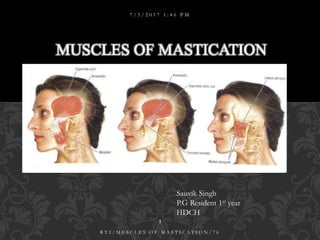
Muscle of mastication
- 1. MUSCLES OF MASTICATION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 1 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 Sauvik Singh P.G Resident 1st year HDCH
- 2. INTRODUCTION EMBRYOLOGY HISTOLOGY MUSCLES OF MASTICATION MASSETER TEMPORALIS MEDIAL PTERYGOID LATERAL PTERYGOID ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF MASTICATION APPLIED ASPECTS CONCLUSION REFERENCES CONTENTS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 2 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 3. MUSCLE- One of the contractile organs of the body OR Animal tissue consisting predominantly of contractile cells Mastication or chewing is the process by which food is mashed and crushed by teeth. During the mastication process, the food is positioned between the teeth for grinding by the cheek and tongue . INTRODUCTION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 3 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 4. Most muscle fibers develop before birth but increase in number and size in early infancy. Motor nerves establish contact with the myocytes, stimulating their activity and further growth by hypertrophy. Failure of nerve contact or activity results in muscle atrophy EMBRYOLOGY 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 4 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 5. Mesodermal Origin Muscles Innervation (Cranial Nerve) Somitomeres 1,2 Superior, inferior, and medial ocular recti; inferior oblique of eye Oculomotor (III) Somitomere 3 Superior oblique of eye Trochlear (IV) Somitomere 4 1st-arch masticatory muscles Trigeminal (V) Somitomere 5 Lateral ocular rectus Abducens (VI) Somitomere 6 2nd-arch facial muscles Facial (VII) Somitomere 7 3rd-arch stylopharyngeus0 Glossopharyngeal (IX) Somites 1,2 Laryngeal muscles Vagus (X) Somites 1–4 Tongue muscles Hypoglossal (XII) Somites 3–7 Sternomastoid, trapezius Accessory (XI) CRANIOFACIAL MUSCLE ORIGINS AND INNERVATIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 5 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 6. According to morphology- Striated, non striated, smooth According to function- Voluntary, involuntary Types- Skeletal- striated & voluntary Cardiac- striated & involuntary Smooth- non striated & involuntary HISTOLOGY 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 6 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 7. HISTOLOGY 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 7 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 8. Skeletal- Elongated and tubular, multiple nuclei located in periphery. Striated muscle has alternating light and dark bands Cardiac- not long as skeletal & are branched cells. Mono or bi nucleated located in center, striated, intercalated. Smooth- Spindle shaped, wide in middle & narrow at both ends, Single centrally located nucleus. No visible striation, but has same contractile protein CHARACTERISTICS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 8 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 9. No capability of mitotic activity, regeneration by satellite cells. If undergo mitotic activity- hyperplasia. Muscle building, satellite cells may fuse with existing muscle cells, thus hypertrophy. Skeletal muscle cells regulate their number and their size by the secretion of a member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), myostatin REGENERATION OF MUSCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 9 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 10. Mastication is a repetitive sequence of jaw opening and closing with a profile in the vertical plane called the chewing cycle. Mastication consists of a number of chewing cycles. The human chewing cycle consists of three phases: 1. Opening phase: the mouth is opened and the mandible is depressed. 2. Closing phase: the mandible is raised towards the maxilla. 3. Occlusal or intercuspal phase: the mandible is stationary and the teeth from both upper and lower arches approximate. THE CHEWING CYCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 10 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 11. Muscles of mastication- originate skull & insert mandible Only mandible moves during mastication and other activities Four muscles are the primary participants in mastication, other accessory muscles. Each of these primary muscles of mastication is paired THE CHEWING CYCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 11 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 12. They are: 1. Masseter 2. Temporalis 3. Lateral pterygoid 4. Medial pterygoid Develop from the mesoderm of the 1st brachial arch. Supplied by the mandibular nerve. PRIMARY MUSCLES OF MASTICATION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 12 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 13. Quadrilateral Covers lateral surface of ramus of mandible. Three layers 1. superficial layer [largest] 2. middle layer 3. deep layer MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 13 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 MASSETER
