Science Form 2 Nutrition notes
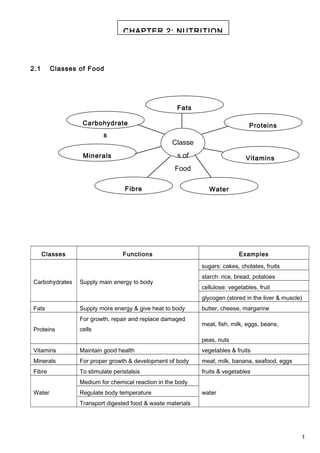
- 1. 2.1 Classes of Food Classes Functions Examples Carbohydrates Supply main energy to body sugars: cakes, cholates, fruits starch: rice, bread, potatoes cellulose: vegetables, fruit glycogen (stored in the liver & muscle) Fats Supply more energy & give heat to body butter, cheese, margarine Proteins For growth, repair and replace damaged cells meat, fish, milk, eggs, beans, peas, nuts Vitamins Maintain good health vegetables & fruits Minerals For proper growth & development of body meat, milk, banana, seafood, eggs Fibre To stimulate peristalsis fruits & vegetables Water Medium for chemical reaction in the body waterRegulate body temperature Transport digested food & waste materials 1 CHAPTER 2: NUTRITION Classe s of Food Carbohydrate s Fats Proteins Fibre Minerals Vitamins Water
- 2. Excess carbohydrates stored as fat in the body. Vitamins A, D, E, K – fats soluble Vitamins B, C – Water soluble Vitamins – required in small quantity for body Vitamins Functions Examples Deficiency diseases A To promote healthy skins & eyes carrot, tomatoes, green vegetables Dry skin , night blindness B Maintain healthy skin & nervous system yeast, liver, vegetables Beri-beri, Pellagra, Anaemia C To increase immunity against diseases guavas, grapes, tomatoes, Scurvy Maintain healthy skin, teeth, gums citrus fruit, vegetables D Maintains healthy & strong teeth & bones milk, eggs, fish Rickets, softening of bones Promotes calcium & phosphorus absorption & teeth E Maintain healthy reproduction system seeds, nuts, egg yolk, whole grain Sterility K Blood clotting liver, egg yolk, green vegetables prolong bleeding Minerals Functions Examples Deficiency diseases Sodium Maintain body fluid balance cheese, meat, table salt muscle cramps Potassium For nerve & muscle activities bananas, fish, meat paralysis, weak muscles Calcium Maintain strong & healthy teeth & bones milk, eggs, anchovies, Rickets, Osteoporosis, Helps blood clotting green vegetables prolong bleeding Iron Formation of haemoglobin in red blood cell liver, egg yolk, meat Anaemia Iodine Make the hormones of the thyroid seafood, seaweed Goitre 2
- 3. gland Phosphorus Help in muscle contraction, make healthy cheese, milk, eggs Rickets, tooth decay, bones, and teeth weak muscle Beri-beri (disease of nervous system) Pellagra (skin disease) Anaemia (shortage of red blood cell) Scurvy (bleeding gums) 3
- 4. Rickets (stunted growth) Goitre (swollen neck) Kwashiorkor (lack of protein) 4 Food Test Classes Type of test Reagent Result Starch Iodin test Iodine brown colour Iodine change into blue black Glucose Benedict's test / Fehling's test Benedict's solution brick-red precipitate formed Proteins Millon's test Millon's reagent white precipitate - red colour Etanol milky solution or white emulsion
- 5. Balanced diet – Diet which contains all seven types of food classes in the right quantities & proportions. 5 Factors affecting balanced diet Factors Explanation Reason Age babies, children, & teenagers need more Babies, children, and teenagers energy than adults more active & life process faster Gender Men need more energy than woman Men are more active than woman of the same age & body size Body size Big size individuals need more energy Big size individual need more than small size individual energy for life process Health Patients’ needs more energy than Patients need more energy to condition someone who is healthy recover from diseases. Type of Heavy work need more energy Heavy work need more job than light work energy to perform Climate Individual live in cold weather need more More energy required in cold weather energy than individual live in warm weather to maintain body temperature
- 6. 6 Calorific value of food Human digestive system
