PMP Chap 5 - Project Scope Management - Part1
- 1. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Plan scope management Collect Requirements Define Scope Create WBS Validate Scope Control Scope Learn Project Management & prepare for PMP exam: • Learn visually • Detailed coverage of all PMP concepts • Sample Questions PM BOK Chapter 5 : Project Scope Management (Part 1) Planning Monitoring & Controlling
- 2. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Chap 5 - Project scope Management Introduction Project Scope Management Definition Scope Definition (Project & Product scope) Scope Management Processes Each Process in details Review of Project Scope management knowledge area Self Assessment
- 3. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Introduction-> Scope definition Scope Definition: • The sum of the products, services and results to be provided as a project.
- 4. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Introduction-> Product & Project Scope Project scope: • The work performed to deliver a product, service, or result with specified features & functions. • Project scope statement. • WBS & WBS dictionary. Product scope: • The features and functions that characterize a product, service or result. • Product Requirements. • Product Specifications.
- 5. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Introduction-> Product & Project Scope Project Scope The “How” Work/Delivery oriented Work that need to be done to Deliver the Product or Service Product Scope The “What” Functional requirement or Product / Services Features & functions that Characterize a product or services Product Scope
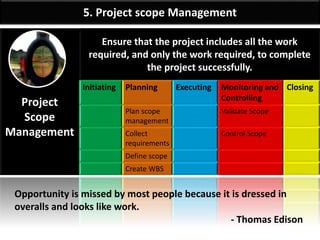
- 6. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Introduction-> Scope Management Definition Scope Management Definition: • It includes processes required to ensure that the project includes all the work required, and only work required to complete project successfully. Project includes all the work required Only the work required Complete project successfully Scope Management ensure For exam assume, you have to determine all requirement as a part of the project.
- 7. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Project scope Management - Importance of scope Project Team needs clear understanding of the work Documentation is key to delivery All documents should be accepted (Sign-off) Clear change control process must be followed for any changes Project success
- 8. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area 5.1 Plan Scope Management: Creating a scope management plan that define how scope will be defined, validated, and controlled. 5.2 Collect Requirements: Determining, documenting, and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives 5.3: Define Scope: Developing a detailed description of the project and product.
- 9. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area 5:4 Create WBS: Subdividing project deliverables and project work into smaller, more manageable components. 5:5 Validate Scope: Formalizing acceptance of the completed project deliverables. 5.6 Control Scope: Monitoring the status of the project & product scope and managing changes to the scope baseline.
- 10. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management Plan Scope Management definition Plan Scope Management - ITTO What is Scope Management Plan? What is Requirements Management Plan? Review Self Assessment
- 11. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com)By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Document how to ensure delivery of Meet Customer Expectations 5.1 Plan scope management How scope is: Defined Developed Monitored Controlled Verified
- 12. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management Definition The process of creating a scope management plan that documents how the project scope will be defined, validated, and controlled. It provides guidance & direction on how scope will be managed throughout the project lifecycle. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Defined ControlledValidated
- 13. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> ITTO Inputs (4) • Project Management plan • Project charter • Enterprise Environmental Factors • Organizational process units Tools & Techniques (2) • Expert Judgment • Meetings Outputs (2) • Scope Management plan • Requirements management plan
- 14. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Input Project Management plan Project Charter Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational process Assets
- 15. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management->Input->PMP Project Management plan Approved subsidiary plans of PMP are used: • Stakeholder Management Plan -> • help to develop strategy to elicit requirements from different stakeholders. • Communication Management Plan -> • How scope changes will be communicated. • Risk Management Plan -> • can help you to deal with any scope related risks. It influence approach taken for planning & managing scope.
- 16. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management->Input->Project Charter Project Charter It provides the project context to plan the scope. Provides project objectives & description. Provides high level product characteristics.
- 17. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management->Input-> EEF & OPA Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational culture Infrastructure Resources Organizational process Assets Policies & procedures. Historical information Lesson learned.
