The value proposition builder
- 1. The Value Proposition Builder Dr. Celen P.Paul
- 3. 3 Define Market Value Proposition “ a start-up is an idea searching for a business model “ • Definition: • A value proposition is a statement of the functional, emotional and self-expressive benefits delivered by the proposed solution that provide value to the target customer. • • A value proposition is a clear, simple statement in 1 sentence and in simple words : “ WHAT do we offer to WHOM and what is his BENEFIT / VALUE “ • The key to generate profitable business 3
- 4. 4 Define Market Value Proposition “ a start-up is an idea searching for a business model “ • Key components / questions: • What you offer and how you offer it to customers • What type of value or benefit is associated with your offering • How much of it the customer can expect • How the value is generated • Why it differs from anything else on the market • Key components : • Relevancy : what & who / where is the (urgent) need / pain • Quantified value : benefit / gain / cost vrs risk / • Unique differentiation: why would customer buy from us • Value ? •Why do we buy things ? Why do we buy things ? Why does he want to buy from ME / US. How to describe the “ urgent “ NEED • List 15 to 20 business values you derive from buying or doing things. e.g. cost savings, time savings, revenue increase, customer / employee satisfaction, emotions,… • Then create a short list that most accurately describes the value your product offers your customers 4 Difference B2C-Sales B2B-Sales •Decision Making : Emotional Rational •Value : Latent Overt / Objective
- 5. 5
- 6. 6 Example : Google‘s Value Proposition Bad : • Google uses a patented page-ranking algorithm to make money through ad placement Good one : • Google is the world‘s largest search engine that allows internet users to find relevant information quickly and easily. Expanded one : • Google is the world‘s largest search engine that automatically provides advertisers with potential customers tailored to the ad content, increasing click-thorugh and conversion rates
- 7. 7 • The components of a good •Value Proposition
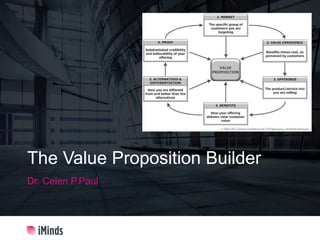
- 8. 8 Value Proposition Builder ( Barnes,et al. 2009 ) 1. Market : • who wants /needs to buy from us • Where is the urgent NEED / low hanging fruits 2. Value experience : 3. Offering : WHAT ?? 4. Benefits : f ( NC, NP, EM ) 5. Differentiation : • Uniqueness • Aaa 6. PoC : Proof of Concept 7. Test market concept : • Interview • Analyse / Adapt • Iterate • Example : iPda - steve jobs 7x
- 9. 9 The Value Proposition Builder™ is a six-step iterative process. 1. First, you need to decide who to talk to. This means analysing and identifying the MARKET segments, or specific clients, or target individuals within those clients for whom your solution has the potential to deliver Value, profitably. 2. Next, analyze and define the VALUE EXPERIENCE that clients get from your organisation from its current activities. You need to define good, bad and neutral experiences, but what will really make a difference are those experiential outcomes that have the power of “Wow!” 3. Then, (re)-define the OFFERINGS mix capable of leveraging your proven Value Experience with the defined target Market group. Fix your first MVP ! 4. When you have done this, you are in a position to assess the BENEFITS of the Offerings in the context of the Value Experience you are able to deliver to the Market group. There is a cost component of benefits here which includes Price and Customer Risks, enabling the calculation of Value where Value = Benefits – Cost. 5. You are then able to go on to work out how that provides ALTERNATIVES & DIFFERENTIATION for your organisation … Please include a competitive analysis or positioning in the VALUE Chain 6. … and back it all up with relevant, substantiated, measurable PROOF. The PoC ! ( Proof of Concept ) Crucially, each element and each step MUST be viewed through the filter of responses already generated. Iterative Process !! So, for example, the Value Experience for a particular situation will be related to specific Market segment(s) or client(s) identified in a Market. Then, the Offering is analysed in terms of the identified Value Experience related to the specific Market segment. And so on. By so doing, you are forced to focus and drill down in ever more specific terms.
