Diagnosing and Treating Diabetes Mellitus
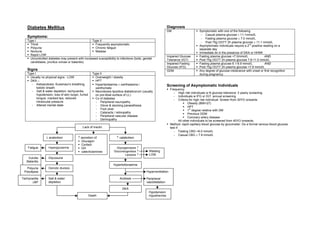
- 1. Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis DM Symptomatic with one of the following - Casual plasma glucose ≥ 11.1mmol/L Symptoms: - Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L Type I Type II - Post 75g OGTT 2h plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L Thirst Frequently asymptomatic nd Asymptomatic individuals require a 2 positive reading on a Polyuria Chronic fatigue separate day Nocturia Malaise Immediate dx in the presence of DKA or HHNK Rapid LOW Impaired Glucose Fasting plasma glucose <7.0mmol/L AND Uncontrolled diabetes may present with increased susceptibility to infections (boils, genital Tolerance (IGT) Post 75g OGTT 2h plasma glucose 7.8-11.0 mmol/L candidiasis, pruritus vulvae or balanitis) Impaired Fasting Fasting plasma glucose 6.1-6.9 mmol/L AND Glucose (IFG) Post 75g OGTT 2h plasma glucose <7.8 mmol/L Signs GDM Any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition Type I Type II during pregnancy. Usually no physical signs - LOW Overweight / obesity DKA – HPT - Ketoacidosis: Kussmaul’s breathing, Hyperlipidaemia ± xanthelasma / Screening of Asymptomatic Individuals ketotic breath xanthomata Frequency - Salt & water depletion: tachycardia, Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (usually - High risk individuals w N glucose tolerance: 3 yearly screening hypotension, loss of skin turgor, furred on pre-tibial surface of LL) - Individuals w IFG or IGT: annual screening tongue, cracked lips, reduced Cx of diabetes - Criteria for high risk individual. Screen from 30YO onwards intraocular pressure - Peripheral neuropathy Obesity (BMI>27) - Altered mental state - Glove & stocking paraesthesia HPT - Foot ulcer st 1 degree relative with DM - Cataracts / retinopathy Previous GDM - Peripheral vascular disease Coronary artery disease - Dermopathy - All other individuals to be screened from 40YO onwards. Method: rapid capillary blood glucose by glucometer. Do a formal venous blood glucose Lack of insulin test if: - Fasting CBG >6.0 mmol/L - Casual CBG ≥ 7.8 mmol/L ↓ anabolism ↑ secretion of: ↑ catabolism Glucagon Cortisol Fatigue Hyperglycaemia GH Glycogenolysis ↑ catecholamines Gluconeogenesis ↑ Wasting Lipolysis ↑ LOW Vulvitis Glycosuria Balanitis Hyperketonaemia Polyuria Osmotic diuresis Polydipsia Hyperventilation Tachycardia Salt & water Acidosis Peripheral ↓BP depletion vasodilatation DKA Hypotension Death Hypothermia
- 2. Treatment (MOH CPG on DM 1999) Initial therapy Significant hyperglycaemia Sulphonylurea or Metformin Aim: Overweight PTs Metformin (causes weight loss) to maintain general health so as to allow the person to live a normal and active live. *α-glucosidase inhibitors: add to diet or other OHGA therapy to improve glucose control, or avoidance of acute hyper/hypoglycaemic complications and chronic vascular complications. as a monotherapy A) Lifestyle modification – first line Rx for type 2 diabetics. Attempt for 2-4 mths C) Insulin Therapy Medical Nutrition Therapy Low saturated fat & cholesterol Indications Low sodium for individuals with HPT Type 1 diabetics Physical Activity & Exercise Recommendation: 3-5X / wk, 60-85% max heart rate, 20- Failure of lifestyle modification and OHGA in glycaemic control in type 2 diabetics 60min each time. Aerobic exercise recommended. During acute illness or stress for glycaemic control in type 2 diabetics Precautions - Proper footwear Regimen (short acting = Actrapid, long-acting = Insulatard) - Adequate hydration Multiple daily injections (regular insulin before each meal + intermediate or long acting - Avoid heavy resistance & isometric exercise insulin as basal insulin) - Avoid exercise when severly hyperglycaemic or 2 injections per day (mixture of regular & intermediate-acting insulin before breakfast and hypoglycaemic for Type 1 diabetics dinner – 2/3 of total daily dose in the morning in ratio of 1:2 of short:intermediate acting Prevention of hypoglycaemia insulin; 1/3 of total daily dose in the evening) - Reduce medication prior to exercise Single injection of intermediate acting insulin at bedtime + OHGA during the day (for Type - Consume some CHO 30-60 min before exercise and 2 diabetics only) after 30 mins of exercise Alternatives: Rapid-acting insulin analogues (eg lispro) – not recommended as for now. - Gradual progression of exercise intensity - Avoid late night exercise Type 1 Diabetics: Multiple daily injection or Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) Smoking cessation Type 2 Diabetics: stepwise therapy with multiple pharmacological therapies needed over Alcohol Alcohol consumption discouraged time to maintain target glucose control. 