Glands histology
- 2. Objectives • Introduction • General Features • Development • Classifications • Examples • Applied
- 3. Gland - Introduction • Some epithelial cells converted in to specialized cells to perform a secretory function - form glands • Definition: An organ of secretion made up of specialized secretory cells; derived from surface epithelium on which it opens
- 4. General Features of Glands • Can be present as “Discrete Organ” or “ in the layers of viscera” • Epithelial in origin (Derived from surface epithelium) • Functional unit of gland is formed by specialized secretory cells known as – Secretory End Piece • Fluid secreted by glands contain enzymes, mucus, hormones, protein, fat etc…
- 5. General Features of Glands • Rate of secretion is modulated by Nervous & Hormonal influence • Secretory end piece of some exocrine glands is surrounded by star shaped contractile cells that lies between cells & basement membrane –Called Myo-epithelial cells –Share features of both epithelium & muscle cell –Help in expulsion of secretions
- 7. Development of Glands Developed as cords of epithelial cells from the surface of membrane Invaginates in to underlying Connective tissue & Form 2 parts Proximal Part Distal Part
- 8. Development of Glands Form duct Connect secretory end piece with surface of epithelium Proximal Part Distal Part Exocrine Glands Differentiated in to the secretory cells Secretory End Piece Pours the secretion through ducts / directly on surface of the glands or epithelium
- 9. Development of Glands DisappearProximal Part Distal Part Endocrine Glands Form islands of the secretory cells permeated / surrounded by the blood capillaries Pours their secretion in to directly in to blood through the blood capillaries Ductless Gland *
- 10. • Develop as invagination of the epithelium into the underlying vascular connective tissue. • Distal part forms glandular or Secretory end Piece – functionally an active portion. • Proximal part - Excretory Duct-opens on the surface of the epithelium = Exocrine Gland • Some cells get detached from the epithelial surface- Ductless or endocrine glands Development of Glands
- 11. Based on Site of Secretion Exocrine With Ducts Endocrine Ductless Exocrine + Endocrine Paracrine Classification of Glands Unicellular / Multicellular Cord & Clump type/ Follicular Type Pancreas & Liver APUD & DNES APUD – Amine Precursor Uptake & Decarboxylation DNES - Diffuse NeuroEndocrine System
- 12. Classifications of Exocrine Glands Based on numbers of cell Unicellular Multicellular Goblet Cell
- 13. Multicellular Exocrine Glands 1. Based on branching pattern of ducts Simple No Branching Compound Branched
- 14. Multicellular Exocrine Glands 2. Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece Tubular Alveolar / Acinar Tubulo- alveolar
- 15. Multicellular Exocrine Glands 3. Based on Nature of Secretion Mucous Serous Mixed / Sero-mucous
- 16. Multicellular Exocrine Glands 4. Based on Manner of Secretion Merocrine Apocrine Holocrine Cytocrine
- 17. Multicellular Exocrine Glands 5. Based on Development of gland Ectodermal Endodermal Mesodermal
- 18. Glands -Based on Site of Secretion • Endocrine :- Ductless • Exocrine :- With Ducts • Exocrine + Endocrine • Paracrine
- 19. • Ductless / Internally secretory gland • Secrete hormones & useful chemical substances in blood capillaries • Cells & blood vessels are supported by connective tissue & surrounded by capsule • 2 types: – Cord & Clump type – Follicular Type Endocrine Glands
- 20. Cord & Clump Type Follicular Type Endocrine Glands Cells arranged in irregular Cords / clumps permeated by capillaries Cells arranged in follicles surrounded by capillaries Secretions directly delivered outward in capillaries Secretions delivered inward inside the follicles
- 21. Cord & Clump Type Follicular Type Endocrine Glands Secretions stored inside the cells “Intra-cellular method” Secretions stored outside the cells inside follicles “Extra-cellular method” E.g. Most endocrine glands Pituitary, Adrenal, Parathyroid, Pineal E.g. Thyroid Gland
- 23. • Act locally / Secretions do not travel through blood • Secrete its products(hormones) in to local extracellular environment • Exert effects only on neighboring cells in vicinity of secreting cells • E.G. – Enteroendocrine cells of GIT – Diffuse neuroendocrine system (DNES) Paracrine Glands
- 24. Entero-endocrine cells of GIT
- 25. • With Ducts / Externally secretory gland • Secrete its products on to the surface through it’s duct • Consist of 3 components – Secretory end piece – Duct System – Supporting Connective tissues • E.G. All Salivary Glands Exocrine Glands Parenchyma Stroma Parenchyma
- 26. Exocrine Glands Lobes Lobules Blood Vessels & Nerves Parenchyma Stroma Inter-lobar Septa Capsule Ducts Inter-lobular Septa
- 27. General Architecture of a Exocrine Gland Parenchyma- • Secretory end pieces- Acini / tubules / tubulo-acinar • Ducts- Intralobular, interlobular, main excretory duct Stroma- • Capsule • Septa (interlobular, interlobar) • Loose inter-lobular connective tissue supporting the parenchyma • Divide the gland into lobes and lobules.