- 7. 1. Digestion – process of breaking down large food molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by body. 2. Physical digestion – breaking down food into smaller particles by teeth. 3. Chemical digestion – breaking down food by enzymes. 7 Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Duodenum Anus Rectum Large intestine Small intestine Organs Functions Mouth Cut & chews the food into smaller molecules Oesophagus Channels food (bolus) to stomach through peristalsis action Stomach Begins the digestion of protein Duodenum Secret pancreatic juices to digest protein, carbohydrate, & fats Small intestine Complete the food digestion and absorb end product of digestion Large intestine Reabsorb water & minerals from indigested food Rectum Store the faeces Anus Removes faeces from body Salivary glands Produce saliva which contain amylase enzyme Liver Secrets bile to emulsify fats Gall bladder Store bile which is secreted by liver Pancreas Produce digestive enzymes (amylase, protease, lipase)
- 8. 4. Peristalsis – Contraction & relaxation of digestive tract to channel the food throughout the digestive tract. 8 Organs Juices Enzyme Functions Mouth Saliva (alkaline) Amylase Starch - Maltose Stomach Gastric juice Protease Protein - Polypeptide or Peptone (acidic) Casein/Rennin Liquid milk protein - Solid form Hydrochloric acid Kills bacteria in the food Duodenum Pancreatic juice Amylase Starch - Maltose (secreted by pancrease) Protease Protein - Polypeptide or Peptone (Alkaline) Lipase Fat - Fatty acid + Glycerol Bile (alkaline greenish fluid secreted by liver) Emulsify fats & oils into globules Small intestine Intestinal juice Maltase Maltose - Glucose Protease Peptone - Amino acid Lipase Fat - fatty acid + Glycerol
- 9. 1. Absorption of end product take place in small intestine through the diffusion process. 2. Length of small intestine – 6 metre. Walls of small intestine is folded to increase its surface area. 3. Features of small intestine: a. Have many finger-like projections known as villi (singular: villus). b. Have many blood capillaries to facilitate absorption. c. Very long about 6 m allows greater absorption. d. Very thin so that small molecules can enter the blood capillaries. e. Moist lining enables food molecules to dissolve easily. 4. Vilus or Villli – the surface of small intestine covered with millions of tiny finger-like projections. 5. Functions of vilus – Absorb digestion food effectively. 9 Food class End product Carbohydrate Glucose Protein Amino acid Fat Glycerol + fatty acid Absorption of digested food Water, minerals, vitamins are need not to be digested because these food are very small and simple molecules that can be absorbed into body.
- 10. 1. Undigested food enters the large intestine. 2. Reabsorption of water & minerals from undigested food (e.g cellulose, fibre) take place. 3. Defecation – process where faeces removed from body. 4. Faeces is formed and stored in the rectum. Then, removed through anus. 1. Good eating habits – Eating nutritious food in right quantities & proportion. 2. Healthy eating habits: a. Eat plenty of vegetables & fruit. 10 Reabsorption of water & defecation Good eating habits
- 11. b. Consume less sugar & salt c. Eat in moderation d. Drink plenty of water e. Chew food thoroughly before swallowing f. Eat nutritious food g. Avoid junk food 3. Unhealthy eating habits: a. Consume high sugar lead to diabetes b. Consume high salt lead to blood pressure c. Consume too much fat lead to high blood cholesterol and heart diseases 4. Constipation – difficulty to defecate hard faeces from body. 5. Causes of constipation – lack of water & roughage in diet. To avoid constipation, must eat food such as fruits, vegetables, and grains. 6. Over weight/ Obesity – Excess body fat which can cause health problem such as diabetes, hypertension, heart diseases, cancer, & failure in respiratory and excretory systems. 7. Causes of obesity – Genetic, lack of exercise, unbalanced nutrition 8. Saturated fat is bad for body because fat will accumulate in the blood stream and cause blockage of blood vessels and lead to heart attack and stroke. 11