BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 2 PART 2 - CELL ORGANIZATION
- 1. BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 2 CELL ORGANIZATION (2.2)
- 2. 2.2 CELL ORGANIZATION Multicellular organisms can feed, respire, excrete, move, respond to stimuli, reproduce and grow. Unicellular organisms are organisms with just a single cell. So how is this organism able to perform all the living
- 3. Lesson Outcomes Understand living process in unicellular organism the movement in unicellular organism the reproduction in unicellular organism the feeding in unicellular organism the exchange of materials in unicellular organism
- 4. CELL ORGANIZATION ORGANISMS UNICELLULAR ORGANISM Single cell organism MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM larger organism with more than one cell
- 5. UNICELLULAR ORGANISM Simple organism consists of a single cell Each cell or organism is a complete unit of life ~able to carry out all living processes
- 6. Amoeba sp.
- 7. AMOEBA
- 8. Living processes of unicellular organism ~~~ Amoeba sp Lives in freshwater lakes, damp soil Enclosed in plasma membrane constantly change shape Also called protozoa
- 9. Feeding Locomotion Living processes of amoeba sp. Reproduction Respiration Excretion Responses to stimuli
- 10. Movement of Amoeba sp. Move by extending temporary pseusopodia or ‘false foot’ The rest of cytoplasm flow slowly into this extension, hence move the organism along
- 11. Feeding of Amoeba sp. Engulf food via phagocytosis Holozoic organism - feed on microbes
- 13. PHAGOCYTOSIS
- 14. PHAGOCYTOSIS
- 15. Respiration of Amoeba sp. O2 CO2 O2 CO2 Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs through the plasma membrane through simple diffusion.
- 16. Excretion of Amoeba sp. • The contractile vacuole is involved in osmoregulation. • Water diffuses into the cell and fills the contractile vacuole. • When the vacuole is filled to its maximum size, it contracts to expel its contents.
- 17. Responses to stimuli • Amoeba sp. reacts by retreating from adverse stimuli such as bright light and acidic solution. • In contrast, favourable stimuli such as contact with food, cause it to move towards the stimuli. Food Light acids
- 18. Reproduction of Amoeba sp. Binary fission - asexual reproduction Once grown to a certain size the nucleus divides Cytoplasm divides 2 daughter cells form. When environment not conducive, divides by spore formation
- 19. THE LIFE OF MR. AMOEBA PROTEUS
- 22. 2.2 CELL ORGANISATION MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM Organism - more than one cell Larger organisms ~Need many different types of cells to carry out life processes Achieved via cell specialisation and cell organisation
- 24. SPECIALISATION OCCURS THROUGH THE PROCESS OF DIFFERENTIATION
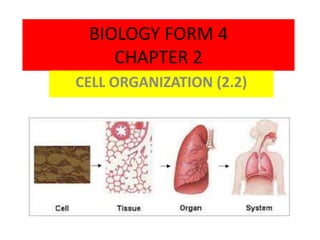
- 31. Cell The smallest unit of life capable of carrying out all Tissue Organ System Organism the functions of living things A group of cells of the same type that perform a specific function in organism Several types of tissue that carry out a particular function Several organs working together to perform a function All the systems make up a multicellular organism.
- 32. Cell organisation in animals
- 33. Some of the humans cells and their functions Cell Function Muscle cell Able to contract and relax and are involved in movement White blood cell Involved in defence of the body against diseases Red blood cell Transports oxygen Nerve cell Receives and sends out nerve impulses Sperm Fertilises the ovum
- 35. Animal Tissue There are 4 major types of tissues in animals: 1. Epithelial tissues 2. Muscle tissues 3. Connective tissues 4. Nerve tissues MENC
- 36. 1. Epithelial Tissue • Form a skin surface and protect the tissue beneath it. • Form a lining layer for tubes or lines the cavities of the body. • Protect against infection, mechanical injuries and dehydration. • Undergo changes to form glands.
- 38. 2. Muscle Tissue • Most abundant tissue in the body Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle • Contraction and relaxation for involuntary body activities (peristalsis along digestive tract) • Voluntary movements • Contract and relax to move the bone • Contract to pump blood to all parts of the body. • Involuntary movements
- 39. Muscle Tissue
- 40. Skeletal Muscle
- 41. Cardiac Muscle
- 42. Smooth Muscle
- 43. 3. Connective tissue • Holds the body together. • For example, bone, cartilage, blood, tendons, ligament.
- 45. Adipose Tissue • Peripheral nuclei due to large fat storage droplet • Deeper layer of skin, organ padding, yellow marrow • Reduces heat loss, energy storage, protection
- 46. Bones For movement, support , protection of organs, mineral storage
- 47. Blood Transport of gases, nutrients, waste products. Body defence against infections.
- 48. Nerve Tissue • Transmits and coordinates messages around the body.
