Extra ocular muscles ppt
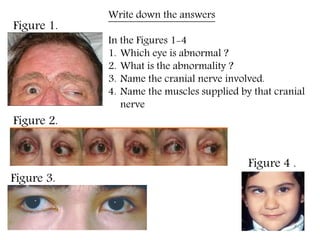
- 1. Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Figure 4 . Write down the answers In the Figures 1-4 1. Which eye is abnormal ? 2. What is the abnormality ? 3. Name the cranial nerve involved. 4. Name the muscles supplied by that cranial nerve
- 3. Extraocular muscles 4 Recti and 2 Obliques Superior rectus Superior oblique Inferior rectus Inferior oblique Medial rectus Lateral rectus Levator palpebrae superioris
- 4. LEVATOR PALPEBRAE SUPERIORIS Origin: Undersurface of lesser wing of sphenoid above optic canal Insertion: Skin of upper eyelids Anterior surface of superior tarsus Muller`s muscle/Superior tarsal muscle Superior conjunctival fornix
- 7. LEVATOR PALPEBRAE SUPERIORIS Nerve supply and Actions Paralysis - PTOSIS Oculomotor nerve, Sympathetics Elevates upper lid
- 8. Equator Optical axis/Axis of Gaze – direction of sight .Primary position of eye Axis of movements Axis of muscles
- 9. Movements Abduction Elevation Depression Adduction Intorsion Extorsion Elevation & Depression – Around the transverse axis Adduction & Abduction – Around the vertical axis Intortion & Extortion – Around the anteroposterior axis
- 10. And the RULE is…..(for recti and oblique) Any muscle inserting medial to vertical axis – Adduction lateral to vertical axis - Abduction superior to AP axis – Intorsion inferior to AP axis – Extorsion For muscle inserting in front of equator i.e RECTI above transverse axis – Elevation below transverse axis - Depression
- 11. ORIGIN OF THE 4 RECTI MUSCLE Common tendinous ring (Annulus of Zinn) •Lateral rectus by 2 heads –Extra head from adjoining greater wing of sphenoid LEFT EYE
- 12. COURSE OF THE 4 RECTI Muscular cone Corresponding wall of orbit Rectus muscle length – 40mm Innervated from intraconal side of the muscle belly at the junction of anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 of the muscle
- 13. INSERTION OF THE 4 RECTI The line connecting the insertion of the recti in series is spiral & is known as spiral line of Tillaux Pierce Tenon’scapsule Sclera in front of the equator Medial rectus is susceptible to injury during anterior segment procedures
- 14. AXES OF THE RECTI MUSCLE Medial and lateral recti in same horizontal plane Superior and inferior recti in same oblique plane, 25⁰lateral to optical axis In the abducted eye the axes coincide
- 15. Action of the RECTI • Medial & lateral recti lie in the same horizontal plane Around a vertical axis Medial rectus - adduction Lateral rectus - abduction
- 16. • Superior rectus Around the transverse axis – rotates the eyeball upwards – Elevation (PRIMARY ACTION) Around the vertical axis - Adduction Around the anteroposterior axis - Intortion • Inferior rectus Around the transverse axis – rotates the eyeball downwards – Depression (PRIMARY ACTION) Around the vertical axis – Adduction Around the anteroposterior axis - Extortion
- 17. Only in the Abducted position of the eyeball the visual axis coincides with the axis of superior and inferior recti In abducted eye Superior rectus – Elevation only Inferior rectus - Depression only
- 18. Superior Oblique muscle Body of sphenoid above and medial to optic canal Winds around trochlea at superomedial part of orbit (functional origin) Insertion behind the equator Postero‐superior quadrant Only eye muscle innervated on the outer surface of muscle belly. Retrobulbar anaesthetic block
- 19. Origin from orbital surface of maxilla Passes backward and laterally below inferior rectus Insertion behind equator parallel to superior oblique Postero‐superior quadrant Inferior Oblique Muscle The oblique muscles always course below the corresponding vertical rectus muscle
- 20. Axis of the Oblique Muscles The obliques lie in the same oblique plane 51⁰medial to optical axis In the adducted eye axes coincide with the optical axis
- 21. • Superior oblique Around the anteroposterior axis – Intorsion(primary action) Around the vertical axis Abduction Around the transverse eaxis – Depression • Inferior oblique Extortion(primary action) Abduction Elevation
- 22. Only in the Adducted position of the eyeball the visual axis coincides with the axis of superior and inferior oblique In Adducted eye Superior oblique – Depression only Inferior oblique – Elevation only
- 23. Superior division of oculomotor:- levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus Inferior division of oculomotor:- medial rectus, inferior oblique, inferior rectus Trochlear nerve - superior oblique Abducent nerve - lateral rectus Nerve Supply of Extraocular Muscles
- 25. Extraocular Muscles Allow accurate positioning of visual axis Determine the spatial relationship between the two eyes Responsible for binocular vision Have the smallest motor unit among skeletal muscles – ratio of nerve fibre to muscle fibre is 1:2(whereas 1:25 in other skeletal muscles) -Yoke Muscles: a muscle of one eye is paired with another muscle of the fellow eye to produce a cardinal gaze -Example: Right LR & Left MR while looking towards right side They develop from ? Preotic/preoccipital somitomeres
- 26. Fascial expansions of Extraocular muscles
- 27. RECTI -Adduct OBLIQUES – Abduct SUPERIORS – Intort INFERIORS -Extort
- 28. Clinical Testing
- 29. Ptosis Eyeball turned down and out Ocular movements restricted Pupil fixed and dilated Loss of accomodation OCCULOMOTOR NERVE PALSY
- 30. ABDUCENS PALSY – Internal squint The right eye unable to abduct External squint- Medial rectus paralysis The right eye unable to adduct OPTHALMOPLEGIA / EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLE PALSY Injury to III, IV, VI cranial nerve Muscle paralysis Unilateral paralysis produces Strabismus /Squint, Diplopia TROCHLEAR NERVE PALSY Eyeball turned upwards and inwards
- 34. TROCHLEAR NERVE PALSY Affected eye rotated up and in. Attempts to compensate lead to the patient tilting their head to the contralateral side.