- 18. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Tools & Techniques Expert Judgment Meetings
- 19. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Tools & Techniques Expert Judgment Input received from Knowledgeable & experienced parties. It can be provided by group or person with specialized, education, knowledge, skills etc E.g., Business SME, Industry Consultants, other PM’s What techniques can be used to capture the requirements? How business acceptance will be done for this project?
- 20. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Tools & Techniques Meetings Project team may attend meetings. Project Manager Sponsor Selected team members Selected stakeholders Any one with scope related responsibilities should attend meetings. Discuss & agree how the requirements will be prioritized. Discuss & agree business acceptance process with business team.
- 21. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Output Scope Management Plan Requirements Management Plan
- 22. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Output -> Scope MP Scope Management Plan How Scope will be: Defined Developed Monitored Controlled Verified. SMP contains how to: How to prepare detailed project scope statement. Enables the creation of the WBS. Establishes how WBS will be maintained and approved. How formal acceptance of deliverables will be obtained. How requests for changes will be controlled & processed.
- 23. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management->Output->Requirements MP Requirements Management Plan Requirement: A capability that is required in a product, service or result to satisfy customer needs. Requirements Management Plan: Describes how requirements will be analysed, documented and managed. Components of RMP How requirements activities will be planned, tracked & reported. Requirements prioritization process. Product metrics that will be used and the rationale for using it. List of attributes that will be captured on Requirements traceability matrix (RTM). Configuration Management to initiate, track & report changes.
- 24. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management->Output->Requirements MP RTM is a grid that links product requirements to deliverables that satisfy them. Helps you to track requirements throughout project life cycle RTM is progressively updated & is part of project documents. Requirements Management Plan
- 25. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope Management -> Data Flow diagram 5.1 Plan Scope Management Scope Management Requirements Manag. plan 5.2 Collect Requirements 5.3 Define Scope 5.4 Create WBS 4.1 Develop Project charter Project charter 4.2 Develop PM plan PM Plan Enterprise / Organization OPA EEF
- 26. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope management -> Review Why Scope Management planning is important? Role of Expert Judgment & Meetings? What Scope Management Plan contains? What Requirements Management Plan contains?
- 27. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope Management -> Question Completion of a product scope is measured against: A) Product Management Plan B) Project Management Plan C) WBS & WBS Dictionary D) Product Requirements C
- 28. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan scope Management -> Question Identify the output of the Plan scope management which is linked to Perform Integrated change control process A) Project scope statement B) Project Management Plan C) Scope Management Plan D) Requirements Traceability Matrix C
- 29. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Learn Project Management & prepare for PMP exam: • Learn visually • Detailed coverage of all PMP concepts • Sample Questions
- 30. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements Collect Requirements definition Collect Requirements- ITTO What are different types of requirements? Focus group meetings & Facilitated workshops? Group decision making & Group creativity techniques? What is Requirements document & Traceability matrix? Review Self Assessment
- 31. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area 5.1 Plan Scope Management: Creating a scope management plan – how scope will be defined, validated, and controlled. 5.2 Collect Requirements: Determining, documenting, and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives 5.3: Define Scope: Developing a detailed description of the project and product.
- 32. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area 5:4 Create WBS: Subdividing project deliverables and project work into smaller, more manageable components. 5:5 Validate Scope: Formalizing acceptance of the completed project deliverables. 5.6 Control Scope: Monitoring the status of the project & product scope and managing changes to the scope baseline.
- 33. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Requirements are a set of demands, necessitates, needs, constraints highlighted by the stakeholders. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Project Manager Business Analyst System analyst Quality Analyst Sponsor Business Users / SME Operations Other Stakeholders Who collects Requirements Who provides Requirements Demands Necessities Needs Constraints 5.2 Collect Requirements
- 34. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements Determining, documenting and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives. It provides the basis for defining & managing the project scope including product scope. Requirements Unambiguous Traceable Complete Consistent Acceptable to stakeholders By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Determining Managing Documenting Project Stakeholder needs & Requirements
- 35. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements The most difficult part of requirement gathering is not the act of recording what the users wants, it is the exploratory development activity or helping users to figure out what they want.
