Cell membrane
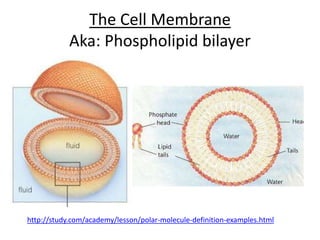
- 1. The Cell Membrane Aka: Phospholipid bilayer http://study.com/academy/lesson/polar-molecule-definition-examples.html
- 2. Warm Up! Part A Using the image provided answer the followings questions: 1. How many layers make up the cell membrane? 2. What is a phospholipid made up of? 3. Would the tails of a phospholipid attract or repel water? 4. What fluid is found on the interior and exterior of the cell? Part B Think of 1 question you have about the cell membrane based on the image.
- 3. Structure of cell membrane
- 4. The Cell (Plasma) Membrane • Separates the interior of a cell from it’s surroundings • Controls the traffic of chemicals in and out of the cell • How the membrane works is due to its structure • The plasma membrane is made of proteins and lipids • The lipids are called phospholipids
- 5. Phospholipids • The head is made of phosphate • Head: HydroPHILIC, POLAR • LOVE WATER • Tails are made of 2 fatty acid molecules • Tails: HydroPHOBIC, NON-POLAR • HATE WATER https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=moPJ kCbKjBs
- 6. Think Time! If you were to drop 10 phospholipids into the water, what would happen? Draw your prediction. X 10 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QQgXfuFyKM4
- 7. Cell (Plasma) membrane • Also called a phospholipid bilayer • Phosphate heads face the watery inside and outside of the cell • Fatty acid tails are shielded from the water • Form barrier • POLAR molecules GET IN – Exp. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen • NON POLAR molecules and LARGE molecules DO NOT GET IT – Exp. Ions: Na+ (charged atoms), and sugar
- 8. Membranes regulate the traffic of molecules • Lots of molecules move across the PM • Two-way traffic, moving in and out of cell • One way molecules move across the PM is by diffusion • Diffusion is the net movement of the particles of a substance from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated • Examples: perfumes, cordial in a glass of water • Diffusion
- 9. Model Diffusion • High to Low concentration • You will have 3 minutes to discuss within the class how to model diffusion and prepare to show it to the teacher. • Work together and communicate!
- 10. Type of Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of movement Requires Energy input from cell? Classification of transport? Types of Substances Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Complete the chart for your notes:
- 11. Transport Through the Membrane – Passive method • Simple Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion • Active Transport
- 12. Simple Diffusion • No transport protein used • Movement WITH the concentration gradient (high to low) • No additional cell energy required • PASSIVE • Examples: water, carbon dioxide and oxygen
- 13. Concentration Gradient - when there is a difference in concentrations • High concentration: more particles • Low concentration: fewer particles • In diffusion, particles move from high to low concentration to reach an equal concentration (equilibrium) on each side.
- 15. Passive Transport • Sugars can not cross the PM easily • They are helped across by transport proteins • This is called facilitated diffusion • In this way ions and small polar molecules can cross • Facilitated diffusion http://click4biology.info/c4b/2/cell2.4.htm#diff
- 16. Type of Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of movemen t Requires Energy input from cell? Classification of transport? Types of Substanc es Simple Diffusion NO With concent. gradient NO PASSIVE WATER, CO2, O2 Facilitated Diffusion Yes: Channel Proteins or Carrier Proteins With concent. gradient NO PASSIVE GLUCOSE Active Transport
- 17. Carrier Proteins
- 18. Channel Proteins
- 19. Osmosis • Osmosis is the passive transport of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high conc to low conc • Imagine a sealed bag containing a sugar solution in a beaker of pure water • Water can pass through the bag (membrane) • Sugar molecules can’t • Solution with higher concentration of solutes – hypertonic • Solution with a higher concentration of water – hypotonic • What will happen? • Isotonic? • Osmosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DpVbcJY4am A
- 20. Comparing Passive & Active Transport
- 21. Type of Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of movement Requires Energy input from cell? Classification of transport? Type of Substan ce Simple Diffusion NO With concent. gradient NO PASSIVE WATER, CO2, O2 Facilitated Diffusion Yes: Channel Proteins or Carrier Proteins With concent. gradient NO PASSIVE GLUCOSE Active Transport Yes: Carrier Proteins Against concent. gradient YES ACTIVE Na+ and K+ ions
- 22. Active Transport • When a cell uses energy to move molecules or ions across a membrane, it is called Active Transport • Transport pumps are needed. These are made from…. • Protein • From area of low concentration to an area of high concentration • Need energy in the form of ATP • Na+ is pumped out of the cell and K+ is pumped in by this process • Large molecules use vesicles – small
- 23. Active Transport
- 24. Other Types of Active Transport • Endocytosis – the process of taking material into the cell by folding in pockets of the cell membrane into pouches called vesicles – Phagocytosis – endocytosis involving large solid particles – Pinocytosis – endocytosis involving liquid • Exocytosis – the process of removing material out of the cell where vesicles merge with the cell membrane to release contents
- 25. 25 EX: Sodium-Potassium Pump 3 Na+ pumped in for every 2 K+ pumped out
- 26. • Exocytosis - moving materials out • Endocytosis: Moving materials in 26 Too large Must be packaged in membrane sacs called vesicles • It requires energy Moving the “Big Stuff”
- 27. Endocytosis is the case when a molecule causes the cell membrane to bulge inward, forming a vesicle. Phagocytosis is the type of endocytosis where an entire cell is engulfed. Pinocytosis is when the external fluid is engulfed. 27
- 28. 28
