Drug discovery and development
- 1. Drug Discovery & Development DR. KARUN KUMAR JUNIOR RESIDENT – II DEPT. OF PHARMACOLOGY
- 2. INTRODUCTION Creation of a new drug involves :- 1. Drug discovery (Research) :- Identification of a potential therapeutic target Selection of a single molecule for testing in humans. 2. Drug development (Development) :- Preclinical studies that support initial clinical trials through approval of the drug by regulatory authorities. 3. Commercialization (Marketing) :- Product Therapeutic application Sales
- 4. Drug discovery process Process by which pharmaceutical, biotechnology, academic & Govt. laboratories identify or screen compounds to find potentially active therap. agents
- 5. Multidisciplinary nature of drug discovery
- 8. Target identification • Target Molecular recognition site to which drug binds • Target may be • Protein molecule • A receptor • Enzyme • Transport molecule • Ion channel • Tubulin • Immunophilin
- 10. Strategies to find new drug targets 1. Conventional strategies a) Analysis of pathophysiology b) Analysis of MOA of existing drugs 2. New strategies a) Disease genes b) Disease-modifying genes
- 11. Disease genes • Abl-kinase Molecular target for Imatinib • Secretase inhibitors Anti-Alzheimer drugs • Most promising field Cancer therapies • Identifying d/s gene Valuable pointers to drug targets
- 12. Disease modifying genes • Most important category • Approaches used :- 1. Gene expression profiling 2. Gene knockout studies
- 13. Gene expression profiling Principle Development of any disease phenotype involves changes in gene expression in cells & tissues involved Method DNA microarray (‘gene chips’)
- 14. DNA microarray
- 16. Gene knockout screening • Generation of transgenic ‘gene knockout’ strains of mice • Examples 1. Inactiv. Of gene for ACE/ATR ↓ B.P. 2. Elim. Of gene encoding GABAA Irrit. In mice 3. Cathepsin K Osteoporosis 4. Melanocortin receptors Obesity • Flatworm & zebrafish Speed up the process
- 17. Target validation • Experimental approach by which a “potential” drug target can be tested & given further credibility • Main approach • Pharmacological mGluR for pain • Genetic • Antisense oligonuceotides • RNA interference • Transgenic animals
- 18. Phase D0 ‘Target identification’ (Research with intent of identifying a therapeutic target) Phase D1 + D2 ‘Lead identification’ (Initial screening to discover chemical template for lead optimization).Tests include HTS,LTS(in vitro & in vivo) Phase D3 ‘Lead optimization’ (Optimiz. & biol. Testing of compound).Outcome Best in potency & selectivity, as well as ADME properties Phase D4 Completion of studies to allow 1st application in man
- 19. Antisense Oligonucleotides Stretches of RNA complementary to gene of interest ↓ Bind to cellular mRNA (Prevent its translation) ↓ Inhibits expression of specific genes ↓ Role of ‘specific genes’ in disease phenotype can be determined
- 20. RNA interference Short lengths of dsRNA (siRNAs) ↓ Activate RISC (RNA induced silencing complex) ↓ Destroys corresponding fmRNA in the cell ↓ Gene silenced
- 22. Important definitions • Screening Testing many compounds in assays relevant to the disease in question • Hit A compound that passes such a ‘screen’ • Primary hit Compound giving positive result in a screening assay • Confirmed hit Compound is confirmed as positive when assay is repeated • Validated hit Confirmed hit that shows selective activity
- 23. • Lead compound A new chemical entity that could be developed in a new drug by optimizing beneficial effects & minimizing S/E Should comply with Lipinski’s rule of 5 :- • Mol. Wt. < 500 Da cLogP < 5 • No. of H bond donors <5 Sum of no. of Ns & Os <10 • Drug candidate End result of lead optimization (A compound judged suitable for precl. & cl. Develop.) • Development compound Drug candidate that has been accepted for further development
- 24. Screening 1. Selectivity screening In vitro tests (If compound is selective to merit further investigation) 2. Pharmacological profiling • In vitro profiling Study on isolated tissues has been the mainstay • In vivo profiling Imaging technologies used • MRI • USG • PET • X-ray densitometry tomography