- 36. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Requirements classification Business requirements Stakeholder requirements Solution requirements Transition requirements Project requirements Quality requirements
- 37. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Requirements classification Business requirements: • Describe the higher-level needs of the organization • Business issues or opportunities, and reasons why a project has been undertaken. Stakeholder requirements: • Describe needs of a stakeholder or stakeholder group. Solution requirements: • Describe features, functions, and characteristics of the product, service, or result that will meet the business and stakeholder requirements.
- 38. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Requirements classification Transition requirements: • Describe temporary capabilities, such as data conversion and training requirements, needed to transition from the current “as-is” state to the future “to-be” state. Project requirements: • Describe the actions, processes, or other conditions the project needs to meet. Quality requirements: • Capture any condition or criteria needed to validate the successful completion of a project deliverable or fulfilment of other project requirements.
- 39. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Requirements classification Solution requirements are further grouped into: • Describe the behaviour of the product. • Examples - processes, data, and interactions with the product. Functional requirements • Describe the environmental conditions or qualities required for the product to be effective. • Examples : Security, Reliability, Performance, Safety, level of service, supportability etc. Non-functional requirements
- 40. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements Inputs(5) • Scope management plan • Requirements management plan • Stakeholder management plan • Project charter • Stakeholder register Tools & Techniques (11) • Interviews • Focus groups • Facilitated workshops • Group creativity techniques • Group decision-making techniques • Questionnaires and surveys • Observations • Prototypes • Benchmarking • Context diagram • Document analysis Outputs (2) • Requirements documentation • Requirements traceabilty matrix
- 41. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input Scope management plan Requirements management plan Stakeholder management plan Project charter Stakeholder register
- 42. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input-> Scope MP Scope Management Plan How Scope will be: Defined Developed Monitored Controlled Verified. SMP will help: Understand what all requirement need to be captured? Who will provide the requirements? What mechanism to be used to capture the requirements (Brainstorming, user stories etc.) What are the acceptance requirements?
- 43. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input->Requirements MP Requirements Management Plan Requirements Management Plan: Describes how requirements will be analysed, documented and managed. RMP will guide: How requirements activities will be planned, tracked & reported. Requirements prioritization process. Product metrics that will be used for prioritization and rationale for using it. Attributes to be captured on RTM.
- 44. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input->Project Charter Project Charter It provides the project context to plan the scope. Provides High level requirements. Provides project description Provides product characteristics.
- 45. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input-> Stakeholder MP Stakeholder management plan How to manage stakeholder & get requirements. Which stakeholder can provide requirements. Understand stakeholder communication requirements Level of stakeholder engagement Helps to ensure stakeholder participation.
- 46. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Input-> Stakeholder register Stakeholder register Identify stakeholder who can provide information on requirements captures major stakeholder requirements Capture key expectations.
- 47. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Tools and Techniques Interviews Focus groups Facilitated workshops Group creativity techniques Group decision- making techniques Questionnaires & surveys Observations Prototypes
- 48. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Tools and Techniques Benchmarking Context diagram Document analysis
- 49. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T & T -> Interviews Interviews Approach to elicit information from stakeholders by directly talking to them. Spontaneous questions Useful to obtain confidential information Project participants Sponsors Other executives Subject matter experts
- 50. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T & T -> Interviews Interviews Formal or informal approach to elicit information by talking directly. Asking prepared & spontaneous questions and recording responses. Conducted on an individual basis, may involve multiple interviewers or interviewees. Interviewing experienced project participants can aid in identifying and defining the features and functions. Interviews are also useful for obtaining confidential information.