2 or more OHGA, or insulin Rx ± OHGA may be required Side effects: B) Pharmacotherapy – when diet & exercise fail to control glycaemia in type 2 diabetics Hypoglycaemia Weight gain Peripheral oedema (cause salt and water retention initially when started) Drugs available Insulin antibody Sulphonylurea Stimulate pancreatic insulin release Higher risk of Local allergy Tolbutamide: short T1/2, gd for elderly hypoglycaemia c.f. other Lipodystrophy at injection site Chlorpropamide: long T1/2, may cause drugs prolonged hypoglycaemia. Other SE: cholestatic jaundice, rash, bld dyscrasia, Monitoring of Blood Glucose Control SIADH Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG) Glibenclamide: risk of severe - Indications hypoglycaemia. Avoid in the elderly - All insulin treated PTs (1-2 days per week) Biguanide Decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis GI side effects - Pregnant women with GDM or pregestational DM (Metformin) Enhance peripheral glucose uptake CI in hepatic & renal - Non insulin treated PT with risk of developing hypoglycaemia Delay glucose absorption insufficiency due to risk - All PTs who fail to achieve glycaemic goals of lactic acidosis - PT education: to interpret results of SMBG and modify Rx accordingly if possible for optimal benefit. α-glucosidase Slow absorption of starch and sucrose in GI side effects: inhibitors the gut by inhibiting disaccharidases. flatulence, bloating, diarrhoea Self-monitoring of Urine Glucose (Acarbose) - Inaccurate as raised renal threshold for glucose might mask persistent Thiazolidinediones Insulin sensitizers hepatotoxic hyperglycaemia. Only for PTs unable or unwilling to perform SMBG (Rosiglitazone) CI: hepatic impairment - target control for SMBG: Repaglinide Prandial glucose regulator(take b4 meals) Hypoglycemia
- 3. premeal h/c postmeal h/c ideal (non-DM) 4.0-6.0 5.0-7.0 optimal 6.1-8.0 7.1-10.0 suboptimal 8.1-10.0 10.1-13.0 unacceptable >10.0 >13.0 Self-monitoring of Urine Ketones Prevention of CVS complications - For type 1 DM, GDM and pregestational diabetes in pregnant women Main complications: CAD, CVA, PVD - Indications Main risk factors to control: HPT, dyslipidaemia, smoking - Acute illness or stress Investigations & examination: - Persistent elevated blood glucose >14 mmol/L - Annual screen for dyslipidaemia - Symptoms of ketoacidosis (N/V, abdo pain, acetone breath) - Annual ECG, BP, BMI - Examination for PVD, femoral bruit (↑ risk of cardiovas dz) & carotid bruit (↑ risk of HbA1c CVA) - Measure of average glycaemia over previous 2-3 months - Frequency: 3-4mthly in unstable glycaemic control, change in thearpy or failure to Management: meet target. 6mthly in stable glycaemic control 1) Hypertension Aim: < 130/80 mmHg Rx: Choice of drug depends on additional benefits eg renal & cardioprotective effects Targets of Glycaemic Control Intensive blood glucose control reduce risk of microvascular disease in PTs with type 1 2) Dyslipidaemia or 2 diabetes (Diabetes Control & Complications Trial (DCCT) & UK Prospective ↑ LDL HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) Diabetes Study (UKPDS)) SE: ↑ liver transaminases (check CK and LFT 2-3 mths after starting Rx, stop if However, intensive treatment increases the risk of hypoglycaemic events ALT/AST >3X N or CK >10X N), myopathy, rhabdomyolysis Therefore, targets must be individualized to the patient Target: 2.5 mmol/L ↑ TG Moderate ↑TG: fibrates. Ideal 4.5-6.4% Not attainable by most diabetic patients SE: cholesterol gallstone dz, myopathy, ↑CK (rhabdomyolysis), ↑ liver enzymes Desired target for pregnant women with GDM or Severe ↑TG: combination fibrate with omega-3 polyunsat. fatty acid pregestational diabetes Target: 1.7 mmol/L Optimal 6.5-7.0% Desired target for diabetic PTs Mixed Drug of choice depend on predominant lipid abN Increased risk of hypoglycaemia Suboptimal 7.1-8.0% Attainable for most diabetic PTs Statin + fibrate combination usually used Unacceptable >8.0% Risk of acute metabolic decompensation &/or Cxs of ↓ HDL Fibric acid defivatives. hyperglycaemia Target: 1.0 mmol/L Requires reassessment & readjustment of therapy. 