- 10. “ ” 10 The components of a good VP 1. Market Positioning Composing the correct product / Market mix ( Ansoff)
- 11. 11 Positioning : questions to ask • Start is a hypothesis : • What is my idea ? What is my proposal ? • Do not suffer from the „ engeneer-syndrom „ • Questions to ask : • Who is your target customer? Who is my potential buyer ? (IDEAL CUSTOMER PROFILE module ) • What kind of problem do you solve for them? Is this an important problem for this customer? Is it an urgent problem? Where is “ Low Hanging Fruit” ? • How do you plan to solve this problem for the customer? What type of benefits will it generate. • Position your solution : here is the process in steps 1. Find out the „ Demand type „ - it will define/ influence the business model 2. Find out in what phase of the technology transfer your market and potential buyers are ( Chasm-principle ) or the PLC-cycle of your market 3. Summarize a viable MVP, test it and start proposing it to the early adapters
- 12. 12 Positioning : 1. Demand Type • Definition of Demand. An economic principle that describes a customer's desire/NEED and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service. Holding all other factors constant, the price of a good or service increases as its demand increases and vice versa. • Why important ? • Because yr TOTAL „GTM- / Marketing & Sales plan“ will depend on it • It will tell you : who to contact, at what org-level, what message to deliver, how to deliver / style and what probable stage of the buying cycle ( Buyers Journey) • Types Of Demand • Steve Blank : ??? incomplete - confusing • New Market / Existing Market / Redefine Existing Market ( Niche / Low-Cost entrant ) • Sirius Decisions
- 13. 13 MVP Whole Product 2. Technology Adoption Life Cycle
- 14. 14 2. Technology Adoption Life Cycle where and how to sell Name % Type Character Sales : Place / Message Innovators 3 Technology enthusiast Central interest / Curious Pleasure of exploring new • Trade shows • Great Technology Early adopters 12 Visionaries Buy new concept early Not technologists First to get the new stuff • Congress, Trade shows • You can be the first • Beat yr competition Early majority 35 Pragmatists Strong sense of practicality Need PoC(oncept) • Meetings, Office • ROI, efficiency, save $$ • Case studies, examples Late majority 35 Conservatives Wait until something has become an established standard Not comfortable with technology • Awareness Campaigns • References Hopefully you prepared yr exit Laggards 15 Conservatives Don’t want anything to do with new technology Just do nothing
- 15. 15
- 16. 16 Crossing Chasm Why is the Chasm / Gap there ? • These 2 groups have not the same expectancy • Visionaires go for a personal win • Pragmatists want a company win, a productivity improvement : ROI • Interviewing will give DIFFERENT answers for each group Technology Adoption Life cycle • Develop in parallel : MVP & Whole Product • Product for early adapters to survive and gathering knowledge • „Wole Product“ for achieving cash cow ( partners / allies ) Pricing / Business Models • Visionaries: value-based pricing • Pragmatists: competition-based pricing • Conservatives: cost-based pricing
- 17. 17 MVP versus „Whole product“ Minimum Viable Product ( MVP ) A Minimum Viable Product is the smallest feature set that lets you start learning about customers. Don't confuse your MVP with a minimal product. Your MVP needs to address your top customer problems and deliver on your Unique Value Proposition. Objective Details Step-by-Step Process Define the minimum feature set needed to solve your top 1-3 problems. For each of the problems outlined earlier, sketch out the top features or capabilities that will address those problems. • Outline a possible solution for each problem • Don't spend too much time detailing • These features will form the basis for your Minimum Viable Product
- 18. 18 Create +Test the MVP Describe the key aspects of your MVP for which you are currently seeking market feedback. Answer the following questions after testing the MVP. • Is our understanding of the customer problem accurate and relevant? • Does the MVP solve the customer’s problem? • Does the product solve the problem better than a viable alternative currently on the market? • Would they use the product? Can they imagine the product as part of their everyday life? • What is their primary concern about buying and implementing the product? • How much would they be willing to pay for the product? • What process would the customer employ when deciding to buy such a product? • Who is involved in the decision-making process? • Whose budget will the funding come from? • Who will be the users of the product?