- 51. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T -> Focus groups Focus groups Bring together prequalified stakeholders & SME to understand their expectations & attitudes. Trained moderator develop a discussion by asking predefined questions. Discussion is focused around a topic. Cons Trained Moderator required Less control Pros Has fix agenda More structured
- 52. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T->Facilitated Workshops Facilitated workshops Objective is to develop a consensus for decision based on Agenda/ goal of workshop. Cross functional team members are involved, can quickly defining cross-functional requirements. Reconciling stakeholder differences. Early issues discovery & resolution Pros Build Trust Foster relationship Improve Communication Joint Application Design/developm ent (JAD): Quality Function Deployment (QFD) User stories
- 53. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T->Facilitated Workshops Facilitated workshops Joint Application Design/development (JAD): • Software development industry. • Bring SME & development team together.
- 54. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T->Facilitated Workshops Facilitated workshops Quality Function Deployment (QFD) • Used in manufacturing industry. • Determine critical characteristics for new products. • Starts by collecting customer needs (Voice of Customer) • Needs are then objectively sorted & prioritized.
- 55. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T->Facilitated Workshops Facilitated workshops User stories : • User stories are widely used with agile methods. • Describe: • The stakeholder who benefits from the feature (role) • What the stakeholder needs to accomplish (goal) • The benefit to the stakeholder (motivation)
- 56. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Group creativity techniques Techniques that are used to generate ideas within a group of stakeholders. Several group activities can be organized to identify product & project requirements. Brainstorming Affinity diagrams Nominal group techniques Idea / mind mapping Multi-criteria decision analysis
- 57. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Brainstorming: To generate and collect Multiple ideas related to project and product requirements. Affinity diagrams: Allows large numbers of ideas to be CLASSIFIED into groups for review and analysis. Nominal group techniques: Enhances brainstorming with a VOTING process used to rank the most useful ideas for further brainstorming or for prioritization Idea / mind mapping: Ideas created through individual brainstorming sessions are CONSOLIDATED into a single map to reflect commonality and differences in understanding, and generate new ideas Multi-criteria decision analysis: Utilizes a decision MATRIX to provide a systematic analytical approach for establishing criteria, such as risk levels, uncertainty, and valuation, to evaluate and rank many ideas.
- 58. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Brainstorming: To generate and collect Multiple ideas related to project and product requirements. Idea Generation & Idea Selection are part of a brainstorming session, while Problem Identification occurs before session & Implementation occurs after session. Brainstorming stages: Problem Identification (Prior activity) Idea Generation Idea Selection (decision making) Implementation (Post activity)
- 59. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Brainstorming: Output of brainstorming session can be used as input to refine & detail idea’s. Brainstorming Affinity diagrams Nominal group techniques Idea / mind mapping Idea’s
- 60. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Affinity diagrams (KJ Method): Allows large numbers of ideas to be CLASSIFIED into groups for review & analysis • Going Through Large Volumes of Data. Stimulate Idea Generation & new Patterns of ThinkingUse it: • When the data sets available are small in number (less than 15)Avoid it: Identify Problem List ideas/issues (Brainstorming) Create affinities Analyse Results
- 61. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Brainstorming Affinity Diagram To generate and collect Multiple ideas related to project and product requirements. Allows large numbers of ideas to be CLASSIFIED into groups for review and analysis.