3) Cardiovascular events + macrovascular dz Low dose aspirin (100-300 mg/day) Most diabetics should aim for ‘Optimal’ control. No macrovascular dz Antiplatelet agents. Check for CI (allergy, blding tendencies, recent Indications for ‘Suboptimal’ target levels (generally PTs at risk of permanent injury from GI bld, active hepatic dz) hypoglycaemia): - Older PTs with significant atherosclerosis - PTs with severe DM Cx or comorbidities (severe CAD, CVA, renal failure, proliferative retinopathy, advanced autonomic neuropathy) - Preadolescent children: unpredictable food intake and activity level, poor compliance to treatment
- 4. Prevention of Renal Complications Diabetic Foot Complications Main risks: ulcers & LL amputations Diabetic nephropathy (DN) accounts for 40% of PTs starting renal dialysis in S’pore Major cause of disability & mortality Type 1 DM usually presents with Microalbuminuria 5-15 yrs after onset Screening: at dx & annually. Type 2 DM usually presents already with overt proteinuria Wagner’s Classification: Rate of decline in GFR = 2-20ml/min/year. a. At risk for lower extremity amputation Screening for Microalbuminuria b. Not at risk for lower extremity amputation Dipstix test Risk factors for lower limb amputation Type 1: annually after 5YO Previous Hx of prev. ulceration Type 2: at dx Ulceration PVD pedal pulses absent absence of gradual temp. intermittent claudication / gradient rest pain absence of hair Dipstix + Dipstix – Peripheral negative Semmes- negative turning fork st 24h UTP Random daytime / 1 void neuropathy Weinstein 5.07 (128kHz) sensation Creatinine clearance urine for alb: creatinine ratio monofilament sensation paraesthesia or negative pin prick anaesthesia sensation Diabetic callus interdigital maceration Positive Negative dermopathy ingrown / mycotic toenails fissuring esp at heels Repeat 2X over 3mths. Microalb. Repeat test annually neglect / poor foot skin &/or tinea pedis dxed if 2 of 3 samples are positive hygiene infection Foot deformity gross foot deformity Charcot changes bunions (rockerbottom foot) * Dipstix only detects > 200mg/L albumin, flat feet Claw, hammer, mallet, Intervention to limit progression to not microalbuminuria high arched feet retracted toes overt nephropathy Abnormal gait Monitor UTP or microalb every 6-12 Poor footwear Slippers, flip-flops, thongs Abnormal wear patterns mths Tight or ill fitting shoes Management: DM neph: Optimal glycaemic control Stage I: glomeular hyperfiltration Smoking cessation Stage II: microalbuminemia (>30 mg/d) Stage III: preoteinuria (>300mg/d)—irreversible from here onwards Not at risk Primary med practitioner & Screening of foot Stage IV: renal impairment (Cr >200) diabetic foot care nurse DM footcare education Stage V: ESRF (Cr >900)—start preparing for dialysis when Cr ~>500 At risk Specialist footcare team Wound debridement Pressure analysis Management: Orthoses / insoles for pressure distribution Glycaemic control Aim for HbA1c <7% Footwear adaptations BP control Aim for <130/80mmHg DM footcare education For those with over nephropathy w proteinuria >1g/day, aim for <125/75mmHg st ACE-I is preferred 1 line drug as it reduces proteinuria and slows rate of decline of GFR. Check electrolytes 7days after introduction, and monitor for ↑K+ or ↓ing GFR Low Protein diet Delay progression of CRF in type 1 diabetics with overt nephropathy Lipid control Reduce proteinuria and rate of decline in GFR in DN Smoking Risk factor in devt of DN
- 5. Diabetic Retinopathy Management: - Yearly follow-up if no retinopathy, shorter interval depending on severity if Leading cause of blindness in adults in S’pore retinopathy present DRP likely in the presence of albuminuria and neuropathy (microvascular Cxs) - Optimal glycaemic control Type 1 DM: 25% at 5yrs, 97.5% after 15 yrs of DM - HPT control Type 2 DM: 28.8% at 5 yrs, 77.8% at 15 yrs of DM - Lipid control - Smoking cessation Classification of DRP - Sight-threatening DRP: laser photocoagulation, occasionally vitretomy Non-Proliferative Mild/moderate NPDR Microaneurysms only Retinopathy (Background diabetic Mild degree of venous loops, retinal No macular edema None (NPDR) retinopathy) hemorrhages, hard