ECG Rhythm Strip Guide: Key Supraventricular and Ventricular Arrhythmias
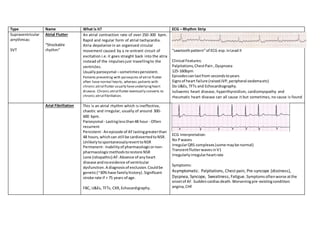
- 1. Type Name What is it? ECG – Rhythm Strip Supraventricular arrythmias: SVT Atrial Flutter “Shockable rhythm” An atrial contraction rate of over 250-300 bpm. Rapid and regular form of atrial tachycardia. Atria depolarize in an organised circular movement caused by a re-entrant circuit of excitation i.e.it goes straight back into the atria instead of the impulsesjust travellingto the ventricles. Usuallyparoxysmal –sometimespersistent. Patients presenting with paroxysms of atrial flutter often have normal hearts, whereas patients with chronic atrial flutter usually haveunderlyingheart disease. Chronic atrial flutter eventually converts to chronic atrial fibrillation. “sawtoothpattern”of ECG esp.inLead II Clinical Features: Palpitations,ChestPain, Dyspnoea 125-160bpm Episodescanlastfrom secondstoyears Signsof heart failure (raisedJVP,peripheral oedemaetc) Do U&Es, TFTs and Echocardiography. Ischaemic heart disease, hyperthyroidism, cardiomyopathy and rheumatic heart disease can all cause it but sometimes, no cause is found Arial Fibrillation This is an atrial rhythm which is ineffective, chaotic and irregular, usually of around 300- 600 bpm. Paroxysmal - Lastinglessthan48 hour - Often recurrent Persistent- Anepisode of AFlastinggreaterthan 48 hours,whichcan still be cardiovertedtoNSR. UnlikelytospontaneouslyreverttoNSR Permanent- Inabilityof pharmacologicornon- pharmacologicmethodstorestore NSR Lone (idiopathic) AF: Absence of anyheart disease andnoevidence of ventricular dysfunction.A diagnosisof exclusion.Couldbe genetic(~30%have familyhistory).Significant stroke rate if > 75 years of age. FBC, U&Es, TFTs, CXR,Echocardigraphy. ECG Interpretation: No Pwaves IrregularQRS complexes(some maybe normal) TransientflutterwavesinV1 Irregularlyirregularheartrate Symptoms: Asymptomatic. Palpitations, Chest pain, Pre-syncope (dizziness), Dyspnea, Syncope, Sweatiness, Fatigue. Symptomsoftenworse atthe onsetof AF. Suddencardiacdeath.Worseningpre-existingcondition: angina,CHF
- 2. Re-entry supraventricular tachycardia An arrhythmia caused by a second connection between atria and ventricles,in addition to the normal conduction system. There are two types: AVRNT (Atrio-Ventricular Node Re-entry Tachycardia) - the second connection is closely related to the AV Rate of 130-250. Narrow QRS complex (except in bundle branch block), P waves are: inverted, masked by QRS complex (AVNRT) or occur halfway between complexes (AVRT), one P wave per QRS complex. AVRT (Atrio-Ventricular Re-entry Tachycardia) - the second connection is not related to the AV node. node. Wolff-Parkinson- White syndrome Usually asymptomatic buy may experience: palpitations, dizziness, syncope, dyspnoea during episodes WPW is caused by the presence of an abnormal accessory electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles. Electrical signals travelling down this abnormal pathway (known as the bundle of Kent) may stimulate the ventricles to contract prematurely (pre- excitation syndrome), resulting in supraventricular tachycardia - atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia. Sinusrhythmandveryshort PR interval DominantR wave inV1 – “Type A” WPW and isassociatedwithaleftsided accessorypathway Notshown – DominantSwave in V1 – “Type B” WPW and indicatesaright sidedaccessorypathway Ventricular arrythmias: Narrow complex tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation SVT It can alsobe causedby sinus tachycardia i.e.the normal physiological response tocertainstimuli whichcause the heartrate torise.
- 3. Broad Complex Tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation Chaoticdepolarisationof the ventricles. Mechanicallythisresultsinanarrestedcardiac pumpfunctionandimmediate death. VFcan onlybe treatedby immediate defibrillation. ECG requiredasap. Bloods– cardiac enzymes(TroponinTandI, CK- MB Irregularrhythm Usuallyoccurs duringan MI. symptomschestpain,tiredness,palpitations Ventricular tachycardia “shockable rhythm” QRS >120ms/3 small squares whichoriginatesin the ventricles. Symptoms: Presentswithfeaturesof ischaemicheart disease orhaemodynamiccompromise. Chest pain, palpitations, dyspnoea,dizziness,syncope and possibly symptomsof heartfailure. The QRS complexesare rapid,wide,anddistorted. The T wavesare large withdeflectionsopposite the QRScomplexes. P wavesare usuallynotvisible. The PRinterval isnotmeasurable. A-V dissociationmaybe present. V-A conductionmayor may notbe present Bradyarrythmias: Heart Block 1st degree – slowdownof conduction. Notreally “block”.JustP-R interval longerthan normal (> 0.2 sec).Treatment:none Long termfollowuprecommended,asmore advancedblockmaydevelopovertime. 2nd degree – some conductionbutnotothers. Intermittentblockatthe AVN (droppedbeats)
- 4. MobitzI: Progressive lengtheningof the PRinterval, eventuallyresultinginadroppedQRS. Usuallyvagal inorigin Must see PR prolongationtomake diagnosisof MobitzI MobitzII: Pathological,mayprogresstocomplete heart block(3rd degree HB) Usually2:1, or 3:1, but may be variable Permanentpacemakerindicated 3rd degree –complete blockbetweenatriaand ventricle P wavesare independentof the wide QRScomplex not usingnormal conductingsystemsoitisan escaped focus Permanentpacemakerneedsfitted Figure 1. Mobitz I Figure 2. Mobitz II Figure 3. 3rd degree/complete heart block Bundle branch block Cessationof appropriate electrical conduction downeitherthe R or L bundle branch. In bothcasesthere is a wide QRScomplex. RBBB- M shapein V1 and an N shape in V6 (the N can also stand for "normal"). The "M" wave here has a small rise(r),a big drop (S) and an even bigger rise(R) givingan rSR wave. Finally,theN is your normal QRS complex but justwider. LBBB - V shape in V1 and an M shapein V6. The "V" wave is also called an rS wave because ithas a very slightrise(r) and a big drop (S) in amplitude.The "M" Figure 4. RBBB
- 5. wave, also called R,is justa largerise(R) with a tiny dip and tiny rise. Can justbe left unless severe and a cardiac pacemaker will berequired. Figure 5. LBBB