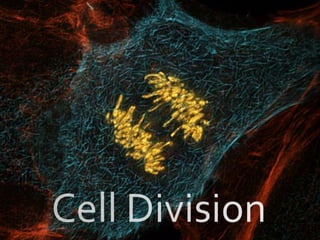
Cell Division/Mitosis
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
37 likes•6,709 views
Cell division allows organisms to grow and reproduce. All cells come from preexisting cells through asexual or sexual reproduction. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is contained in chromosomes that condense and duplicate before the cell divides. The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis, where the cell makes copies of its contents and divides into two daughter cells through cytokinesis. Precise control mechanisms regulate cell division, but errors can lead to uncontrolled growth and cancer.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Anatomy & Physiology Lecture Notes - Muscles & muscle tissue

Anatomy & Physiology Lecture Notes - Muscles & muscle tissue
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Chapter 4-cell division, mitosis, DNA, protein production

Chapter 4-cell division, mitosis, DNA, protein production
Mitosis- with an animated explanation of the concept 

Mitosis- with an animated explanation of the concept
Similar to Cell Division/Mitosis
Similar to Cell Division/Mitosis (20)
Cell division in eukaryotic and prokaryotics I.pptx

Cell division in eukaryotic and prokaryotics I.pptx
Recently uploaded
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Recently uploaded (20)
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Cell Division/Mitosis
- 2. Cellular Reproduction Organism’s life begins as one cell Rudolf Virchow (1858) stated: All cells come from cells Prokaryotes divide only to reproduce Asexual repro: 1 parent 2 daughters AKA Binary fission (“dividing in half”) One set of DNA duplicates, cell divides
- 3. Eukaryotic cells divide for reproduction, growth, and replacement of cells Other organisms (plants & animals especially) reproduce through sexual reproduction Sperm + Egg offspring Offspring gets two sets of genetic information, one from each parent
- 4. The Chromosome DNA is contained in structures called chromosomes within the nucleus of the cell “chroma” color, “soma” body Most of the time, chromatin fills the nucleus Tangled mass of fibers of DNA & protein When a cell begins to divide, the chromatin condenses and coils into chromosomes Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule containing thousands of genes
- 6. The Chromosome Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its chromosomes DNA replication! Once duplicated, the chromosomes have sister chromatids with identical genes, joined at a centromere When the cell divides, half goes to each daughter cell
- 8. The Cell Cycle Sequence of events from the time a cell divides to when it forms two daughter cells Serves to double the cell’s parts, then splits Stages: Interphase 90% Mitotic phase 10%
- 10. Mitotic Phase Unique to eukaryotes Ends with 2 identical cells Sub-stages of Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokenisis
- 11. Prophase Sister chromatids are attached at centromere Centrioles separate and extend spindle fibers Nucleolus disappears and nuclear envelope breaks down Kinetochores form on each chromatid, spindle fibers attach
- 14. Metaphase Centrosomes at poles Chromosomes lined up at metaphase plate (cell’s equator) Kinetochores of sister chromatids face opposite poles
- 16. Anaphase Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart forming daughter chromosomes Chromosomes move centromere first towards opposite poles Cell elongates
- 18. Telophase & Cytokenisis Cell continues to elongate Daughter nuclei appear at poles Nuclear envelopes reform Spindle fibers disappear Cytoplasms separate, new cell membranes form
- 20. Cytokenisis Cell pinches into two cells Called a cleavage furrow Plants are a little different Vesicles save materials from cell wall Form a plate at center of dividing cell Cell plate fuses to cell wall, 2 cells
- 27. Factors that Affect Cell Division Most reasons are unknown “Growth Factors” Proteins need for division; if not present it stops Cell-cycle control system A system of proteins in the cell that trigger & coordinates major events in the cell cycle Make checkpoints
- 28. Factors that Affect Cell Division Anchorage dependence Cells must be in contact with a solid surface Density-dependant inhibition Division will slow as the population grows more dense
- 29. When It All Goes Wrong Cell-cycle control system malfunctions Cells divide excessively and in the wrong places; creates tumors Benign: normal cells Malignant: cancerous, invasive Will divide indefinitely if not treated
- 30. When It All Goes Wrong Types of Cancers Carcinoma Skin, stomach lining Sarcoma Supporting tissues, bones Leukemia & Lymphoma Blood producing tissues, bone marrow Treatments Aim to stop the spread of cancerous cells by stopping division Chemotherapy (meds) and/or Radiation
Editor's Notes
- G1 (G=gap): cell increases its supply of proteins and organelles and grows larger, begins after cell division; the chromosomes are singleS: DNA synthesis (replication) occurs, 1 chromosome becomes sister chromatids (In S, DNA replication results in duplicate chromosomes, one chromosome with two sister chromatids. Sister chromatids are held together by the centromere)G2: synthesis of proteins critical to cell division, leads into mitotic phase
- AD: keeps cells from replicating where they shouldn’t (tumor)DDI: if a space opens, they will fill it in (ex. Healing a cut)