEST SHOW, DON’T TELL. Communicate your vision in an impactful and meaningful way by creating experiences, using illustrative visuals, and telling good stories. COLLABORATE TO INNOVATE. Bring together innovators with various backgrounds and viewpoints. Enable breakthrough testing insights in order to allow solutions that emerge from the diversity. EMBRACE FEEDBACK. Testing is not simply a way to validate your idea. We test to learn. Not only do we not get the solution right, but we sometimes also fail to frame the problem correctly. Testing inspires to reframe and focus your point of view.
- 31. Arrange your feedback and draw a mini-synthesis in order to decide what to take further into your next iteration. USER WONDERS USER CRITICIZES USER IDEATES Feedback Capture Grid TEST USER LIKES
