Uveitis Eye presentation- Darayus
- 1. Anterior Uveitis by;Anterior Uveitis by; Darayus P.GAZDERDarayus P.GAZDER
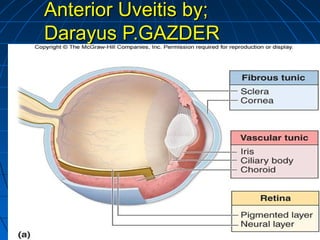
- 2. Anatomy and diseases of the uveaAnatomy and diseases of the uvea Anatomy: Uvea is the vascular coat of eye ball and lies between the sclera and retina. Uvea is composed of three parts 1) Iris, 2) Ciliary body 3) Choroid. These three portions are intimately connected and a disease of one part also affects the other portions though not necessarily to the same degree. DPG
- 4. 1) Iris: •Iris is a circular diaphragm placed in the anterior part of the eye ball and perforated in the center i.e. pupil.(4mm in diameter) •It is slightly pushed forward by the lens which gives it the appearance of a truncated cone, •It arises from the middle of anterior surface of ciliary body.
- 5. The anterior surface of iris is divided into 2 zones by a zigzag line called collarets Anterior surface has two zones: 1) Pupillary zone: is flat and has a dark border at the pupillary margin , known as papillary ruff. It is smooth and flat. Junction of papillary and ciliary zone is marked by a smooth ridge known as collaret. 2) Ciliary zone: It presents a series of radial streaks (Due to underlying radial blood vessels and crypts). Crypts are depressions, where endothelial cells are missing.
- 6. Structure: 1.Anterior limiting layer: is anterior most condensed part of stroma and contains melanocytes and fibroblasts. The definitive colour of iris depends on this layer 2.Stroma: Consists of loosely arranged CT, in which are embedded the SPM, DPM, vessels, nerves, pigment cells and other cells a)Sphinter pupillae: forms 1 mm broad circular band surrounding the pupil. Its supplied by parasympathetic nerve fibers, through the 3rd nerve and causes constriction of pupil. b) Dilator pupillae: are radial fibers extending from root of iris to pupillary margin. Its supplied by cervical sympathetic nerves and causes dilation of pupil. 3.Posterior epithelium consists of 2 layers of pigmented epithelium situated in the posterior surface of iris. Function of the iris: 1- Regulates the entry of light into the eye by changing the size of papillary aperture.
- 7. Forward continuation ofForward continuation of choroidchoroid Triangular in shape:Triangular in shape: Anteriorly gives attachmentAnteriorly gives attachment to the iristo the iris Outer side lies against scleraOuter side lies against sclera Inner side towards theInner side towards the posterior chamberposterior chamber and vitreousand vitreous Ciliary bodyCiliary body
- 8. It is divided into two portions anterior (pars plicata ) and posterior (pars plana). A) Pars Plicata: Anterior 1/3rd (about 2mm) which consists of: 1) Ciliary muscle, non striaded consisting of: 1. Longitudinal fibers. 2. Circular fibers. 3. Radial fibers. 3. Radiating fibers.