- 14. 1.SUPERFICIAL LAYER ORIGIN: Maxillary process of the zygomatic bone and anterior 2/3rd of lower border of zygomatic arch. FIBRES: Passes downwards & backwards at 45 degrees. MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 14 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 15. INSERTION: Lower part of the lateral surface of the ramus of mandible. MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 15 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 16. 2. MIDDLE LAYER : ORIGIN : Medial aspect of 2/3rd of zygomatic bone & posterior 1/3rd of lower border of zygomatic arch. FIBRES : Passes vertically downwards. INSERTION : Upper part of ramus of the mandible. MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 16 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 17. 3. DEEP LAYER : ORIGIN: Deep surface of zygomatic arch. FIBRES: Passes vertically downwards. INSERTION: Upper part of ramus & coronoid process of mandible. MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 17 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 18. NERVE SUPPLY: Masseteric nerve, a branch of anterior division of mandibular nerve. ACTIONS: 1. Elevates mandible to occlude teeth in mastication. 2. Small effect in side-to-side movements, protraction & retraction. MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 18 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 19. SUPERFICIAL: skin Platysma risorius zygomaticus major parotid gland Muscle is crossed by parotid duct branches of facial nerve transverse facial vessels MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 19 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 20. DEEP: Temporalis – lower part mandibular ramus Masseteric nerve & artery A mass of fat seperates it in front from buccinator & buccal nerve POSTERIOR MARGIN: Overlapped by parotid gland ANTERIOR MARGIN: Projects over buccinator & is crossed by facial nerve MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 20 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 21. Dissected muscle consist of 6 alternating musculo-aponuerotic layers, which is divided into 3 planes Anterior and posterior fan contains 3-3 musculo-aponuerotic layers Superficial/prior- 60* angulation with Frankfort horizontal plane Deep/alter lamina- 60* angulation with Frankfort horizontal plane Intermediate- 90* angulation with Frankfort horizontal plane MASSETER 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 21 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 22. Fan shaped muscle, fills the temporal fossa. ORIGIN: Whole of the temporal fossa except the part formed by zygomatic bone. Deep surface of temporal fascia. TEMPORALIS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 22 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 23. FIBRES: Converge & descends into a tendon which passes through the gap between zygomatic arch & side of skull. Anterior fibers -- oriented vertically. Posterior fibers – horizontally. Intermediate fibers -- obliquely TEMPORALIS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 23 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 24. INSERTION: Margins & deep surface of coronoid process, Anterior border of the ramus of mandible almost to last molar. NERVE SUPPLY: Two deep temporal branches from anterior division of mandibular nerve. TEMPORALIS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 24 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 25. SUPERFICIAL : Skin Auricularis anterior & superior Temporal fascia Superior temporal vessels Auriculo temporal nerve Temporal branches of facial nerve Zygomatico temporal nerve Epicranial aponeurosis Zygomatic arch Masseter. RELATIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 25 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 26. DEEP: Temporal fossa Lateral pterygoid Superficial head of medial pterygoid A small part of buccinator Maxillary artery & its deep temporal branches Deep temporal nerves Buccal nerve & vessels Anterior border is separated from the zygomatic bone by a mass of fat. RELATIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 26 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 27. Elevates the mandible to close the mouth & approximate the teeth. The movement requires both the upward pull of the anterior fibers & backward pull of the posterior fibers. Contributes to side- to- side grinding movements. Posterior fibers retracts the mandible. Vitti & Basmajian (1977) suggests that the temporalis is active in forcible elevation, but not in slow elevation with out occlusion. ACTIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 27 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 28. LATERAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 28 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 Short, conical, thick muscle with two heads.