- 62. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Nominal group techniques: Enhances brainstorming with a VOTING process, used to rank most useful ideas for further brainstorming or for prioritization. The issue is controversial or there is heated conflict. Some group members are much more vocal than others. The group does not easily generate quantities of ideas. Some group members think better in silence. All or some group members are new to the team. Used When
- 63. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Idea / mind mapping: Ideas created through individual brainstorming sessions are CONSOLIDATED into a single map to reflect commonality & differences & generate new ideas. Used for: Thinking through complex problems. Summarizing information & note taking. Consolidating information from different research sources. Presenting information showing overall structure of your subject. 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity
- 64. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T-> Group Creativity Multi-criteria decision analysis: Uses a decision MATRIX to provide a systematic approach for setting criteria, such as risk levels, uncertainty, to evaluate & rank ideas. Use for ranking ideas. Quantify requirements using decision matrixes. Matrix uses factors like risk level, time estimates, Cost & benefits etc. # Defect description Duratio n Complexity Impact on modules Total 1 Login process 1 -> 5 Medium -> 7 Minor -> 5 2 Payroll processing 4 -> 7 Complex ->10 Minor -> 5 3 Send payroll instructions to banks 8 -> 10 Complex ->10 Major -> 10 4 Send Tax deductions to Govt. tax dept. 10 -> 10 Complex ->10 Major -> 10 # Development Duration Value 1 More than a week 10 2 2 to 7 days 7 3 Less than 2 days 5 # Development complexity Value 1 Complex 10 2 Medium 7 3 No impact 5 # Impact to other area’s Value 1 Major 10 2 Medium 7 3 Minor 5 5+7+5 = 17 7+10+5 = 22 10+10+10=30 10+10+10=30
- 65. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Group decision- making techniques Assess multiple alternatives that will be used to generate, classify, and prioritize product requirements. Unanimity: EVERYONE agrees on a single course of action. (Delphi technique) Majority: Agree more than 50 % of the members of the group. Plurality: LARGEST block in a group decides, even if a majority is not achieved. Dictatorship: ONE individual makes the decision for the group 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T -> Group decision
- 66. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Questionnaires & surveys These are written set of questions designed to quickly accumulate information from large number of respondents. Most appropriate with varied audiences. Used when Quick turnaround is needed. Used when respondents are geographically dispersed. Statistical analysis is appropriate. 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T-> Questionnaires & surveys
- 67. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Observations Provides a direct way of viewing individuals in their environment performing their jobs & carrying out processes. Problem with this method: Generally Observer see what he expects to see. Hawthorne Effect: Short term improvement in observing worker. Helpful in dealing with processes, when people using product have difficulty to articulate their requirements. 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T ->Observations Observe & collect requirements
- 68. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Prototypes Iterative cycles: Mock-up creation User experimentation Feedback generation Prototype revision. Process continue till enough feedback cycles performed Requirements are sufficiently complete Move to a design or build phase 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T&T ->Prototypes If you are not confident about the requirement or developing something new, then prototype can be used to gather requirement. A working model of the expected product can be developed to get early feedback on requirements.
- 69. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Benchmarking Comparing actual or planned practices, such as processes & operations, to those of comparable organizations. The organizations compared during benchmarking can be internal or external. Used: Identify best practices Generate ideas for improvement Basis for measuring performance. 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T & T -> Benchmarking Standard: EN 60529
- 70. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T & T -> Context diagram Context diagram Visually depict product scope by showing a business system (process, computer system), & how people & other systems interact with it. Shows scope & boundaries of a system at a glance No technical knowledge is required to understand Can benefit a wide audience Human Resources Employees Gov’t Insurance BanksDepts. Payroll system Payroll changes Deductions PaychequesReports T & A Reports Taxes Tax related policies Reports Rate, policy changes Payments
- 71. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> T & T -> Document analysis Document analysis Elicit requirements by analysing existing documentation Identifying information relevant to requirements. Business plans Agreements Requests for proposal Current process flows Logical data models Business rules repositories Application software documentation Business process or interface documentation Problem/issue logs Policies Procedures Regulatory documentation (laws, codes, ordinances)
- 72. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Requirements documentation Requirements traceability matrix 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Output
- 73. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->Output->Requirements Documents Business requirements •Objectives for traceability •Business rules Stakeholder requirements •Stakeholder communication •Reporting Solution requirements •Functional and non functional •Technology & standard Transition requirements Project requirements •Level of service, performance, compliance •Acceptance criteria Quality requirements Requirements documentation It describes how individual requirements meet the business need for the project. Example: Software projects: BRS – business requirements specification, Reporting requirements Assumptions Dependenc -ies Constraints
- 74. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Req. -> Output -> Requirements Traceability matrix Requirements traceability matrix RTM is a grid that links product requirements to deliverables that satisfy them. Ensure each requirement adds business value by linking it to business objectives. Track requirements throughout project life cycle Provides a structure for managing changes to the product scope.
