Mechanism of Normal Labor
- 1. Mechanism of Normal labor Presented By Heera KC Nursing Co-ordinator, (MSc. Nursing, Maternal Health) 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 1
- 2. Objectives • Define the term mechanism of labor. • State the principles common to all labor. • Enlist the normal conditions that is followed during normal mechanism. • List out the cardinal movements during mechanism of labor. • Explain in detail the mechanism of labor. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 2
- 3. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 3
- 4. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 4 Bony landmarks on the brim of the pelvis separating the true from the false pelvis; 1-Symphysis pubis. 2-Pubic crest. 3-Pubic tubercle. 4-Pectineal line. 5- Iliopubic eminence. 6-Iliopectineal line. 7-Sacroiliac articulation. 8-Anterior border of the ala of sacrum and 9-Sacral promontory
- 5. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 5
- 7. Transverse Diameters of the Fetal Skull Biparietal Diameter 9.5 cm Between the 2 parietal eminences Bitemporal Diameter 8.5 cm. The distance between the anterio- inferior ends of the coronl suture. Bimastoid Diameter 7.5 cm. Between the 2 mastoid processes Supra-subparietal 8.5 cm It extends from a point placed below one parietal eminence to the point placed above the parietal eminence of opposite side.
- 8. Length Attitude of head/presentation 1-Suboccipito-bregmatic Nape of neck to centre of bregma 9.5 cm. Complete flexion vertex 2-Suboccipito-frontal Nape of neck to in front of bregma 10 cm. Partially deflexed vertex Vertex 3-Occipito-frontal Root of nose to occipital protuberance 11.5 cm. Deflexed vertex Vertex 4-Mento-vertical Point of chin to above posterior fontanelle 14 cm. Partial extension Brow 5-Submento-bregmatic From below chin to centre of bregma 9.5 cm. Full extension Face 6-Submento-vertical From below chin to infront of post. fontannelle 11.5 cm. Incomplete extension face The anterio- posterior diameters of the head
- 9. Length Presentation 1-Suboccipito-bregmatic 9.5 cm. Flexed vertex 2-Suboccipito-frontal 10 cm. Partially deflexed vertex 3-Occipito-frontal 11.5 cm. Deflexed vertex 4-Mento-vertical 14 cm. Brow 5-Submento-bregmatic 9.5 cm. Face 6-Submento-vertical 11.5 cm. Face Not fully extended 6
- 10. The important diameters of fetal skull
- 11. Fetal skull showing important sutures, fontanels and diameters of obstetric significance
- 12. MECHANISM OF NORMAL LABOUR • The series of movements that occur on the head in the process of adaptation during its journey through the pelvis is called mechanism of labor. • Is a series of passive movements of the fetus in the passage through the birth canal. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 12
- 13. Why it is important to understand the mechanism of normal labor? • Knowledge and recognition of the normal mechanism enables midwife to anticipate next step in the process of descent. • Helps to ensure that the normal process is recognized, • That woman gives birth safely and positively or • Early assistance can be sought if any problem arises. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 13
- 14. Principles common to all labour • Descent takes place. • Which ever part leads and first meets the pelvic floor will rotate forwards until it comes under the symphysis pubis. • Whatever emerges from the pelvis will pivot around the pubic bone. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 14
- 15. Conditions for normal mechanism in occipito anterior position • Lie -longitudinal • Presentation - cephalic • Position - right or left occipitoanterior • Attitude - flexion 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 15
- 16. Varieties of cephalic presentations in diff erent attitude1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 16 Conditions for normal mechanism in occipito anterior position
- 17. Conditions for normal mechanism in occipito anterior position 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 17 • Denominator - occiput • Presenting part - posterior part of the right parietal bone or sub- occipital part. The position and relative frequency of the vertex at the onset of labor
- 18. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 18
- 19. Conditions for normal mechanism in occipito anterior position Cont… • Engaging diameter- biparital 9.5 cm 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 19 • Engagement: Head should be well engaged in pelvic brim and cavity.