- 9. Meridional fibers on contraction pull the suprachoroidal forwards and release the suspensory ligament allowing the lens to become more convex as in accommodation. 2) The pars plicata has about 70 ciliary processes. They secrete aqueous. 3) Stroma consisting of CT, pigments and blood vessels. B) Pars Plana: posterior 2/3rd (4mm) which consists of pigmented and non pigmented epithelium. Functions of ciliary body: 1. Brings about accommodation.(CM) 2. Formation of aqueous.(CP)
- 10. 3) Choroid: Choroid is the analogue of pia-arachnoid of the brain and serves the same purpose of supplying nutrition to the neural portion of eye i.e. retina. Up to the outer plexiform layer. Choroid is composed of five portions. 1.The outer most is SUPRACHOROIDEAL LAMINA, between the choroid and sclera. It’s a membrane of collagen fibres, macrophages and fibroblasts. Deeper to it are three vascular layers. 2. Layer of LARGE BLOOD VESSELS is outer most. 3. Next comes MEDIUM SIZED BLOOD VESSELES. 4. and SMALL BLOOD VESSELES or CHOROIO-CAPILLARIES. Layer of choriocapillaries is the most important. It serves to provide nutrition to the outer layers of retina. The choriocapillaries are much wider than the capillaries elsewhere. Their diameter varies from 10 to 30 microns. 5. The innermost layer is avascular known as MEMBRANE of BRUCHS. This is composed of elastic and cuticular lamina and pigment epithelium of retina is intimately attached to it. DPG
- 13. UveitisUveitis It is an inflammation of the uveal tract.It is an inflammation of the uveal tract. Anterior Uveitis is defined as, InflammationAnterior Uveitis is defined as, Inflammation of the uveal tract from the iris up to theof the uveal tract from the iris up to the plars plicata of ciliary body.plars plicata of ciliary body. Includes:Includes: a) Iritis; Inflammation of irisa) Iritis; Inflammation of iris b) Iridocyclitis; Inflammation of iris and parsb) Iridocyclitis; Inflammation of iris and pars plicata of ciliary body are involved.plicata of ciliary body are involved. The most common form of intraocular inflammatory diseaseThe most common form of intraocular inflammatory disease Highest in age range 20-50 (20-30 is peak)Highest in age range 20-50 (20-30 is peak) UnilateralUnilateral One of the serious “red eye” conditionsOne of the serious “red eye” conditions DPG
- 14. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Classification (ANATOMICAL)Classification (ANATOMICAL) Uveitis by location:Uveitis by location: • Anterior UveitisAnterior Uveitis IritisIritis IridocyclitisIridocyclitis • Intermediate UveitisIntermediate Uveitis Pars planitisPars planitis • Posterior UveitisPosterior Uveitis ChoroiditisChoroiditis RetinitisRetinitis VasculitisVasculitis • PanuveitisPanuveitis DPG
- 15. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Classification (CLINICALLY)Classification (CLINICALLY) Uveitis by time course:Uveitis by time course: • AcuteAcute < 6 weeks duration< 6 weeks duration May be recurrentMay be recurrent • ChronicChronic > 6 weeks duration> 6 weeks duration White eyeWhite eye Mild signs of inflammationMild signs of inflammation Mild or no symptomsMild or no symptoms DPG
- 16. GranulomatousGranulomatous:: Contains epitheloid, giant,Contains epitheloid, giant, lymphocyteslymphocytes Non granulomatous:Non granulomatous: Polymorpholeukocytes cellsPolymorpholeukocytes cells HistologicallyHistologically
- 17. 1) Infective:1) Infective: Microorgansim enters the uveal tract via bloodMicroorgansim enters the uveal tract via blood Infective agents includeInfective agents include Bacteria: Tb, Syphilis, leprosyBacteria: Tb, Syphilis, leprosy Virus: Herpes ZosterVirus: Herpes Zoster Fungi: Candida albicans (IC PT)Fungi: Candida albicans (IC PT) Worms: toxocariasisWorms: toxocariasis 2) Traumatic: usually secondary to a direct blow from a blunt object 3) Drugs: Rifabutin, sulfonamides, pamidronate Etiology:Etiology: DPG
- 18. 4) Inflammatory causes — HLA B-27 associated — this HLA antigen is present in 30—70% of patients with anterior uveitis, half of whom have an associated systemic disease such as: ankylosing spondylitis psoriatic arthritis reactive arthritis inflammatory bowel disease Non-HLA-B27 associated uveitis may result from numerous underlying systemic conditions such as: sarcoidosis juvenile idiopathic arthritis Behçet disease Etiology:Etiology:
- 19. Acute Anterior UveitisAcute Anterior Uveitis Presentation: Sudden in onset,Presentation: Sudden in onset, A) Photophobia B) Unilateral pain C) Redness D) LacrimationA) Photophobia B) Unilateral pain C) Redness D) Lacrimation E) Decreased visionE) Decreased vision 2) Visual Acuity: is good at presentation except when there2) Visual Acuity: is good at presentation except when there is severe hypopyon [It is a feature of intense inflammation inis severe hypopyon [It is a feature of intense inflammation in which cells settle in the inferior part of the anterior chamber,which cells settle in the inferior part of the anterior chamber, simply it is pus in the anterior chamber]simply it is pus in the anterior chamber]
- 20. 3) External examination:3) External examination: Circumcorneal (ciliary) injection in acute anterior uveitisCircumcorneal (ciliary) injection in acute anterior uveitis has a violaceous hue {Dilation of ciliary +conjunctivalhas a violaceous hue {Dilation of ciliary +conjunctival vessels}vessels}
- 21. 4) Endothelial dusting:4) Endothelial dusting: by myriads of cells ( Gives aby myriads of cells ( Gives a dirty appearance to the cornea)dirty appearance to the cornea)
- 22. 4) Keratic precipitates (KP)4) Keratic precipitates (KP) are cellular deposits onare cellular deposits on the corneal epithelium.Their characteristics andthe corneal epithelium.Their characteristics and distribution may indicate the probable type of uveitis.distribution may indicate the probable type of uveitis. They are inflammatory cells that settle on the cornealThey are inflammatory cells that settle on the corneal epithelial layer.epithelial layer.
