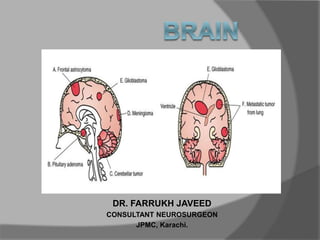
Brain tumors for Undergraduate Students
- 1. DR. FARRUKH JAVEED CONSULTANT NEUROSURGEON JPMC, Karachi.
- 2. LOBES OF THE CEREBRUM PARIETAL LOBE TEMPORAL LOBE FRONTAL LOBE LIMBIC LOBE OCCIPITAL LOBE
- 3. FRONTAL LOBE The frontal lobe is the area of the brain responsible for higher cognitive functions. Problem solving • Memory • Language • Motivation • Judgment • Impulse control • Social and sexual behavior.
- 4. TEMPORAL LOBE The temporal lobe plays a role in emotions, and is also responsible for smelling, tasting, perception, memory, understanding music, aggressiveness, and sexual behavior. The temporal lobe also contains the language area of the brain.
- 5. PARIETAL LOBE The parietal lobe plays a role in our sensations of touch, smell, and taste. It also processes sensory and spatial awareness, and is a key component in eye-hand co- ordination and arm movement. The parietal lobe also contains a specialized area called Wernicke’s area that is responsible for matching written words with the sound of spoken speech.
- 6. OCCIPITAL LOBE The occipital lobe is at the rear of the brain and controls vision and recognition.
- 7. LANGUAGE Wernicke’s area is a specialized portion of the parietal lobe that recognizes and understands written and spoken language. Wernicke’s area surrounds the auditory association area. Damage to this part of the brain can result in someone hearing speech, but not understanding it. Wernicke’s Area Auditory Association Area
- 8. HEARING There are two auditory areas of the brain: • The primary auditory area (brown circle) is what detects sounds that are transmitted from the ear. It is located in the sensory cortex. • The auditory association area (purple circle) is the part of the brain that is used to recognize the sounds as speech, music, or noise.
- 9. SPEECH Broca’s area is where we formulate speech and the area of the brain that sends motor instructions to the motor cortex. Injury to Broca’s area can cause difficulty in speaking. The individual may know what words he or she wishes to speak, but will be unable to do so. Broca’s Area
- 10. MOTOR CORTEX The motor portion of the cerebrum is illustrated here. The light red area is the premotor cortex, which is responsible for repetitive motions of learned motor skills. The dark red area is the primary motor area, and is responsible for control of skeletal muscles. Different areas of the brain are associated with different parts of the body. Injury to the motor cortex can result in motor disturbance in the associated body part.
- 11. SENSORY CORTEX The sensory portion of the cerebrum is illustrated here. Different areas of the brain are associated with different parts of the body, as can be seen below. Injury to the sensory cortex can result in sensory disturbance in the associated body part.
- 12. CEREBELLUM The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem, and is the center for body movement and balance.
- 13. INCIDENCE OF CNS TUMORS One-third of CNS tumors are metastatic lesions One third are gliomas and One-third is of nonglial origin.
- 14. World Health Organization (WHO) Classification Categorized & considered by cell layer of origin Tumors of Neuroepithelial tissue Tumors of Meninges Tumors of Craniospinal Nerves Hematopoietic Neoplasms Germ Cell Tumors Sellar Tumors Metastatic Tumors
- 15. Brain Tumors in General Presentation – Headache, seizure, neurological deficit, visual loss, personality changes, etc History – Progressive onset of symptoms (weeks to months) Physical Exam – Depends upon brain region affected
- 16. HEADACHE ONSET • ABRUPT(waking from sleep) • Triggered by exertion or Valsalva CHANGE • First or worst • Change or progression in pattern • New headache >50yrs • New headache in cancer or AIDS pts ASSOCIATED • Abnormal neurological exam • Neurological symptoms > 1 hours • Associated with altered / loss of consciousness
- 19. DIAGNOSIS Imaging Studies – CT, MRI, PET Laboratory Studies – Important for systemic tumors and metastasis, e.g. leukemia • Treatment & Prognosis Varies per histology of specific tumors
- 20. CARE OF THE BRAIN TUMOR PATIENT Steroids Help resolve edema and symptoms associated with it Can confuse the issue of lymphoma, because rapid “disappearance” is seen for lymphoma, followed by recurrence Anti-convulsants Recommended particularly for supra tentorial & epileptogenic areas, e.g. mesial temporal lobe, and with past h/o seizures
- 21. Treatment Options in general for Intracranial Tumors Need Biopsy for definitve identification… then one or combination of the following: Surgery Radiation Therapy Whole brain Focused beam Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery Chemotherapy Systemic Local
- 22. COMMON INTRAAXIAL TUMORS IN ADULTS Supratentorial Infratentorial Metastasis Metastasis Gliomas Fibrillary Astrocytoma Anaplastic Astrocytoma Glioblastoma Multiforme Oligodendroglioma Hemangioblastoma
- 23. COMMON INTRAAXIAL TUMORS IN PEDIATRICS Supratentorial Infratentorial Astrocytoma Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma PNET (Medulloblastoma) PNET Ependymoma DNET Brainstem Astrocytoma Ganglioglioma Although cancer is rare in children, brain tumors are the most common type of childhood cancer after leukemia and lymphoma.