- 35. ABDUCENS PALSY
- 45. Third nerve palsy results in an inability to move the eye normally in all directions. Injury to the third nerve can occur anywhere along its path, from where it originates within the brain to where it innervates the muscles that move the eyeball. Third nerve palsy prevents the proper functioning of the medial, superior, and inferior recti, and inferior oblique muscles. As a result, the eye cannot move up, down, or in. When at rest, the eye tends to look down and to the side, due to an inequality of muscle functioning. The muscle responsible for keeping the upper eyelid open (levator palpebrae superioris) is also affected, resulting in a drooping upper eyelid (ptosis
- 48. phthalmoplegia, also called extraocular muscle palsy, paralysis of the extraocular muscles that control the movements of the eye. Ophthalmoplegia usually involves the third (oculomotor), fourth (trochlear), or sixth (abducens)cranial nerves. Double vision is the characteristic symptom in all three cases
- 54. The optical axis of the eye (the line from the center of the cornea to the fovea) points straight ahead during straight-ahead gaze, but the axis of the orbit points about 23 degrees laterally. The superior and inferior recti originate from the back of the orbit, and so their direction of pulling is not parallel to the optical axis. As a result, although the superior rectus primarily elevates the eye, it also has smaller adducting and intorting effects. (Similarly, although not indicated in the Þgure, the inferior rectus primarily depresses but also adducts and extorts a little.)
- 55. The pulling direction of the obliques is not aligned with either the optical axis or the orbital axis, and their actions change with the direction of gaze. The superior oblique inserts in the posterior half of the eye and pulls diagonally forward. A, As a result, during straight-ahead gaze, although it primarily intorts the eye, it also pulls the back of the eye a little bit medially and upward (i.e., abducts and depresses a little). B, During adduction, the direction of pull is more nearly in line with the optical axis, and the same muscle depresses more and intorts less. C, During abduction, the direction of pull can wind up perpendicular to the optical axis, and the action becomes purely intorsion. (Similarly, although not indicated in the Þgure, the inferior oblique primarily extorts when the eye is abducted, but it also elevates and abducts in other directions of gaze.)
Editor's Notes
- A layer of invol smooth muscle fibres arise from the aponeurosis of LPS andis attached to superior tarsal plate, innervated by sympathetics, denervation- ptosis.
- Ocular rotations are for the most part under vol. control, whereas torsional movements cant be vol. initiated
- When the visual axis in its primary position, directed to the horizon, Medial rectus rotates the eye medially – adduction Lateral rectus rotates the eye laterally – abduction around a vertical axis. Medial & lateral recti lie in the same horizontal plane
- The eye's major blood supply comes from the ophthalmic artery. The lateral muscular branch of the ophthalmic artery supplies the lateral rectus, superior rectus, and superior oblique muscles. The medial muscular branch supplies the inferior rectus, medial rectus, and inferior oblique muscles. Medial and lateral muscular branches of the artery give rise to 7 anterior ciliary vessels, which travel with the 4 rectus muscles to provide circulation for the anterior segment of the eye. Each rectus muscle has 2 anterior ciliary vessels, except for the lateral rectus muscle, which has 1 vessel. These vessels pass anteriorly to the episclera and supply the anterior segment of the eye, including the sclera, limbus, and conjunctiva.
- The role of eye movts is to bring the image of objects of visual interest onto the fovea of the retina and to hold the image steady in order to achieve the highest level of visual acuity..several types of eye movts are required to ensure that these conditions are met. Moreover the movements of both eyes must be near perfectly matched to achieve the venefits of binocularity
- In the setting of an eye movement problem, isolating which muscle or CN is the culprit can be tricky. When trying to isolate a problem, it can help to check movement in the direction in which that muscle is the primary mover. This can be assessed as follows: Superior oblique: Depresses the eye when looking medially Inferior oblique: Elevates the eye when looking medially Superior rectus: Elevates the eye when looking laterally Inferior rectus: Depresses the eye when looking laterally Medial rectus: Adduction when pupil moving along horizontal plane Lateral rectus: Abduction when pupil moving along horizontal plane