- 23. 5) Aqueous Cells5) Aqueous Cells seen in the anterior chamber:seen in the anterior chamber: Are indicative of active inflammation, more commonly seen inAre indicative of active inflammation, more commonly seen in iridocyclitis than iritis. Theyiridocyclitis than iritis. They are graded according to the numberare graded according to the number observed in an oblique slit beam. 3 mm long and 1 mm wide, withobserved in an oblique slit beam. 3 mm long and 1 mm wide, with maximum light intensity and magnification.maximum light intensity and magnification. .. 6) Anterior vitreous cells indicate Iridocyclitis.
- 24. 7) Aqueous Flare7) Aqueous Flare in anterior chamber( Tyndall phenomenon):in anterior chamber( Tyndall phenomenon): is due to scattering of light by proteins that have leaked into theis due to scattering of light by proteins that have leaked into the aqueous humour due to breakdown in blood aqueous barrier .aqueous humour due to breakdown in blood aqueous barrier . Its graded by interferometry using a flare meter.Its graded by interferometry using a flare meter.
- 25. Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Grading of cells and flare Grade Flare Cells 0 Complete absence No cells 1+ Faint flare (Barely detectable) 5 to 10 cells in view 2+ Moderate flare (Iris and lens details still clear) 10 to 20 cells in view 3+ Marked flare (Iris and lens details hazy) 20 to 50 cells in view 4+ Intense flare (Coagulated aqueous, no circulation, fibrinous exudate) 50+ cells in view 1) Improvement of inflammation is a 2step decrease in the level of activity or a decrease to inactive 2) Worsening is either a 2step increase in the level of activity or an increase to the maximum grade
- 26. 8) Low IOP: This is due to reduced secretion of aqueous by ciliary epithelium. Occasionally It may be elevated (Hypertensive uveitis) as in herpatic uveitis 9) Miosis: Is due to sphincter spasm b/c of inflammation and may cause formation of posterior synechiae unless the pupil is pharmacologically dilated 10) Prognosis: Its very good. Complications and poor visual prognosis are related to delay or inadequate management.
- 27. 11) Posterior synechiae:11) Posterior synechiae: Are adhesions between the iris and anterior lensAre adhesions between the iris and anterior lens capsule. Which may form with case during an attack ofcapsule. Which may form with case during an attack of acute anterior uveitis and also in eyes with moderate toacute anterior uveitis and also in eyes with moderate to severe chronic anterior uveitissevere chronic anterior uveitis
- 28. Posterior synechiae extending for 360 degrees around thePosterior synechiae extending for 360 degrees around the pupillary border give rise to a forward bowing of thepupillary border give rise to a forward bowing of the peripheral iris (Iris bombe)/ This may lead to the closure ofperipheral iris (Iris bombe)/ This may lead to the closure of the angle [Secondary glaucoma]/ As the trabecularthe angle [Secondary glaucoma]/ As the trabecular meshwork is blocked it causes an increase in Aqueous inmeshwork is blocked it causes an increase in Aqueous in anterior chamber, therefore increasing IOP!!anterior chamber, therefore increasing IOP!!