- 25. SIGNS OF EXTRA AXIAL LOCATION CSF cleft Displaced subarachnoid vessels Cortical gray between mass and white matter Displaced and expanded subarachnoid spaces Broad dural base Bony reaction
- 26. The T2W-images show a schwannoma located in the cerebellopontine angle (CPA). CSF Cleft (yellow arrow) Displaced subarachnoid Space (blue arrow) Gray Matter between mass and White matter (curved arrow) Wide CSF spaces (long arrow)
- 27. Meningioma (Enplaque variety) broad dural base and a dural tail of enhancement(blue arrow) There is hyperostosis in the adjacent bone (yellow arrow) lesion enhances homogeneously
- 28. A hyperintense contrast enhancing lesion with extension to the prepontine area (blue arrows) and into the foramen magnum (red arrow). This Lesion proved to be Ependymoma
- 29. Above image shows a diffusely infiltrating intra-axial tumor occupying most of the right hemisphere with only a minimal mass effect. Low-grade astrocytoma.
- 30. Midline Crossing Tumors Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) frequently crosses the midline by infiltrating the white matter tracts of the corpus callosum. Radiation necrosis can look like recurrent GBM and can sometimes cross the midline. Meningioma is an extra-axial tumor and can spread along the meninges to the contralateral side. Continued
- 31. GBM Radiation Necrosis Meningioma
- 32. CALCIFICATIONS Intraaxial Tumors Extraaxial Tumors Astrocytomas (20%) Meningiomas (25%) Craniopharyngiomas (90%) Oligodendrogliomas (80%) Chordomas Metastasis Chondrosarcomas Ependymomas (50%) Choroid plexus papilloma (25%) Ganglioglioma (40%)
- 33. The CT shows a mass with calcifications, which extends all the way to the cortex. The most likely diagnosis is Oligodendroglioma.
- 34. A calcified mass seen in the suprasellar region, causing obstructive hydrocephalus. Craniopharyngiomas are slow growing,calcified, cystic tumors arising from remnants of Rathke's cleft. They are located in the suprasellar region and primarily seen in children with a small second peak incidence in older adults.
- 35. On the coronal and sagittal TW1I there is a large mass centered around the sella with a broad dural base. & extension into the sella. CT shows densely calcified tumor.
- 37. DIFFUSION WEIGHTED IMAGING Normally water protons have the ability to diffuse extracellularly and loose signal. High intensity on DWI indicates restriction of the ability of water protons to diffuse extracellularly. Restricted diffusion is seen in abscesses, epidermoid cysts and acute infarction In most tumors there is no restricted diffusion - even in necrotic or cystic components. This results in a normal, low signal on DWI.
- 38. We see restriction in above left extreme image as it is hyperintense, while lower extreme left image shows no restriction.
- 39. Schwannoma extending into the middle cranial fossa with homogeneous enhancement (right). Primary Lymphoma shows vivid enhancement (left).
- 40. Contrast Enhancement Meningioma Schwannoma Lymphoma Choroid Plexus Papilloma
- 41. Contrast Enhancement Hemangioblastoma Pilocytic Astrocytoma Ganglioglioma
- 42. Above image shows glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The enhancement indicates that this is a high-grade tumor There is also a cystic component with ring enhancement..
- 43. RING ENHANCEMENT 1. Metastasis 2. Glioblastoma Multiforme 3. Tuberculoma 4. Abscess, 5. Infectious disease Toxoplasma 6. Multiple Sclerosis 7. Chronic hematoma
- 45. Many non- tumorous lesions can mimic a brain tumor.
- 46. Infections and vascular lesions can also mimic a CNS tumor.
- 47. METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR History – Rapidly progressive onset of symptoms (weeks vs. months) Most common sources are LUNG, BREAST (in women), Thyroid, RENAL, & G.I. tract
- 48. DIAGNOSIS Imaging Studies – MRI: Tumor at grey-white matter junction, usually associated with edema Systemic work-up includes CT scan of chest, abdomen and pelvis Mammography Bone scan Diagnostic Laboratory Studies CBC, ESR, LFTs,
- 50. TREATMENT For solitary lesion or less than 4 lesions all < 3 cm. – biopsy if undiagnosed, plus Gamma Knife For > 3 cm. tumor, surgery followed by WBRT For > 4 lesions, biopsy for diagnosis, plus whole brain radiation therapy Prognosis: 7 – 12 mos.