- 28. Based on Number of cells: • Unicellular • Multicellular Exocrine Glands - Classification
- 29. • Has only single cell • Interspersed among other non-secretory epithelial cells • E.G. – Goblet cells in respiratory & intestinal tract • Secrete mucous by partial destruction of cell memb. • In H&E staining – looks empty • Mucous stained by PAS (Periodic acid schiff) & Alcian Blue staining Unicellular Gland
- 30. Unicellular Gland PAS (Periodic acid schiff) Alcian Blue
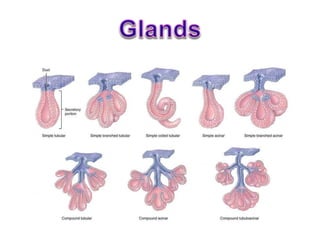
- 31. Exocrine glands Based on number of ducts • Simple(single duct) • Compound(minor & major ducts) Based on shape of secretory piece: • Simple tubular/ alveolar • Simple branched tubular/ alveolar • Simple coiled tubular • Compound tubular/ acinar • Compound tubulo-alveolar / acinar
- 32. • Simple: – Secretion poured to surface by un-branched duct • Compound: – Duct divides in to branches to form elaborated / complex duct system; – Each smaller terminal duct receive secretion from it’s own secretory end piece – These ducts unite to form larger ducts which finally drain on to surface Based on Number of Ducts:
- 33. • Tubular: (Simple / Compound) – Secretory end piece is like tubule – Straight, branched or coiled Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece: Simple Straight Intestinal Crypts Simple Coiled Sweat Gland Simple Branched Uterine gland Fundic & pyloric glands of stomach Compound Cardiac glands of stomach & Brunner’s gland of duodenum
- 34. Simple Straight Tubular Gland Intestinal Crypts
- 35. • Alveolar: (Simple / Compound) – Secretory end piece Flask shaped with large lumen – Un-branched or branched Simple Un-branched Urethral Glands Simple Branched Sebaceous & Tarsal Glands Compound Mammary gland betn puberty & 1st Pregnancy Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece:
- 36. • Acinar: (Mostly Compound) – Secretory end piece Round shaped with small lumen – Mostly branched Compound Acinar Pancreas Parotid Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece:
- 37. • Tubulo – Alveolar / Acinar: – Combination of both Tubular & alveolar / Acinar – Mostly branched Compound Tubulo – Alveolar / Acinar Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Lactating mammary gland Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece:
- 38. Simple Glands
- 39. Compound Glands
- 40. According to Mode of secretion: • Merocrine • Apocrine • Holocrine • Cytocrine Exocrine glands
- 41. • Merocrine: – A.K.A.: Eccrine / Epicrine – Secretion discharged through intact cell membrane – By Exocytosis – No loss of cytoplasm Based on Mode of Secretion: E.G. Protein content of mammary gland Parotid Pancreas Typical sweat gland
- 43. • Apocrine: – Apical portion (luminal) of cell disintegrate to discharge its secretion – Nucleus & basal portion remain intact from which cell can regenerate – Partial loss of cytoplasm Based on Mode of Secretion: E.G. Lipid content of mammary gland Atypical sweat gland (Axilla & Groin) Ceruminous gland of Ear Moll’s Gland in Eyelid Modified Sweat gland
- 45. • Holocrine: – Entire cell disintegrate to discharge its secretion – Result in death of cell – Complete loss of cytoplasm Based on Mode of Secretion: E.G. Sebaceous gland Tarsal Glands in Eyelid
- 47. • Cytocrine: – Cell are released as secretion Based on Mode of Secretion: E.G. Spermatozoa from Testis Ovum from Ovary Bone Marrow
- 50. According to Nature of secretion: • Serous • Mucous • Mixed Exocrine glands Mucous Serous Mixed
- 51. Serous Acinus / Gland • Secretion: Thin, watery, – Rich in enzymes, protein in nature • Cells: Pyramidal & Small with Indistinct boundaries • Cytoplasm: Granular (Zymogen) – Rich in rER – Stain darkly with H/E stain • Nuclei: rounded & basal / central • Size of lumen: Small • Function: Enzymatic • E.G.: Parotid & Lacrimal glands
- 52. • Secretion: Thick Viscous – Which collects in the apical part • Cells: Low Columnar & Large with distinct boundaries • Cytoplasm: Mucinogen droplets – Stain very lightly with H/E stain & – Looks empty • Nuclei: Flattened & basal (mucoid pushes nuclei towards base) • Size of lumen: Large • Function: Protection & Lubrication • E.G.: Sublingual glands Mucous Acinus / Gland
- 53. • Contain both serous & mucous secretory units • Sometimes serous cells form crescentic caps on mucous acini called as Serous Demilunes Mixed Acinus / Gland
- 54. Serous Thin, watery Proteinaceous Zymogen granules Central rounded Small Lumen Indistinct Darkly stained Enzymatic action Parotid Gland Mucous Thick, viscous Mucopolysaccharides Mucinogen droplets Flat & peripheral Large Lumen Distinct Lighly stained Protection & lubrication Sublingual gland Consistency Content Cytoplasm Nucleus Lumen Cell boundaries H&E Staining Function Examples
- 55. Serous Acini Mucous Acini
- 56. Serous Acini Mucous Acini
- 57. According to Development: • Ectodermal – Glands of skin, Mammary gland, Lacrimal gland, – Salivary glands, Pituitary gland & Chromaffin organs • Mesodermal – Suprarenal cortex, Gonads, Kidney & Spleen • Endodermal – Thyroid, Parathyroid, Thymus – Liver, Pancreas, Prostate – Urethra, Bulbo-urethral gland, Greater vestibular gland – Glands in lining epithelium of respiratory tract Exocrine glands
- 58. Clinical • ADENOMA: Benign tumors arising in the gland • ADENOCARCINOMA: Malignant growth in the gland