- 29. InvestigationsInvestigations CBC,Blood ESRCBC,Blood ESR Serological test for syphilis, toxoplasmosisSerological test for syphilis, toxoplasmosis and histoplasmosisand histoplasmosis Test for antinuclear antibodies, RH factorTest for antinuclear antibodies, RH factor Skin tests include tuberculin, toxoplasminSkin tests include tuberculin, toxoplasmin testtest Radiological investigations include X-rayRadiological investigations include X-ray chest forchest for pulmonary symptoms — e.g. sarcoidosis, tuberculosis sacroiliac joints and lumbar spine forsacroiliac joints and lumbar spine for suspected spondyloarthropathy as a diagnosis.
- 30. Chronic Anterior UveitisChronic Anterior Uveitis 1) Presentation:1) Presentation: insidious and patients areinsidious and patients are asymptomatic.asymptomatic. 2) External examination:2) External examination: Shows a white eye,Shows a white eye, occasionally the eye may be pink due to inflammatoryoccasionally the eye may be pink due to inflammatory activity.activity. 3) Aqueous flare:3) Aqueous flare: may be more marked than cells inmay be more marked than cells in eyes with prolonged activity and severity may act as aneyes with prolonged activity and severity may act as an indicator of disease activity.indicator of disease activity.
- 31. 4) KP:4) KP: (Waxy and greasy)(Waxy and greasy) Are clusters of cellular deposits on the corneal epitheliumAre clusters of cellular deposits on the corneal epithelium composed of epithelioid cells, lymphocytes and polymorphscomposed of epithelioid cells, lymphocytes and polymorphs Large KP:Large KP: are usually of the 'mutton fat' variety. With aare usually of the 'mutton fat' variety. With a greasy,greasy, waxywaxy appearance. Typically occurring inappearance. Typically occurring in granulomatous uveitis, occurring on the inferior 1/3granulomatous uveitis, occurring on the inferior 1/3rdrd of theof the corneal endothelium, in a paterrn known as Arlts triangle.corneal endothelium, in a paterrn known as Arlts triangle.
- 32. 5) Iris nodule:5) Iris nodule: are features of granulomatousare features of granulomatous inflammationinflammation Aggregations of lymphyocytes and epitheloid cells.Aggregations of lymphyocytes and epitheloid cells. a. Koeppea. Koeppe nodules are small and situated at the pupillary marginnodules are small and situated at the pupillary margin b. Busacca nodulesb. Busacca nodules involve the iris surfaceinvolve the iris surface
- 33. 6) Iris atrophy:6) Iris atrophy: Sectoral occurs in herpes simplex and zosterSectoral occurs in herpes simplex and zoster 7) Duration:7) Duration: Prolonged, inflammation may lastProlonged, inflammation may last for months to yearsfor months to years
- 34. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – ManagementManagement Goals of managementGoals of management • Preserve visual acuityPreserve visual acuity • Eliminate ocular inflammationEliminate ocular inflammation • Identify the source of inflammationIdentify the source of inflammation • Prevent formation of synechiaePrevent formation of synechiae • Control the IOPControl the IOP
- 38. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Complications:Complications: Four major complications existFour major complications exist • Cataract: Very common, causes opacities on theCataract: Very common, causes opacities on the lens(CAU)lens(CAU) • Secondary glaucomaSecondary glaucoma • Cyclitic membrane: Due to organization of exudateCyclitic membrane: Due to organization of exudate present behind the lenspresent behind the lens • Phthisis bulbi:Phthisis bulbi: Shrunken Disorganized eyeball, b/c ofShrunken Disorganized eyeball, b/c of ciliary shock there is a decrease in aqueous productionciliary shock there is a decrease in aqueous production and hypotony.and hypotony.