- 75. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Req. -> Output -> Requirements Traceability matrix Requirements traceability matrix Business needs Project objectives Project scope Deliverables Product design Product development Test scenarios Reference to detailed requirements Acceptance Criteria's Tracing includes, but is not limited to, tracing requirements for the following: Above information on RTM gets updated throughout the lifecycle of the project.
- 76. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Control Requirements -> Data Flow diagram 5.1 Plan Scope Management Scope Management plan Requirements Management plan 5.2 Collect Requirements 5.3 Define Scope 5.4 Create WBS 4.1 Develop Project charter Project charter 13.1 Identify Stakeholder Stakeholder Register Requirements documents Requirements Traceability matrix 5.5 Validate scope 5.6 Control scope 13.2 Plan Stakeholder management HR Management plan 8.1 Plan Quality Management 12.1 Plan procurement management
- 77. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements -> Review What is Requirements ? What are different types of requirements? What are Focus group meetings & Facilitated workshops? What are Group decision making & Group creativity techniques? What is Requirements document? What is Traceability matrix?
- 78. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Learn Project Management & prepare for PMP exam: • Learn visually • Detailed coverage of all PMP concepts • Sample Questions
- 79. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3. Define Scope Define Scope definition Define Scope - ITTO What is Product analysis? What is alternative generation? What is Project scope statement? Review Self Assessment
- 80. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.1 Plan Scope Management: Creating a scope management plan – how scope will be defined, validated, and controlled. 5.2 Collect Requirements: Determining, documenting, and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives 5.3: Define Scope: Developing a detailed description of the project and product. 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area
- 81. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5:4 Create WBS: Subdividing project deliverables and project work into smaller, more manageable components. 5:5 Validate Scope: Formalizing acceptance of the completed project deliverables. 5.6 Control Scope: Monitoring the status of the project & product scope and managing changes to the scope baseline. 5. Project scope Management Knowledge Area
- 82. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3. Define Scope -> Introduction Process of developing a detailed description of the project and product. Describes project, service or result boundaries by defining which of requirements collected will be included & excluded. Detailed Description Project Scope Statement Requirements – Inclusion & exclusion
- 83. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Provide detailed understanding of requirements to be delivered (Deliverables list) Provide description of Product, Service or results. Define Requirements – Inclusion & Exclusion Refine Assumptions, constraints & dependencies. Finalize acceptance criteria's 5.3. Define Scope -> Introduction Project Scope Statement
- 84. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3. Define Scope -> Introduction Project success : Detailed & unambiguous scope. Ensures all assumptions and constrained are analyzed and agreed. It Improves accuracy of Cost, time & resource estimates. Helps in future for detailed resource assignments It is an iterative process.
- 85. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Inputs (4) • Scope management plan • Project charter • Requirements documentation • Organizational process assets Tools & Techniques (4) • Expert judgment • Product analysis • Alternatives generation • Facilitated workshops Outputs (2) • Project scope statement • Project Documents updates 5.3. Define Scope
- 86. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Scope Management Plan Project Charter Requirements Document Organizational Process Assets 5.3 Define Scope-> Input
- 87. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Input->Scope Management Plan Scope Management Plan It defines boundaries & framework to define the project scope. It describes how scope will be: Defined Developed Monitored Controlled Verified.