- 20. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 20 Station Conditions for normal mechanism in occipito anterior position Cont…
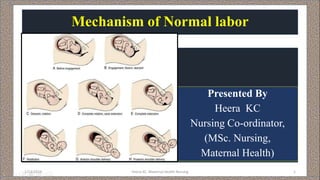
- 21. Mechanism of labour with occiput anterior position • Engagement • Descent • Flexion • Internal rotation of the head • Crowning of the head • Extension of the head 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 21 Restitution of the head External rotation of the head and internal rotation of the shoulder Lateral flexion of the body with expulsion of fetus
- 22. Engagement • The greatest (horizontal plane) transverse diameter BPD while passes through the pelvic inlet the head is said to be engaged. • In LOA, fetal head enters pelvic brim with occiput (denominator) lying in relation to left iliopectineal eminence, sinciput at right sacroiliac joint and sagittal suture lying on the right oblique diameter of maternal pelvis. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 22
- 23. Engagement 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 23
- 24. Engagement Cont… • The engaging transverse diameter of fetal head is biparietal 9.5 cm and the sub-occiput bregmatic 9.5 cm. Both the diameter remain on the same plane. • In primigravida- 38-42 weeks • In multigravida- late first stage or after rupture of membrane. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 24
- 25. • Asynclitic refers to a fetal head that is not parallel to the anteroposterior plane of the pelvis. • The head is synclitic when the sagittal suture lies midway between the symphysis pubis and the sacral promontory. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 25 Asynclitism and Synclitism
- 26. Engagement Cont… • Due to lateral inclination of the head, the sagittal suture does not strictly correspond with the available transverse diameter of the inlet. • Either deflected anteriorly toward the symphysis pubis or posteriorly toward the sacral promontory. • Such deflection of the head in relation to the pelvis is called asynclitism. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 26 Asynclitism.
- 27. • When the sagittal suture lies anteriorly, the posterior parietal bone becomes the leading presenting part and is called posterior asynclitism or posterior parietal presentation. • This is more frequently found in primigravidae because of good uterine tone and a tight abdominal wall. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 27 Mild degrees of asynclitism are common but severe degrees indicate cephalopelvic disproportion.
- 28. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 28 Head brim relation prior to engagement: (A) Anterior parietal presentation; (B) Head in synclitism; (C) Posterior parietal presentation
- 29. • When the sagittal suture lies more posteriorly with the result that the anterior parietal bone becomes the leading presenting part and is then called anterior parietal presentation or anterior asynclitism. • It is more commonly found in multiparae. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 29
- 30. 2. Descent 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 31 • Provided that there is no undue bony or soft tissue obstruction, descent is a continuous process. • Often begins before the onset of labour. • Slow or insignificant in first stage but pronounced in second stage. • Completed with the expulsion of the fetus.
- 31. 2. Descent 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 32 • In primigravidae, it occurs during the later weeks of pregnancy when engagement of the head provides confirmation that vaginal delivery is probable. • In multigravid women, muscle tone is often more lax and therefore, descent and engagement of the fetal head may not occur until labour actually begins.
- 32. Factors affecting the descent • Uterine contraction and retraction • Bearing down efforts by woman • Direct pressure from the fetal head specially after rupture of the membrane and full dilatation of the cervix • Pressure exerted by the amniotic fluid • Extension and straightening of the fetal head 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 33
- 33. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 34
- 34. Flexion • Some degree of flexion of the head - noticeable at the beginning of labor but complete flexion uncommon. • As the head meets the resistance of the birth canal during descent, full flexion is achieved. • If pelvis is adequate, flexion is achieved due to the resistance offered by the cervix, walls of the pelvis or by the pelvic floor. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 35
- 35. Flexion Cont… • Flexion is essential for descent, since it reduces the shape and size of the plane of the advancing diameter of the head. • The fetal spine is attached nearer the posterior part of the skull; pressure exerted down the fetal axis will be more forcibly transmitted to the occiput than the sinciput. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 36
- 36. Flexion Cont… • The effect is to increase flexion which results in smaller presenting diameters which will negotiate the pelvis more easily. • At the onset of labour, the sub-occiput- frontal diameter 10 cm is presenting part. • With greater flexion the suboccipito-bregmatic diameter 9.5 cm and occiput becomes the leading part. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 37
- 37. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 38
- 38. • It is a movement of great importance without which there will be no further descent. • Internal rotation brings the anteroposterior diameter of the fetal head into the alignment with the maternal pelvis. 4. Internal rotation of the head
- 39. • Internal rotation is a turning forwards of whatever part of the fetus reaches the gutter shaped pelvic floor first. • During contraction the leading part is driven downwards onto the pelvic floor. • The resistance of this muscular diaphragm brings about rotation. . Internal rotation of the head
- 40. Slope of pelvic floor: The gutter like pelvic floor helps rotation. Levator ani muscles, pelvic body • Also called the rotation by law of pelvic floor (Hart’s rule). Resistance - an important determinant of rotation. (Rotation often delayed following epidural anaesthesia) Theories which explain the anterior rotation of the occiput are:
- 41. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 42
- 42. • The muscles are gutter shaped and slope down anteriorly so whichever part of the fetus first meets the lateral half of this slope, will be directed forwards and towards the center. Theories which explain the anterior rotation of the occiput are:
- 43. Pelvic shape: • Forward inclination of the side walls of the cavity, • narrow bispinous diameter and • Long anteroposterior diameter of the outlet • Results in long axis of the head to accommodate in the maximum available diameter, i.e. anteroposterior diameter of the outlet leaving behind the smallest bispinous diameter. Theories which explain the anterior rotation of the occiput are:
- 44. • Law of unequal flexibility (Sellheim and Moir): The internal rotation is primarily due to inequalities in the flexibility of the component parts of the fetus. Theories which explain the anterior rotation of the occiput are:
- 45. Prerequisites of anterior internal rotation of the head • well-flexed head, • efficient uterine contraction, • favorable shape at the midpelvic plane, and • tone of the levator ani muscles. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 46
- 46. • In well flexed vertex presentation, the occiput leads and meets the pelvic floor first and rotates anteriorly through 1/8th of a circle. • In LOA position, occiput rotates 45◦ (1/8th ) from the left towards midline (from the left iliopecineal eminence to the symphysis pubis), where it can escape under the pubic arch and allow the sub-occipital region to pivot on the lower border of the symphysis pubis.