- 19. “ ” 19 The components of a good VP 2. Target Market - WHO ? Composing the correct product / Market mix ( Ansoff)
- 20. 20 WHO ? : Market segmentation definitions • Market Segmentation is the sub-dividing of customers into homogenous sub-set of customers where any sub-set may conceivably selected as market target to be reached with distinct Marketing Mix – Philip Kotler • Market segmentation is the process of dividing the whole market of goods or services in groups of people with similar needs. By making this division there is a high chance that each group responds in favour to a specific market strategy. - PPC
- 21. 21 WHO ? = Target segmentation • Market Segmentation: • Dividing a market into distinct groups with distinct needs, characteristics, or behavior who might require separate products or marketing mixes. • Target Market • Consists of a set of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve • Evaluating Market Segments • Segment size and growth • Segment structural attractiveness • Level of competition • Substitute products • Power of buyers • Powerful suppliers • Company objectives and resources
- 22. 22 Seven Steps to Successful Segmentation for Startups • Step 1: Determine where you really are within the startup life cycle. Relative position in chasm / demand type • Step 2: Create as broad idea of an addressable market and then break it down in to all possible sub-segments. Use CSF’s and MPRS • Step 3: Create customers profiles for all remaining sub- segments. Use problem/Need search process • Step 4: Assess profiles again critical flaws criteria and eliminate those that fail • Step 5: Assess remaining profiles against selection variables continuously until top segment remains. Define Beachhead… • Step 6: Test target segment against SWOT and performance goals • Step 7: If no segment apparent, repeat process
- 24. “ ” 24 The components of a good VP 3. Value
- 25. 25 Value and Value Perception „ Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day. Teach a man to fish and you feed him for a lifetime „ - old Chinese proverb
- 26. 26 Value Proposition Difference B2C-Sales B2B-Sales • Decision Making Emotional Rational • Value Latent Overt Key components : A value proposition is a clear statement • Relevancy : what & who • Quantified value • Unique differentiation = ONE sentence
- 27. 27 Uniqueness This requires to differentiate the offer against competition. How to become the preferred choice of the target market ? 1. Evaluate the following : • Match competitor in all but one. • In at least one element of value you need to excel. • Value proposition for company and for product separate 2. Uniqueness Scale : • Rate the quality and uniqueness • Use a 1-5 scale to rate • Outcome must be better than 3 3.Value Proposition Evaluation Matrix • Total must be more then 2 Score Value Market size Compete Barrier of Entry 1 limited small heavy low 2 substantial medium limited extensive 3 strong medium heavy low 4 unique large low extensive 5 unique large exclusive extensive Desire / NEED Rank 0 1 2 Exclusivity 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 2 0 2 4
- 28. 28 Perceived Value • Perceived Value = ( Impact – Cost ) / RISK o Impact = The emotional & analytical end-state vision of the buyer Real benefits vrs Perceived ones o Cost = the cost of everything that must be purchased, allocated or incurred to realize that goal Including the change/pain and adaptation of all internal processes o Risk = discounted by various factors that could derail benefit realization or create buyer uncertainty ● Valuable conversations are timely, relevant and in context o Timely = Phasing. Where in their problem solving processare they ? Where on a maturity chart are they ? o Relevant = what are the customer's problems ? How do they solve them ? o In context = who is involved in solving problem ? Why do they care ?