exudates, Macular edema threatening or involving macular centre Focal / grid macular laser Microaneurysms cotton wool spots NPDR Mild/moderate None Hard exudates Severe NPDR (Pre- One of the following: Severe/ very severe Consider scatter laser Cotton wool spots proliferative diabetic Retinal hemorrhages or PDR Non high-risk & high-risk Scatter laser w/o delay Retinal h’age retinopathy) microaneurysms in 4 quadrants Advanced Scatter laser w/o delay Venous beading Venous beading in 2 quadrants Non-resorbing vitreous opacities, traction retinal Vitreous surgery Intraretinal microvascular detachment threatening or involving the macula, abnormalities in 1 quadrant combined rhegmatogenous & traction retinal Very severe NPDR 2 or more signs of severe detachment or progressive fibro-proliferative DRP (Severe pre-proliferative retinopathy diabetic retinopathy Proliferative Non high-risk PDR 1-2 of the following: Retinopathy new vessels (PDR) new vessels at or near the optic neovascularization disk vitreous h’age moderate or severe new vessels (>1/4 disk area) vitreous hemorrhage High-risk PDR 3 or more of the features above Advanced PDR extensive neovascularisation, vitreous hemorrhage or fibro- vascular proliferation with or w/o retinal detachment Clinically any of the following Significant Macular thickening of the retina at or w/in 500 microns of the centre of the Edema (CSME) macula retinal thickening hard exudates at or w/in 500microns of the centre of the macula, hard exudates if associated with thickening of the adjacent retina areas of retinal thickening 1 disk area or larger, any part of which is w/in 1 disc diameter of the centre of the macula Eye examination schedule (fundal photography, indirect ophthalmoscopy with slit-lamp or direct ophthalmoscopy through dilated pupils) st 1 examination Routine minimum F/U Type 1 DM w/in 3-5 yrs of dx Yearly Type 2 DM At diagnosis Yearly st Pregestational DM Prior to conception & during Depends on 1 trimester st 1 trimester screening
- 6. Hypoglycaemia Venous blood glucose <3.0 mmol/L a/w typical S&S relieved upon correction of bld Morbidity of severe hypoglycaemia glucose CNS Coma Brain damage Usually in diabetic pts treated with insulin or sulphonylureas Convulsions Impaired cognitive function TIA/Stroke Intellectual decline Causes Heart Arrhythmias MI Missed / delayed / inadequate meals Alcohol / salicylates / β-blockers Eye Vitreous hemorrhage Worsening of DRP Gastroparesis Other endocrine disorders – GH & Others Hypothermia Accidents Unexpected / unusual exercise cortisol insufficiency Deficient glucose counter-regulation Sepsis & shock Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia Infection Poorly designed insulin regimen Liver failure / congenital metabolism Factitious disorders Errors in OHGA / insulin dose / schedule Cardiac failure Renal failure Symptoms Autonomic activation Sweating Pallor Trembling Hunger Tachycardia Anxiety Neuroglycopenia Confusion Inability to concentrate Drowsiness Incoordination Speech difficulty Seizures Focal neuro deficits Non-specific Nausea Headache Tiredness Management 1. Monitoring: ECG, pulse oximetry, vital signs 2. Supplemental low-flow O2 3. Check capillary blood glucose stat 4. Hx & examination: medication hx, recent change in drug / doses, recent & chronic illnesses 5. Investigations: venous blood glucose, U/E/Cr, LFT, FBC 6. Treatment Conscious PT Oral carbohydrate rich drink Unconscious PT IV access available: IV dextrose 50% 40-50ml No IV access: IM/SC glucagon 1mg (not for hypoglycaemia due to sulphonylurea or liver failure) Chronic alcoholism IV thiamine 100mg Adrenal insufficiency IV hydrocortisone 100-200mg Associated injuries Tetanus prophylaxis 7. Continued glucose monitoring: capillary blood glucose every 30 mins for first 2 hrs, Digitally signed by DR WANA HLA SHWE hourly thereafter. DN: cn=DR WANA HLA SHWE, c=MY, o=UCSI University, School of Medicine, KT-Campus, Terengganu, 8. Persistent altered mental state despite resolution of hypoglycaemia: CT head to exclude ou=Internal Medicine Group, email=wunna. other causes hlashwe@gmail.com Reason: This document is for UCSI University, School of 9. Disposition: depends on aetiology, severity, response and comorbidities. Admit all cases Medicine students. Date: 2009.03.05 09:01:51 +08'00' due to sulphonylureas due to long half-live of the agent.