- 47. • This causes a slight twists on the neck of the fetus as the head is no longer in direct alignment with the shoulder. • The antero-posterior diameter of the head now lies in the widest (antero-posterior) diameter of the pelvic outlet, facilitating an easy escape.
- 48. • The occiput slope beneath the sub-pubic arch and crowning occurs. • When the head no longer recedes between contractions and the widest transverse diameter (biparietal) is born.
- 49. • Torsion (twisting of the neck) : Torsion of the neck is an inevitable phenomenon during internal rotation of the head. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 50
- 50. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 51
- 51. • After internal rotation of the head, further descent occurs until the sub-occiput lies underneath the pubic arch. • At this stage, the maximum diameters of the head (biparietal diameter 9.5 cm) stretches the vulval outlet without any recession of the head even after the contraction is over called ‘crowning of the head’. 5. Crowning of the head
- 54. • Delivery of the head takes place by extension through ‘couple of force’ theory. • Head in a downward direction, pelvic floor offers a resistance in the upward and forward direction, • downward and upward forces neutralize and remaining forward thrust helping in extension. 6. Extension of the head
- 55. • vertex, brow, face and chin which sweep the perineum. • Immediately following the release of the chin through the anterior margin of the stretched perineum, the head drops down, bringing the chin in close proximity to the maternal anal opening. • The subocciputo-frontal diameter 10 cm distends the vaginal outlet. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 56 6. Extension of the head Cont…
- 57. • The twist in the neck of the fetus that resulted from internal rotation is now corrected by a slight-untwisting movement. • Visible passive movements of the head to undo the twist in the neck, that took place during internal rotation of the head. • In a vertex, LOA, the occiput restitutes 1/8th of a circle to the left, back to where it was before internal rotation took place. 7.Restitution of the head
- 58. • The occiput thus points to the maternal thigh of the corresponding side to which it originally lay. • Whether the position is right or left and the midwife knows whether she is delivering an LOA or an ROA . 7.Restitution of the head Cont…
- 59. • Similar to internal rotation of the head. • In LOA – Shoulders are in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic cavity. • Anterior shoulder rotates forwards bringing the shoulders into the antero-posterior diameter of the outlet. • Occurs with uterine contraction after the head is born. 8. Internal rotation of the shoulders
- 60. • Movement of rotation of the head visible externally due to internal rotation of the shoulders. • As the anterior shoulder rotates towards the symphysis pubis from the oblique diameter, Carries the head in a movement of external rotation through the 1/8th of a circle in the same direction as restitution. 9. External rotation of the head
- 61. • Anterior shoulder slips beneath the sub-pubic arch and the posterior shoulder passes over the perineum. 9. External rotation of the head
- 62. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 63
- 63. Remainder of the body born by lateral flexion as the spine bends side way through the curved birth canal. Anterior shoulder first. The anterior shoulder slips beneath the sub-pubic arch and the posterior shoulder passes over the perineum. 10. Lateral flexion of the body with expulsion of fetus
- 66. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 67
- 67. REFERENCES • D.C.,Dutta’s.(2004) Textbook of obstetrics.6th Edition. New central Book Agency. • Fraser, DM. , Cooper, MA.(2006) Myles Textbook for Midwives .14th edition. Churchill Livingstone. • Roshani,T. ,(2005) Mannual of Midwifery B.3rd Edition. Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandar. • Subedi, D., Gautam, S.,(2011) Midwifery Nursing part II. 2nd edition. Medhavi Publication.
- 68. 1/13/2019 Heera KC: Maternal Health Nursing 69 Summary