- 25. Animal models of disease 1. Acute physiological & pharmacological models • Seizures induced by electrical stimulation of the brain Epilepsy • Histamine induced bronchoconstriction Asthma • Eddy’s hot plate test Pain • Injection of LPS & cytokines Septic shock • Elevated plus maze test Anxiolysis
- 26. 2. Chronic physiological or pharmacological models • Use of Alloxan / Streptozotocin Type I DM • Inducing brain ischemia Stroke • Inducing coronary ischemia IHD • “Kindling” Epilepsy • Self-admin. of opiates/nicotine Drug dependence
- 27. • Cholesterol fed rabbits Hypercholesterolemia & atherosclerosis • Immunization with myelin basic protein MS • Admin. Of MPTP Parkinson’s disease • Transplant. Of malignant cells into immunodef. Animals Progressive tumors (Cancer)
- 28. 3. Genetic models 1. SHR 2. Seizure-prone dogs 3. Rats insensitive to ADH 4. Obese mice 1. CF 2. DMD 3. Leptin gene (mutated in ob/ob mice) 5. Alzheimer’s disease (APP)
- 29. Validity criteria (Willner 1984) 1. Face validity Accuracy with which model reproduces the phenomena char. human d/s 2. Construct validity Extent to which etiology of human disease is reflected in model 3. Predictive validity Extent to which manipulation (drug t/t) is predictive of effects in the human disorder
- 30. Identification of hits 1. Compound centered approach Traditional Compound is identified ↓ Biological profile is explored ↓ If compd. displays desirable pharmacologic activity ↓ Compound is refined & developed further
- 31. 2. Target centered approach Putative drug target (receptor/enzyme) is identified ↓ Researchers search for compounds which interact with target (agonist/antagonist/modulator) Search maybe: 1. Systematic Uses info. About structure of target as a starting point 2. Shotgun approach All compounds in a large library of substances are tested in a high-speed automated assay
- 32. High-throughput screening • Simplest target centered approach • Uses a target based assay & robotic automation to test thousands of compounds in a few days time • 2 critical aspects :- 1. A large library of compounds must be available for screening 2. Assay (Simple/sophisticated) that leads to rapid identification of true hits must be developed
- 33. Lead identification Library is “run through” the assay (96/384-well plate) ↓ ‘Primary hits’ are examined more closely ↓ Further screening is done (To eliminate false positives & false negatives) ↓ Leads are advanced in ‘lead optimization’ process
- 34. Lead optimization Physical, chemical, biological & pharmacological properties of promising lead molecules (that appear to interact with the target in a desirable way) are Characterized & refined with the ultimate goal Of selecting a single molecule to enter into Clinical testing & formal drug development
- 35. Factors causing termination 1. Failure to demonstrate efficacy in a rigorous animal model of human disease 2. Low bioavailability 3. Extensive/complex metabolism Potentially dangerous reactive metabolites 4. Toxic effects in preliminary animal toxicology studies 5. In vitro evidence that molecule may damage DNA 6. Extremely difficult chemical synthesis
- 36. Drug development
- 37. • All activities involved in transforming a compound from drug candidate Product approved for marketing by appropriate regulatory authorities • Falls in 3 main parts :- 1. Technical development Ensuring quality of end- product 2. Investigative studies Safety & efficacy 3. Managerial functions Co-ordination, documentation & liaison with regulatory authorities
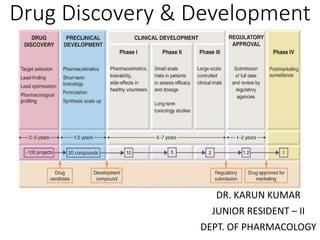
- 38. Stages of drug development Stage No. of yrs. Synthesis/isolation of compound 1-2 Preclinical studies (Scr.,eval.,pk. & short term toxicity test. in animals) 2-4 Scrutiny & grant of permission for clinical trials 0.25-0.5 Pharmaceutical formulation, standardization of chemical/biological/immuno-assay of the compound 0.5-1 Clinical studies: Phase I,II,III trials; Long term animal toxicity testing 3-10 Review & grant of marketing permission 0.5-2 Post-marketing surveillance No fixed duration