- 29. 29 Value Perception matrix (Forrester ) 1. Keep it simple - 2. Buyer requires different configurations or solutions /large portfolio 3. Buyer has problem that needs sophisticated knowledge transfer to solve 4. complex 1 3 2 4 1 2 4 3
- 30. 30
- 31. 31 Porter Value Chain Internal Value Chain useful to: • layout cost building • Vulnarability against competition • Position in external value chain External Value Chain useful to: • Understand back- & forward integration • Understand competition, players • Contribute 5-forces analysis Important notice ! As a start-up you should not be too worried about competition, but be aware of external value chain.
- 32. 32 Porter 5 - Forces
- 33. 33 Example : internal value chain
- 34. 34 Example : external value chain
- 35. “ ” 35 The components of a good VP 4. Result
- 36. 36 Once you’ve clarified your value proposition, you can use it in your: • Voicemails • Email messages • Conversations • Presentations • Proposals In short, in every customer interaction. The key word is OUTCOMES!
- 37. 37 The best ones include these 3 components: So what makes a value proposition powerful & effective? • Business driver • Movement • Metrics
- 38. 38 Tips • A business driver is related to an important objective that your prospects are measured on. The best business drivers are very specific. Being specific makes you stand out from your competitors. Here are some examples… • Profitability Cost of goods sold Productivity Revenue Costs • Speed to market Customer satisfaction Quality Returns Reviews • New clients Market Share Competitive advantage Turnaround time • Because people only change if a new option is better than the status quo and can positively impact their key business drivers. • “Movement” words like these belong in value propositions: Eliminate Speed Up Raise Minimize Decrease Cut Shrink Increase Maximize • Metrics : Strong Value Propositions Have Metrics Too Dollars/Euros Time frames Percentages To your prospects, 19.7% is much more believable than 20%.
- 39. “ ” 39 The components of a good VP 5. Validate with Test & Interviews
- 40. 40 Prepare to talk to customers • What are the key political, regulatory, economic, environmental, social, cultural and technological trends that affect the space you are in? • What are the key issues facing customers in this space? • Who are the key stakeholders? • Who are the analyst firms, analysts, journalists, bloggers and conference presenters that talk about relevant issues and technology? • What are the main conferences and events? • What are the main media outlets that keep people informed about the industry and its technology? • Prepare your list of questions and issues to address in your customer meeting / talk / interview
- 41. 41 Understand Customer Problem and Need • What problem causes the pain or frustration? Sketch a scenario in which the customer attempts a task and feels pain as a result. • How does the customer try to cope with the problem now? • What is causing the problem? What is interfering with a speedy solution? What goes wrong and why? • How much money is the customer losing, either in additional costs or lost revenue? Quantify the pain. • Who is the individual who feels the pain first and how does it “waterfall” up or down? • Who else feels the pain? The customer’s customers? Suppliers? Partners? Investors? Think Plan ExecuteAnalyse Adapt Phase 1 Test customers / prospect‘s perception • of the problem and • his urgency / need to solve it
- 42. 42 Initial Approach : Search not execute a structured process for testing business model hypothesis Think Plan ExecuteAnalyse Adapt Think Plan ExecuteAnalyse Adapt Understand Customer Problem and Need Develop Validate Develop Sustainable Business Model Adaptive Learning When not enough paying customers GTM ?
- 43. 43 Evaluate market feedback • Is the market problem urgent? Will customers care if the problem is not solved? Do they have another way to solve this problem? • Is the market problem pervasive? Determine if the identified market problem applies to a significant percentage of your desired target market. • Will your buyers pay to have this problem solved? • On the basis of the answers to the above questions, which direction should you take?
- 44. 44 Update your problem statement Write a brief description of the specific problem your target customers face, as well as the impact of the problem and its pervasiveness. Include the following information: • The objective of their work: What are they trying to achieve? • How they perform their work • The problem they face • How the problem impacts their objective
- 45. 45 Describe your product vision Write a statement that describes your product vision, which identifies one or more of the following: • Your target customers and their problem • The product solution you are making • How the user goes about their job and will use the product solution • Customer outcomes and benefits • Three- and five-year scenarios for your product and company
- 46. “ ” 46 The components of a good VP 5. Use Workbook if necessary