- 7. Diabetic Ketoacidosis 4) Urinary catheter – monitor urine output Absolute or relative decrease in insulin level in the presence of excess glucagon. 5) IV volume replacement Usually in type 1 DM First hr NS 15-20 ml/kg/h (~1-1.5L) Common presentation: PT devt infection causing LOW and PT stop insulin Rx. Nxt 2-4 hr 0.45% NS 10-20ml/kg/h (~1 pint q1-4 hrly) Causes When S. glucose < 14mmol/L Change to Paeds D/S (D5W/0.45% NS) o Infections Monitor urine output hourly o Infarction – MI, CVA, GIT, peripheral vasculature Check U/E/Cr/Glu, beta-hydroxybutyrate & venous pH q2-4 hrs o Insufficient insulin Correct fluid deficit (4-6L) w/in first 24 hrs, but serum osmolality should not o Intercurrent illness drop by > 3 mOsm/kg/hr to prevent cerebral edema Diagnostic criteria 6) Early Potassium replacement + + 1) Hyperglycaemia Blood glucose ≥14mmol/L S. K < 3.3 mmol/L Give 20-40 mmol K per hr until K+ >3.3mmol/L 2) Hyperketonaemia Ketonaemia or ketonuria (can be given as 2/3 KCl & 1/3 KHPO4 when S. PO4 is 3) Metab acidosis Arterial pH <7.3, bicarbonate <15mmol/L <0.3mmol/L) + + S. K 3.3-4.9 mmol/L Give 10-15 mmol K per hr + + + + Dehydration: usually about 4-6 L, due to osmotic diuresis. a/w loss of Na & K S. K > 5.0 mmol/L Check S. K every 2 hrs, hold off K+ infusion + + + o K loss due to displacement of intracellular K by H o Fluid deficit initially from intracellular compartment. Later, depletion of 7) Restore acid-base balance extracellular fluid result in haemoconcentration, hypovolaemia, & hypotension ± Give NaHCO3 only if severe hyperkalaemia or arterial pH <7.0 (hydration and renal ischaemia & oliguria insulin will help correct less severe metabolic acidosis) Potassium depletion: IV 8.4% NaHCO3 50-100ml in 200-400ml sterile water over 1-2 hrs (=50- o Plasma concentration a poor indicator of total deficit. 100mmol). Repeat in 2 hrs if necessary. + o Drop in K will occur after starting insulin Rx due to dilution by IV fluids, 8) Insulin administration + + movt of K into ICF and continued renal K loss. Bolus IV SI 0.15 units/kg Low dose continuous 0.1 units/kg/hr (5unit/hr in 50kg PT), adjust to obtain Clinical features infusion rate of drop in S. glucose by 3-4 mmol/L/hr. Symptoms Signs Monitor blood glucose hrly Polyuria N/V Dehydration Acetone breath When blood glucose Halve IV SI infusion rate to 0.05-0.1 units/kg/hr & add Polydipsia Cramps Hypotension Hypothermia <14mmol/L dextrose in IV fluid LOW Blurred vision Tachycardia Confusion / Aim for bld glucose level of 8-12 mmol/L Weakness Abdo pain Kussmaul breathing drowsiness / coma Maintain SI infusion until acidosis clears *raised amylase w/o pancreatitis & leukocytosis due to stress reaction common 9) Treat precipitating factor Complications 10) Admit Cerebral oedema: treat with Thromboembolism 11) Admit MICU if hypotensive/oliguric & refractory to initial rehydration, mental mannitol & oxygen DIVC obtundation/coma or total serum osmolarity >340mOsm/kg ARDS Acute circulatory