- 41. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – PathophysiologyPathophysiology Non-granulomatousNon-granulomatous • No pathogenNo pathogen • Responsive to topical treatmentResponsive to topical treatment GranulomatousGranulomatous • Pathogen inducedPathogen induced • Less responsive to topical treatmentLess responsive to topical treatment
- 42. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – PathophysiologyPathophysiology Inflammatory response causesInflammatory response causes breakdown of the blood-aqueousbreakdown of the blood-aqueous barrierbarrier Plasma protein -> FlarePlasma protein -> Flare Cells are WBCCells are WBC Fibrin derives from clotting factorsFibrin derives from clotting factors Deposition of cells and proteinsDeposition of cells and proteins • KPKP • HypopyonHypopyon
- 43. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – PathophysiologyPathophysiology Circumlimbal injectionCircumlimbal injection • Due to common blood supply with uvealDue to common blood supply with uveal vesselsvessels Lack of normal oxygen supply to irisLack of normal oxygen supply to iris • Vessel growth factors releasedVessel growth factors released • Leaky new vessel growth on irisLeaky new vessel growth on iris • Rubeosis IridisRubeosis Iridis • Extension of vessels into AC angleExtension of vessels into AC angle • ACGACG
- 44. Anterior Uveitis - IntroductionAnterior Uveitis - Introduction Associated with traumaAssociated with trauma Associated with systemic diseaseAssociated with systemic disease Has vision threatening complicationsHas vision threatening complications
- 45. Anterior Uveitis - PrevalenceAnterior Uveitis - Prevalence Risk factorsRisk factors • Associated systemic conditionsAssociated systemic conditions • Blunt traumaBlunt trauma • Previous historyPrevious history
- 46. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – History & SymptomsHistory & Symptoms History of blunt traumaHistory of blunt trauma History of associated systemic conditionHistory of associated systemic condition If acute:If acute: • Painful eyePainful eye • Watery eyeWatery eye • PhotophobiaPhotophobia • Mild to moderate reduction in visionMild to moderate reduction in vision If chronic:If chronic: • No symptomsNo symptoms
- 47. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Monocular Visual AcuityMonocular Visual Acuity measurementmeasurement Slit lamp biomicroscopySlit lamp biomicroscopy TonometryTonometry Gonioscopy?Gonioscopy?
- 48. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Monocular Visual Acuity measurementMonocular Visual Acuity measurement • Reduced to 6/6-6/9 in mild diseaseReduced to 6/6-6/9 in mild disease • Reduced to 6/9-6/30 in moderate diseaseReduced to 6/9-6/30 in moderate disease • Reduced to <6/30 in severe diseaseReduced to <6/30 in severe disease Visual Acuity reduced due to:Visual Acuity reduced due to: • Corneal oedemaCorneal oedema • Aqueous flareAqueous flare • Aqueous cellsAqueous cells • Cystoid macular oedema (CME)Cystoid macular oedema (CME)
- 49. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Slit lamp biomicroscopySlit lamp biomicroscopy • Circumlimbal injectionCircumlimbal injection • AC flare and cellsAC flare and cells • Keratic precipitates (KP)Keratic precipitates (KP) • Pupil miosisPupil miosis • HypopyonHypopyon • Band KeratopathyBand Keratopathy
- 50. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Slit lamp biomicroscopySlit lamp biomicroscopy • Fibrin in the ACFibrin in the AC • Cells in the anterior vitreousCells in the anterior vitreous • Peripheral Anterior Synechiae (PAS)Peripheral Anterior Synechiae (PAS) • Posterior synechiaePosterior synechiae • Rubeosis iridisRubeosis iridis • Mutton fat KP (granulomatous disease)Mutton fat KP (granulomatous disease) • Iris nodules (granulomatous disease)Iris nodules (granulomatous disease)
- 51. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs TonometryTonometry • IOP reducedIOP reduced • IOP unaffectedIOP unaffected • IOP elevated (corneal oedema)IOP elevated (corneal oedema) GonioscopyGonioscopy • PASPAS
- 57. Posterior synechiae extending for 360 degrees around thePosterior synechiae extending for 360 degrees around the pupillary border give rise to a forward bowing of thepupillary border give rise to a forward bowing of the peripheral iris (Iris bombe)/ This may lead to the closure ofperipheral iris (Iris bombe)/ This may lead to the closure of the angle [Secondary glaucoma]/ As the trabecularthe angle [Secondary glaucoma]/ As the trabecular meshwork is blocked it causes an increase in Aqueous inmeshwork is blocked it causes an increase in Aqueous in anterior chamber, therefore increasing IOP!!anterior chamber, therefore increasing IOP!!
