Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to Palpation of spleen final
Similar to Palpation of spleen final (20)
Generalrulesofabdomenalexamination 140413161534-phpapp02

Generalrulesofabdomenalexamination 140413161534-phpapp02
More from Kurian Joseph
More from Kurian Joseph (20)
Palpation of spleen final
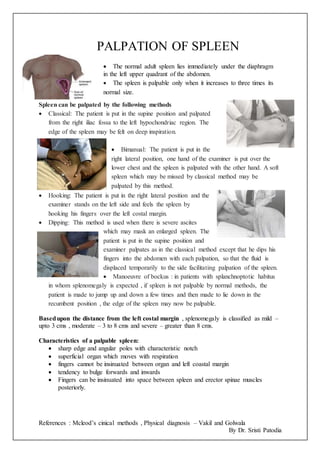
- 1. References : Mcleod’s cinical methods , Physical diagnosis – Vakil and Golwala By Dr. Sristi Patodia PALPATION OF SPLEEN The normal adult spleen lies immediately under the diaphragm in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. The spleen is palpable only when it increases to three times its normal size. Spleen can be palpated by the following methods Classical: The patient is put in the supine position and palpated from the right iliac fossa to the left hypochondriac region. The edge of the spleen may be felt on deep inspiration. Bimanual: The patient is put in the right lateral position, one hand of the examiner is put over the lower chest and the spleen is palpated with the other hand. A soft spleen which may be missed by classical method may be palpated by this method. Hooking: The patient is put in the right lateral position and the examiner stands on the left side and feels the spleen by hooking his fingers over the left costal margin. Dipping: This method is used when there is severe ascites which may mask an enlarged spleen. The patient is put in the supine position and examiner palpates as in the classical method except that he dips his fingers into the abdomen with each palpation, so that the fluid is displaced temporarily to the side facilitating palpation of the spleen. Manoeuvre of bockus : in patients with splanchnoptotic habitus in whom splenomegaly is expected , if spleen is not palpable by normal methods, the patient is made to jump up and down a few times and then made to lie down in the recumbent position , the edge of the spleen may now be palpable. Basedupon the distance from the left costal margin , splenomegaly is classified as mild – upto 3 cms , moderate – 3 to 8 cms and severe – greater than 8 cms. Characteristics of a palpable spleen: sharp edge and angular poles with characteristic notch superficial organ which moves with respiration fingers cannot be insinuated between organ and left coastal margin tendency to bulge forwards and inwards Fingers can be insinuated into space between spleen and erector spinae muscles posteriorly.
