Glycine receptor
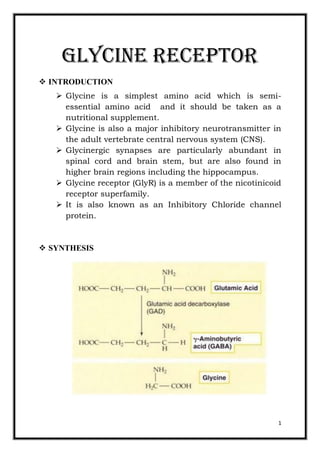
- 1. 1 Glycine Receptor INTRODUCTION Glycine is a simplest amino acid which is semi- essential amino acid and it should be taken as a nutritional supplement. Glycine is also a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Glycinergic synapses are particularly abundant in spinal cord and brain stem, but are also found in higher brain regions including the hippocampus. Glycine receptor (GlyR) is a member of the nicotinicoid receptor superfamily. It is also known as an Inhibitory Chloride channel protein. SYNTHESIS
- 2. 2 STRUCTURE Glycine receptors exist as pentameric proteins, homo- oligomers of the α isoforms (α1, α2, α3 or α4) or hetero-oligomers which also contain the β-subtype variant (β1) which is essential for targeting the receptor to the synapse. Receptors are arranged as five subunits surrounding a central pore, with each subunit composed of four α helical transmembrane segments. There are presently four known isoforms of the α- subunit (α1-4) of GlyR that are essential to bind ligands (GLRA1, GLRA2, GLRA3, GLRA4) and a single β-subunit (GLRB). The adult form of the GlyR is the heteromeric α1β receptor, which is believed to have a stoichiometry (proportion) of three α1 subunits and two β subunits (3α : 2β) or four α1 subunits and one β subunit (4α :1β). GlyR is also composed of Gephyrin together with α and β subunits. Gephyrin is an enchoring protein required for the postsynaptic clustering of GlyRs.
- 3. 3 TYPES OF RECEPTOR The GLRA1 gene is located on chromosome 5p32. In situ hybridisation studies have shown GLRA1 to be expressed in the spinal cord, brain stem and colliculi. GLRA1 trancripts together with GLRA3, predominate in the postnatal CNS, replacing GLRA2, which is more abundant in embryonic and neonatal neurones. The GLRA2 gene is located on chromosome Xp22.2- 22.1. GLRA2 is expressed in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex and thalamus. GLRA2 trancripts predominate in the neonatal and embyonic CNS, decreases after birth and are replaced postnatally by those of GLRA1 and to a lesser extent, GLRA3. The GLRA3 is expressed in the cerebellum, olfactory bulb and hippocampus. GLRA3 trancripts, together with GLRA1, predominate in the postnatal CNS, replacing GLRA2, which is more abundant in embryonic and neonatal neurones. The β-subnit reduces single channel conduction and alters pharmacology and contributes to agonist binding. MECHANISM Glycine is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult CNS which acts by Ligand gated Ion Channel, whereas it is excitatory during embryonic development and around birth. This is due to a positive Chloride equilibrium potential of the postsynaptic neurons, which results in chloride efflux upon GlyR activation, causing depolarisation.
- 4. 4 In general, the chloride equilibrium potential shifts to negative value owing to active chloride extrusion by the K+ / Cl- co-transporter. Thus GlyR activation becomes hyperpolarizing and therefore inhibitory. With regard to the source of energy, ion transporters fall into two categories: primary active transporters are directly fueled by ATP, while secondary active transporters take the energy for transport of the driven ion from the electrochemical gradient of another ion species. The ubiquitous primary active transporter, the Na-K ATPase, generates plasmalemmal K+ and Na+ gradients that provide the main source of energy for most secondary active transporters.
- 5. 5 Extrusion of Cl– via KCC mediated K-Clcotransport is driven by the K+ gradient, while uptake of Cl– in many neurons is driven by NKCC1 that exploits the plasmalemmal Na+ gradient as its energy source for Na-K-2Cl cotransport. The KCC2cotransporter operates at near-equilibrium, which permits maximization of the efficiency of harvesting energy from the K+ gradient to fuel the extrusion of Cl–. The sodium-independent Cl- / HCO3- exchanger may act as a significant Cl– uptake mechanism in neurons. In addition to its role in neuronal Cl– homeostasis, HCO3- acts as a significant carrier of depolarizing current. FUNCTION To prevent tissue injury To enhance anti-oxidant capacity To promote protein synthesis and wound healing To improve immunity For biosynthesis of Heme, Creatinine & Glutathione REGULATION The GlyR beta subunit contains a putative tyrosine phosphorylation site. Protein Tyrosine Kinase (PTK) regulate the function of GlyRs on the tyrosine - 413 residue of the beta subunit.