- 39. Phases of Precl. & Clinical Development Phase Primary goal Dose Patient monitor Number of participants Preclinic al Testing of drug in non- human subjects Unrestricted A graduate level researcher-Ph.D. In vitro & in vivo animal models Phase 0 Oral bioavailability & half- life of drug Subtherapeutic Clinical researcher 10 people Phase I Testing of drug on healthy volunteers (safety) Subtherapeutic with asc. Doses Clinical researcher 20-100 people Phase II Testing of drug on patients (efficacy & tolerability) Therapeutic dose Clinical researcher 100-300 people Phase III Testing of drug on pts. (confirm efficacy) Therapeutic dose Clinical research. & Physician 1000-2000 people Phase IV Post-marketing surveillance (A/E, D-D I) Therapeutic dose Physician Anyone seeking treatment Phase V Translational research No dosing None All reported use DeMets D., Friedman L. and Furberg C.(2010).Fundamentals of Clinical Trials. Springer 4th Edition Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, (2011) 12th Edition
- 40. Preclinical development Aim Meet all requirements before a new compound is deemed ready to be tested for the 1st time in humans Work falls into :- 1. Safety pharmacology Testing to check that drug does not produce hazardous acute effects 2. Preliminary toxicological testing Eliminate genotoxicity & determine maximum non-toxic dose of drug (given daily for 28 days & tested in 2 species)
- 41. 1. Pharmacokinetic testing (ADME studies) in laboratory animals 2. Chemical & pharmaceutical dev 3. Pharmacokinetic testing (ADME studies) in laboratory animals 4. Chemical & pharmaceutical development Assess feasibility of large scale synthesis & purification 5. Assess stability of compound under various conditions 6. Develop a formulation suitable for clinical studies • Work done in accordance with GLP
- 42. IND • New drug ready to be studied in humans a Notice of Claimed Investigational Exemption for a New Drug (IND) must be filed with the FDA • It includes :- 1. Info. on the composition and source of the drug 2. Chemical and manufacturing information
- 43. • Includes :- 1. Info. on the composition and source of the drug 2. Chemical and manufacturing information 3. All data from animal studies 4. Proposed plans for clinical trials 5. Names and credentials of physicians who will conduct the clinical trials 6. A compilation of the key data relevant to study of the drug in humans that has been made available to investigators and their institutional review boards
- 44. Phase 0 (Microdosing study) • Developed by FDA & EMA as “cost-cutting” tools Very low doses (1/100th of estimated human dose or max. of 100 µg total dose of candidate drug) are administered to healthy volunteers ↓ Pharmacok worked out using AMS with radiolabelled drug/LC-MS to measure ultra low drug levels
- 45. • Subpharm. dose No toxic / therapeutic eff. But yields human pharmacokinetic information • Elaborate animal studies & costly phase I human trials could be avoided for candidate drugs • Useful in more precise selection of doses for phase I study • They are promising & most regulatory authorities are willing to allow & consider them
- 46. Phase I • Studies carried out Phase I clinics (All vital func. Are measured & emergency/resuscitative facilities avail.) • Clinical investigators Clinical pharmacologists • Trial subjects Healthy volunteers (25-100) • Objectives :- 1. Check for safety (Drug affects CV, hepatic or renal functions adversely) 2. Check for tolerability (Drug produces unpleasant symptoms like headache, nausea & vomiting)
- 47. 1. 3. 2. 3. 3. Determine whether humans & animals show significant pharmacokinetic differences 4. Determine a safe clinical dosage range in humans (Common rule Begin with 1/5th or 1/10th of MTD in animals & calc. it for 70 kg body wt.) 5. Determine the pharmacokinetics of the drug in humans (Whether deficiency in drug effect is due to lack of absorption / faster elimination) 6. Detect any predictable toxicity
- 48. Pharmacokinetic parameters 1. Cmax Peak drug &/or metabolite concentration 2. Tmax Time to peak drug &/or metabolite conc. 3. AUC0-∞ Area under conc.-time curve e.p. to inf. 4. AUC0-T AUC calc. to a specific time point T 5. T1/2 Time taken for level of drug to dec. by 1/2 6. VD Volume of distr. 7. CL Clearance 8. MRT Mean residence time (Avg. time a drug molecule rem. In body after rapid i.m. injection)