- 58. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques &Diagnostic Techniques & SignsSigns Circumlimbal injection
- 59. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques &Diagnostic Techniques & SignsSigns Circumlimbal injection
- 60. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Grading of cells and flare Grade Flare Cells 0 Complete absence No cells 1+ Faint flare (barely detectable) 5 to 10 cells in view 2+ Moderate flare (iris and lens still clear) 10 to 20 cells in view 3+ Marked flare (iris and lens hazy) 20 to 50 cells in view 4+ Intense flare (coagulated aqueous, no circulation, fibrin visible) 50+ cells in view
- 61. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques &Diagnostic Techniques & SignsSigns Keratic Precipitates
- 62. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Hypopyon vs Hyphaema
- 63. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Hypopyon vs Hyphaema
- 64. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Band Keratopathy
- 65. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Fibrin in aqueous
- 66. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Fibrin in aqueous
- 67. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Posterior Synechiae
- 72. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques &Diagnostic Techniques & SignsSignsRubeosis Iridis
- 73. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques &Diagnostic Techniques & SignsSigns Iris Nodules
- 74. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Severe Acute Anterior Uveitis
- 75. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Diagnostic Techniques & SignsDiagnostic Techniques & Signs Gonioscope view of Peripheral Anterior Synechiae (PAS)
- 76. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – ManagementManagement Chronic - Early referral to GP if not beingChronic - Early referral to GP if not being managed currentlymanaged currently Recurrent acute episode – Urgent referralRecurrent acute episode – Urgent referral to GP for prescription of treatmentto GP for prescription of treatment regimen and monitoringregimen and monitoring Acute episode, previously undiagnosed –Acute episode, previously undiagnosed – Urgent referral to hospital eye casualtyUrgent referral to hospital eye casualty departmentdepartment All patients – check IOP. If raised refer toAll patients – check IOP. If raised refer to GP or casualty depending on levelGP or casualty depending on level Counsel patients on importance ofCounsel patients on importance of
- 77. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – ManagementManagement Treatment regimenTreatment regimen • Topical Corticosteroid therapyTopical Corticosteroid therapy Reduce inflammationReduce inflammation Reduce exudate leakageReduce exudate leakage Increase cell wall stabilityIncrease cell wall stability Inhibit lysozyme release by granulocytesInhibit lysozyme release by granulocytes Inhibit circulation of lymphocytesInhibit circulation of lymphocytes • CycloplegiaCycloplegia Relieve painRelieve pain Prevent posterior synechiaePrevent posterior synechiae Stabilize the blood-aqueous barrierStabilize the blood-aqueous barrier • Systemic steroid therapySystemic steroid therapy • Systemic NSAID therapy (aspirin, ibuprofen)Systemic NSAID therapy (aspirin, ibuprofen)
- 78. Anterior Uveitis –Anterior Uveitis – Associated ConditionsAssociated Conditions Blunt TraumaBlunt Trauma Ocular SurgeryOcular Surgery Juvenile Chronic ArthritisJuvenile Chronic Arthritis Ankylosing SpondylitisAnkylosing Spondylitis Reiter’s syndromeReiter’s syndrome SarcoidosisSarcoidosis TuberculosisTuberculosis Herpes ZosterHerpes Zoster Herpes SimplexHerpes Simplex SyphilisSyphilis Hypermature CataractHypermature Cataract Lens RuptureLens Rupture Sympathetic ophthalmitisSympathetic ophthalmitis Fuch’s heterochromic iridocyclitisFuch’s heterochromic iridocyclitis