- 53. Discards toxic waste products Produces off spring Breaks down complex food into simple substances for easy absorption by body cells Absorbs and transports oxygen and discards carbon dioxide Systems
- 54. Transports food substances, oxygen, hormones and others to the entire body Provides bodily support and protection to solf internal Defends the body against disease Systems organs Produces hormones that control the bodily activities
- 55. Skin surface to protects the tissue beneath it. Coordinates and controls all bodily activities related to impulses and reactions Helps in movement of the body. Systems
- 58. systems organs tissues cells
- 59. Cell organisation in plants
- 60. Some of the plants cells and their functions Cell Function Parenchyma cell For support and storage Xylem Transports water and mineral salts Sieve tube element Transports organic product of photosynthesis Companion cell Regulates the metabolic activity of sieve tube element Epidermal cell For protection and covering of other cells beneath
- 61. Tissues of plants Meristemic tissue permanent tissue Epidermal tissues Ground tissues Vascular tissues • Small cell, thin walls, large nuklei, dense cytoplasm, no vacuole. • Young, actively dividing • Form a layer to cover, protect entire surface of plant and reduces water loss • Provides support and strengthens the plants • Transports water, food and support
- 62. 1. Meristematic tissues Tip of shoot Tip of root Cambium • Small cell, • thin walls • large nuclei • dense cytoplasm, • no vacuole. • Young, actively dividing
- 64. 2. Epidermal • Form a layer to cover, protect entire surface of plant and reduces water loss
- 65. 3. Ground tissue Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Provides support and strengthens the plants
- 66. 4. Vascular tissue • Xylem -Transportation of water and minerals from the roots to shoot systems & support • Phloem - Transportation of food that is synthesized in leaves to whole plant.
- 68. Plant Systems SHOOT SYSTEM Bears flowers, fruits, buds and leaves ROOT SYSTEM Anchors the plant, absorbs water and mineral, stores food.
- 73. The process to regulate and maintain internal environment - HOMEOSTASIS Necessity: to maintain optimal internal environment so that cells can function optimally
- 74. What is internal environment? 1. Interstitial fluid 2. Blood plasma
- 75. Homeostasis of Body Fluids 1. intracellular fluid = within cells = cytoplasm 2. extracellular fluid = outside cells intercellular fluid = tissue fluid = interstitial fluid plasma = fluid portion of blood Composition of fluids change as substances move between compartments nutrients, oxygen, ions and wastes move in both directions across capillary walls
- 77. HOMEOSTASIS Factors to Maintain: - Internal factors : 1. Physical: • Temperature • Blood pressure • Osmotic pressure 2. Chemical: • Salt • Sugar • pH
- 79. How is this (homeostasis) controlled? Negative Feedback Mechanism
- 81. Homeostasis of Blood Glucose Level
- 82. Homeostasis of Body Temperature
- 84. Why are these cells so unique? • They can perform their function optimally! • Red blood cell – without nucleus – they have a lot of spaces for hemoglobin so a lot of oxygen can be carried. • Bone – they have calcium
- 85. THE END
- 86. • Area of Focus: Levels of Biological Organization. Atom Molecule Cell Organelle Tissue Cell Organ Organ System Cell Organism Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 87. Types of animal cell Characteristics Functions Epithelial tissues •Consist of epithelial cells arranged in a continuous layer •Cover the body surface or line the cavities within the body •Protect the underlying cells from mechanical injuries •Absorb food and water by diffusion •Form secretory gland Nervous tissues •Consist of nerve cells called neuron •Found in brain and spinal cord •Send & receive impulses to coordinate the activities of the body
- 88. Muscle tissues •Consisting of muscle cells which can contract to perform work •3 types : smooth muscle, skeletal muscle & cardiac muscle •Cause body movement by means of contraction Connective tissues •Consist of elastic & non-elastic fibre •Blood, adipose tissues, cartilage & bone. •Join together body structures, as well as protect, hold and support the cell in the body •Can store & transport material
- 89. Types of plant tissues Characteristic Functions Epidermis tissue •Consisting of one layer of cells •Examples : epidermis of leaves, stems & roots •Covers the entire surface of the plant •Protect underlying tissues from physical damage & infection •Reduces water loss •Epidermal cells of leaf differentiate to become guard cells while those at the root, become root hair cells. Meristem tissue •Consists if undifferentiated cells which are able to divide •Occurs at the tip of roots & shoots & in the cambium of stems & roots •Produces new cells by cell division
- 90. Vascular tissue •Consists of xylem tissues & phloem tissues •Transport water & mineral salts from roots to the stems & leaves by xylem tissues •Transport dissolved nutrients such as glucose from the leaves to the roots & stems by phloem tissues •Xylems tissues provide support to the plants Ground tissue •Consists of parenchyma mesophyll tissues, collenchyma & sclerenchyma tissues •Produces food by photosynthesis & stores food produced •Provides support & strengthens the plant