failure 12) Monitoring Cardiac failure H/C Aim for rate of When H/C <14mmol/L q1hr decrease of 3- Halve IV SI infusion rate to 0.05-0.1 units/kg/hr Management 4mmol/L/hr Change IV fluid to D5W/0.45%NS 1pint q1-4hr 1) Supplemental high-flow O2 Then aim to maintain H/C of 8-12 mmol/L + 2) Monitoring: ECG, pulse oximetry, vital signs q15min, blood glucose, ketones, K & acid- Labs U/E/Cr/Glu, beta- Monitor K+, ketonaemia and metab acidosis base balance q1-2hrs q2- hydroxybutyrate & When acidosis clear (pH >7.3 & HCO3 >15) 3) Lab – assess DKA & look for cause 4hrs venous pH start SCSI q4hr U/E/Cr/Ca/Mg/PO4/Glucose FBC stop SI infusion after overlap of SCSI of 1 hr Urinalysis for ketones & leucocytes DIC screen if septic Urine dipstick Blood culture Serum Ketones (beta- CXR hydroxybutyrate) Cardiac enzymes ABG ECG
- 8. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Non-Ketotic state (HHNK) C.f DKA: clinical course runs into days rather than hours, and there is greater fluid (6- + 10L) and K loss. PTs are usually more sensitive to insulin, thus less insulin is required Diagnostic criteria 1 Hyperglycaemia Blood glucose ≥33mmol/L 2 Hyperosmolality S. total osmolality >330mOsm/kg H2O or effective S. osmolality >320 mOsm/kg H2O* 3 Metab acidosis Arterial pH >7.3, bicarbonate >15mmol/L 4 No ketonaemia or ketouria + *Effective S. osmolality = 2XNa + glucose level + urea ** exclude other causes of obtundation if s. osmolality is not high enough Thromboembolic Cxs common: prophylactic SC heparin may be required Management Similar to DKA with certain exceptions 1) Supplemental High-flow O2 + 2) Monitoring: ECG, pulse oximetry, vital signs q15min, blood glucose & K q1-2hrs 3) Labs FBC U/E/Cr/Ca/Mg/PO4 Serum osmolality ABG Urinalysis 4) Look for cause – ECG, CXR 5) Urine catheter – monitor urine output 6) IV Volume replacement Significant tissue NS rapid bolus until perfusion improves & BP stabilizes st hypoxia 1L NS w/in 1 hr, another 1L over nxt 2 hrs Then 1 L 0.45% NS over nxt 4 hr Hypertensive or sig. 0.45% NS + hyperNa (>155mmol/L) when S. glucose reaches 16mmol/L, switch to IV D5W + 7) K replacement – same as DKA 8) Monitoring 9) Insulin administration Insulin infusion 0.1 units/kg/hr Adjust to maintain bld glucose at 14-16 mmol/L until S. osmolality ≤315 mOsm/L & PT is mentally alert Digitally signed by DR WANA 10) Monitoring HLA SHWE H/C (& venous Aim for rate of When H/C <16mmol/L DN: cn=DR WANA HLA SHWE, c=MY, o=UCSI bld glucose if decrease of 3- Halve IV SI infusion rate to 0.05-0.1 units/kg/hr University, School of Medicine, H/C reads 4mmol/L/hr Change IV fluid to D5W 1pint q1-4hr KT-Campus, Terengganu, ou=Internal Medicine Group, “HHH”) Then aim to maintain H/C of 14-16 mmol/L until email=wunna.hlashwe@gmail. q1 hr plasma osmolarity ≤315mOsm/kg & PT is alert com Reason: This document is for Labs U/E/Cr/Glu & Monitor K+, ketonaemia and metab acidosis UCSI year 4 students. q2-4hrs beta- Date: 2009.02.19 09:28:42 +08'00' hydroxybutyrate