- 88. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Input -> Project Charter Project Charter Formally authorizes a project & provide PM with authority to apply org. resources to project activities Project Purpose or Justification Measurable objectives & success criteria's High level requirements High level project description High level risks Stakeholder list Project approval requirements
- 89. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Input->Requirements Doc. Requirements Document Assumptions Dependenc -ies Constraints It describes how individual requirements meet the business need for the project. Business requirements •Objectives for traceability •Business rules Stakeholder requirements •Stakeholder communication •Reporting Solution requirements •Functional and non functional •Technology & standard Transition requirements Project requirements •Level of service, performance, compliance •Acceptance criteria Quality requirements
- 90. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Expert Judgment Product Analysis Alternatives Generation Facilitated Workshops 5.3 Define Scope-> Tools and Techniques
- 91. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Expert Judgment Subject mater experts Consultants & Contractors Stakeholders, including customers or sponsors Professional and technical associations Industry groups Other units within the organization It is often used to analyse the information used to develop the project scope statement. Helps include & exclude requirements. 5.3 Define Scope-> T&T-> Expert Judgment
- 92. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Product Analysis Product analysis can be an effective tool to evaluate product. Especially, when product is output of the project. Improve the project teams understanding of the Product. Translating high-level product descriptions into tangible deliverables. Product Breakdown System analysis Requirements analysis System engineering Value engineering Value analysis 5.3 Define Scope-> T & T -> Product Analysis
- 93. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) • Optimize the overall value of the project from inception to operations. • Aim is to achieve the lowest life cycle cost. Value engineering: • Cost reduction tool that considers whether function is really necessary. • Finding least expensive way to deliver scope. (Developing function at a lower cost without degrading performance or quality) Value analysis: Product Analysis Product Analysis Techniques: 5.3 Define Scope-> T & T -> Product Analysis
- 94. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> T & T -> Alternative Generations Alternatives Generation Generates Creative thoughts. Identify distinct approaches. Consider all options Finally develop potential option Brainstorming Lateral Thinking Analysis of Alternatives Develop many OPTIONS to identify different approaches to execute & perform project work.
- 95. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.2 Collect Requirements->T&T->Facilitated Workshops Facilitated workshops Objective is to develop a consensus for defining scope. Cross functional team members are involved, can quickly defining cross-functional requirements. All key stakeholders will participate. Define scope Meet the variety of expectation (diverse participants) Resolve stakeholder differences Reach common understanding of the project scope.
- 96. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Project scope Statement Project documents updates 5.3 Define Scope-> Output
- 97. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Output -> Project scope Statement Project scope Statement It is the description of the project scope major deliverables, Assumptions & Constraints Scope Statement Product scope description Acceptance Criteria Deliverables Exclusions Constraints Assumptions
- 98. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Project scope Statement • Characteristics – Product, Service or Result. Product scope description • All required conditions that need to be meet to accept the deliverables. Acceptance Criteria • Unique – Product, Service or Result. Deliverables 5.3 Define Scope-> Output -> Project scope Statement
- 99. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Output -> Project scope Statement Project scope Statement • What is excluded from project scope. Exclusions • Limits that impact project execution or product/service delivery. Constraints • Factors assumed to be true for defining/finalizing project scope statements. Assumptions
- 100. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Output -> Project scope Statement Project Charter Project Purpose or Justification Measurable obj & success criteria's High level requirements description Summary milestone schedule Stakeholder list Project approval requirements Project scope Statement Project scope description Acceptance criteria Project deliverables Project exclusions Project constraints Project assumptions
- 101. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Output->Project documents updates Project documents updates Project documents updates are required due to change in scope Stakeholder Register • Stakeholder expectations • Stakeholder Requirements Requirements documents • New/Change in requirements Requirement Traceability Matrix • New/update deliverable & product requirement links
- 102. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope -> Data Flow diagram 5.1 Plan Scope Management Scope Management plan 5.2 Collect Requirements 5.3 Define Scope 5.4 Create WBS 4.1 Develop Project charter Project charter Requirements documents 6.5 Estimate Activity Duration 6.6 Develop Schedule Project Scope Statements Project document updates 6.3 Sequence Activities Project documents Enterprise / Organization OPA
- 103. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope-> Review Define Scope - Project scope , Product scope Define Scope is Iterative process What is Product analysis? What is alternative generation? What is Project scope statement? Difference between Project Scope statement & Project Charter
- 104. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) 5.3 Define Scope -> Question All of the below are inputs to Define Scope process EXCEPT: A) Project Charter B) Requirements Document C) Organizational process assets D) Project Management Plan D
- 105. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Learn Project Management & prepare for PMP exam: • Learn visually • Detailed coverage of all PMP concepts • Sample Questions
- 106. By: Anand Bobade (nmbobade@gmail.com) Thank you!! Visit Slide Share website & you will find other Knowledge area presentation… Please share!!