- 51. GLIOMAS Presentation Depends upon brain location, usually H/A over several weeks, seizure, vomiting, visual chages or word finding difficulty Physical Exam – Depends upon brain region affected Diagnostic Imaging Studies – CT, MRI
- 53. Treatment Surgery, Radiation, Chemotherapy (varies with age group & type) Survival depends on pathology: – Pilocytic astrocytoma: resection Æ cure; Grade 1 Astrocytoma (nuclear atypia) – 8-10 yrs; Grade 2 Anaplastic astrocytoma (+endothelial proliferation) – 2 yrs Grade 3 (+necrosis) GBM – 11 months
- 54. MENINGIOMA Presentation Meningiomas occur in middle aged females more frequently History Meningiomas are usually slow-growing (months to years) CT/MRI: Show meninges- based tumor (usually), with variable amount of edema
- 57. TREATMENT Meninigiomas: Gross total resection curative Need for radiation therapy depends on grade Prognosis – Meningiomas: Can be cured with gross total resection with favorable prognosis
- 58. PITUITARY ADENOMA Presentation Headache, visual defect (classically bitemporal hemianopsia), endocrine abnormalities (dependent upon hormone secreted) – Prolactinoma most common ACTH with Cushing’s disease (w/hypertension, stria, buffalo hump, morbid obesity); GH with acromegaly
- 60. History Slow-growing, over months to years Headache with progressive visual loss Most common presentation is bitemporal hemi anopia Diagnostic Laboratory Studies Endocrine panel Test IGF-1 for GH-secreting tumor; Use dexamethasone suppression test for Cushing’s disease vs. ectopic Cushing’s syndrome
- 62. Treatment Medical treatment for Prolactinoma only with dopamine antagonists Surgical excision usually initial treatment (usually transnasal approach), with Gamma Knife for recurrence vs. local focused radiation Prognosis Generally benign, so proportional to gross total resection & control of endocrine effects;
- 63. Vestibular schwannoma Presentation Hearing difficulty in affected ear, vertigo, headache/facial weakness/facial numbness if large tumor compressing trigeminal nerve
- 64. Physical Exam Evaluate facial weakness & hearing ability Diagnostic Imaging Studies MRI Brain with MRA/MRV OTHERS Audiometry
- 66. Treatment Surgical resection if >3 cm. or causing excessive mass effect, brainstem compression; GK for smaller lesions (<3 cm.) Prognosis Benign tumor, so good with total excision and lack of recurrence
- 67. Lymphoma Presentation Sporadic, more common in immunosuppresed or immunocompromised patients (e.g. HIV+); may or may not be systemic @ presentation. Spinal cord (epidural) compression or carcinomatous meningitis Multiple cranial nerve deficits
- 69. Diagnostic Imaging Studies CT / MRI Brain Treatment Biopsy for establishing diagnosis, followed by radiation; chemotherapy (intra thecal methotrexate) has shown increased survival
- 70. PROGNOSIS No treatment 2.5 months.; XRT 10 months Intraventricular methotrexate 41 months. Prognosis worse in AIDS pts. (4 months)
- 71. Pineal Region Tumors Presentation Headache, Hydrocephalus (if large) Physical Exam May develop Perinaud’s syndrome (up gaze palsy, convergence, and accomodation impairment)
- 72. Diagnostic Imaging Studies MRI Diagnostic Laboratory Studies CSF can be sent for markers – AFP, HCG, PLAP
- 73. Tumor located in the pineal region with calcifications. This is most likely a germinoma.
- 74. Treatment Depends upon histology: Germinoma – biopsy & irradiate; Pineoblastoma: resect & irradiate Prognosis Depends upon histology: Pineocytoma better than germinoma, pineoblastoma
- 77. Multifocal Disease Multiple tumors in the brain usually indicate metastatic disease. Primary brain tumors are typically seen in a single region
- 78. Some tumors can be multifocal as a result of seeding metastases: this can occur in medulloblastomas (PNET-MB), ependymomas, GBMs and oligodendrogliomas. Meningiomas and schwannomas can be multiple, especially in neurofibromatosis type II.
- 80. COMMON CP ANGLE TUMORS Schwannoma Meningioma Epidermoid Arachnoid cyst Paraganglioma Metastasis
- 81. Cystic schwannoma of Left CP Angle.
- 93. CYSTIC TUMORS WITH MURAL NODULE
Editor's Notes
- The most common tumors in adults are listed in the table on the left. Note that metastases are by far the most common. It is important to realize that 50% of metastases are solitary. Particularly in the posterior fossa, metastases should be in the top 3 of the differential diagnostic list. Hemangioblastoma is an uncommon tumor, but it is the most common primary intra-axial tumor in the adult. Supratentorially, metastases are also the most common tumors, followed by gliomas.
- Bony changes are seen in bone tumors like chordomas, chondrosarcomas and metastases. They can also be secondary, as is seen in meningiomas and other tumors.