- 6. 6 AGONIST Glycine : Endogenous glycine receptor agonist Taurine : Non-selective, endogenous glycine receptor partial agonist β-Alanine : Endogenous glycine agonist, more selective than taurine L-Alanine : Glycine receptor agonist Hypotaurine : Non-selective endogenous glycine receptor agonist L-Serine : Weak endogenous glycine receptor agonist
- 7. 7 GLYCINE Glycine is an amino acid, a building block for protein. SOURCE :It is found primarily in gelatin and silk fibroin and used therapeutically as a nutrient. MECHANISM OF ACTION :In the CNS, there exist strychnine- sensitive glycine binding sites as well as strychnine- insensitive glycine binding sites. The strychnine-insensitive glycine-binding site is located on the NMDA receptor complex. The strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor complex is comprised of a chloride channel and is a member of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. The putative antispastic activity of supplemental glycine could be mediated by glycine's binding to strychnine-sensitive binding sites in the spinal cord. This would result in increased chloride conductance and consequent enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission. The ability of glycine to potentiate NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission raised the possibility of its use in the management of neuroleptic-resistant negative symptoms in schizophrenia. PHARMACOKINETIC :It is absorbed from small intestine via an active transport mechanism and it is metabolized in liver. USE : Glycine is used for treating schizophrenia, stroke, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and some rare inherited metabolic disorders. It is also used to protect kidneys from the harmful side effects of certain drugs used after organ transplantation as well as the liver from harmful effects of alcohol. Sometimes it can also be used to treat leg ulcers and heal other wounds by applying on the skin. Glycine is also used as a sweetener, emollient, emulsifying agent and solubilizing agent.
- 8. 8 ANTAGONIST Selective o Strychnine: toxic, colorless, bitter crystalline alkaloid obtained from nux-vomica o Brucine: closely related to strychnine, highly toxic alkaloid present in nux-vomica o Tutin: potent antagonist Non-selective o Bicuculline: Phthalide-isoquinoline compound o Caffeine: A crystalline compound found in tea and coffee, a stimulant of CNS o Picrotoxin: A bitter compound used to stimulate the respiratory and nervous system o Pitrazepin: Competitive glycine receptor antagonist DISOREDERS 1. Hyperekplexia (Startle Disease) Hyperekplexia is a hereditary neuromotor disorder resulting from the mutation of Glrα and Glrβ genes cause an impairment of glycinergic transmission on the chromosome 5q33 – q35 It is characterised by an exaggerated startle reaction in response to unexpected auditory or visual stimuli often followed by a short period of generalised stiffness. It is treated by administration of the drug Clonazepam.
- 9. 9 2. Bovine Myoclonus A congential recessive startle syndrome is called myoclonus. It is due to a deletion of single base pair in the α1 subunit gene, leading to a frameshift and a premature stop codon. This mutation induces a dramatic reduction in the surface expression of functional GlyR. 3. Non-ketoticHyperglycinemia Non-ketotichyperglycinemia is an autosomal disorder caused by a defect in the enzyme system that breaks down the amino acid glycine, resulting in an accumulation of glycine in the body’s tissues and fluids. It is caused by the genetic mutation in the genes that encode the components of the glycine cleavage enzyme system. The treatment involves : Sodium benzoate is used to reduce serum glycine levels and Dextromethorphan is used to reduce seizures and improve alertness. 4. Glycinuria Glycinuria is also an autosomal disorder resulting from the impaired renal tubular reabsorption of glycine. This will lead to increased excretion of glycine but serum glycine level is normal leading to the increased risk of oxalate stones.
- 10. 10 REFERENCE http://physrev.physiology.org/content/84/4/1051.lo ng http://www.ucl.ac.uk/pharmacology/dc-bits/c-and- sivilotti-2004-tins.pdf https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24236782_fig1 _Figure-1-Ion-Transport-Mechanisms-Underlying- GABA-A-and-Glycine-Receptor-Mediated https://www.tocris.com/pharmacologicalBrowser.ph p?ItemId=4979#.WAfQe-B97IU http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0 165614702021387 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8540234_ Function_and_structure_in_glycine_receptors_and_so me_of_their_relatives http://dcscience.net/lewis98.pdf http://www.guiametabolica.org/sites/default/files/B rochure_NonKetotic_Hyperglicemina_def.pdf http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00145