- 49. Dosing & blood sampling schedule for phase I studies
- 50. Phase II • Drug studied for 1st time in pts. with target disease • Main purpose Gather evidence that drug has effects suggested by preclinical trials • End points :- 1. Definitive end point (Measures drug effect directly Pain relief [analgesic]) 2. Surrogate end point (Predictive of the definitive end point Reduction in tumor size[anticancer])
- 51. Phase IIa • “Proof of concept”/ “Proof of claims” • Preliminary evidence of efficacy & safety • Up to 200 pts. are studied Potential therapeutic benefits & side effects are observed • Establishment of dose range for more definitive therapeutic trials in phase IIb • Study design Single blind (Subject unaware if he is taking placebo/positive control/new drug)
- 52. Phase IIb • Dose-finding studies • To confirm efficacy with statistical significance • Determine the optimal dose & dosing regimen • Large no. of patients used (200-400) • Study design Double blind (3rd party holds the code identifying each medication & this code is not deciphered until all clinical data has been coll.)
- 53. Phase III • Large scale, multicentered randomized double blind trials to further establish safety & efficacy • Made using “Double-blind cross over” designs to minimize errors • NDA After completion of phase III trials, sponsors file a “New Drug Application” with the drug control authorities of that country • NDS If documentation is acceptable & in compliance, drug enters market with NDS
- 54. Double blind Cross Over Design Pt. grp. (randomi zed) Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 I Standard drug Placebo New drug II Placebo New drug Standard drug III New drug Standard drug Placebo
- 55. Phase IV • Surveillance phase during the post marketing clinical use of the drug • Used to discover • Relatively rare side effects • Previously unknown drug interaction • Previously unknown therapeutic use detected by a chance discovery
- 56. Phase V • Aims to bridge the gap between basic and clinical research1 • Encompasses laboratory studies, clinical demands, public health and health management, policies and economics1 • Crucial in the evolution of contemporary biomedical science1 • It is used to signify the integration of a new clinical treatment into widespread public health practice2 1-Translational research: from benchside to bedside.N C Keramaris, N K Kanakaris, C Tzioupis, G Kontakis, P V Giannoudis Academic Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Leeds Teaching Hospitals, University of Leeds, Great George Street, Leeds LS1 3EX, UK.Injury (Impact Factor: 1.93). 07/2008; 39(6):643-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2008.01.051 Source: PubMed 2-Margaret A. Rogers (June 2009). "What are the phases of intervention research?". American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. Retrieved Jan 8, 2013.
- 57. Preclinical safety assessment 1. Exploratory toxicology • Rough estimate of toxicity (2 weeks) • Provides an indication of main organs & physiological systems involved 2. Regulatory toxicology (GLP) • Reqd. by regulatory authorities/EC before compound can be given for 1st time to humans • Studies reqd. to support an application for marketing approval
- 58. Timing of safety assessment
- 59. Genotoxicity • Mutagenicity Chemical alteration of DNA sufficient to cause abnormal gene expression in the affected cell & its offspring • Chromosomal damage • End results Carcinogenesis & Teratogenicity (detected by long-term animal studies)
- 60. Toxicokinetics “Generation of pharmacokinetic data, either as an integral component in the conduct of non-clinical toxicity studies, or in specially designed supportive studies, in order to assess systemic exposure” (ICH Guideline S3A) • Pharmacokinetics applied to toxicological studies
- 61. Toxicity measures 1. NTEL Largest dose in most sensitive species 2. LD50 Estimated dose reqd. to kill 50% expt. An. 3. NOAEL Largest dose causing neither tissue toxicity nor undesirable physiological effects 4. MTD Largest dose tested causing no obvious signs of ill-health 5. NOEL Threshold for producing any observed pharmacological or toxic effect
- 62. THANK YOU