- 29. ORIGIN: UPPER HEAD: Infra temporal surface & infra temporal crest of the greater wing of sphenoid bone. LOWER HEAD: Lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate. NERVE SUPPLY: A branch from anterior division of mandibular nerve. LATERAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 29 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 30. LATERAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 30 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 31. FIBRES: Passes backwards & laterally, and converge to insert. INSERTION: Pterygoid fovea of the mandible, articular disc, Capsule of the T.M.J. Insertion is postero lateral & at a slightly higher level than origin. LATERAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 31 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 32. Early 3rd mth I.U, muscle inserts into mesenchyme that condenses around developing condyle, but, part of it’s tendon sweeps backward above the condyle & gets inserted into the portion of Meckel’s cartilage that later forms the head of the malleus. -Harpman & Woollard (1938). This part of tendon become inserted into the articular disc of T.M.J & it’s attachment to the malleus does not persists. - Rees (1954) LATERAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 32 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 33. Opening the mouth – by pulling forward the condylar process of mandible & articular disc, while head of the mandible rotates on the articular disc. During closure of mouth, the backward gliding of the articular disc & condyle is controlled by slow elevation of lateral pterygoid, while the masseter & temporalis restore the jaw to the occlusal position. - Posselt (1952). ACTIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 33 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 34. 2. Left lateral pterygoid & right medial pterygoid turn the chin to left side as a part of grinding movements. 3. Medial & lateral pterygoids of two sides act together & protrude mandible, so that the lower incisors projects infront of the upper. Upper head is involved mainly in chewing. Lower head is in protrusion. ACTIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 34 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 35. Relations LATERALPTERYGOID REATIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 35 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 Body_ID: HC030020 The mandibular ramus and masseter, the maxillary artery - which crosses either deep or superficial to the muscle Superficially - superficial head of medial pterygoid and the tendon of temporalis. Deep - deep head of medial pterygoid, the sphenomandibular ligament, middle meningeal artery, mandibular nerve. Upper border - temporal and masseteric branches of the mandibular nerve. Lower border -lingual and inferior alveolar nerves. The buccal nerve and the maxillary artery pass between the two heads of the muscles
- 36. ORIGIN: SUPERFICIAL HEAD (SMALL SLIP) Lateral surface of the pyramidal process & maxillary tuberosity. DEEP HEAD (QUITE LARGE) Medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate & the grooved surface of the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. FIBRES: Runs downwards, backwards & laterally. MEDIALPTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 36 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 37. Attached by a strong tendinous lamina to the postero inferior part of the medial surface of the mandibular ramus & angle, as high as mandibular foramina & almost as forward as the mylohyoid groove. NERVE SUPPLY: A branch from the mandibular nerve. INSERTION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 37 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 38. MEDIAL PTERYGOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 38 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 39. SUPERFICIAL: Separated from lateral pterygoid muscle & ramus of mandible by lateral pterygoid plate, maxillary artery, Inferior alveolar vessels & nerves, Lingual nerve, Spheno mandibular ligament. Process of the parotid gland separated from masseter by lower part of the ramus of mandible RELATIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 39 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 40. Elevates the mandible. Acting with lateral pterygoid, it protrudes the mandible. When the medial & lateral pterygoid’s of one side act together, the corresponding side of mandible is rotated forwards to the opposite side, with the opposite mandibular head as a vertical axis. Alternating activity in the left & right sets of muscles produces side-to-side movements, which are used to triturate food. ACTIONS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 40 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 41. In 1996, researchers at the UNVERSITY OF MARYLAND identified a new muscle in the skull and named it SPHENOMANDIBULARIS. ORIGIN AND INSERTION: It extends from the lateral surface of the sphenoid bone to the medial surface of the coronoid process and ramus of the mandible. The muscle is believed to be either a fifth muscle of mastication or a previously unidentified component of an already identified muscle. NERVE SUPPLY: It is supplied by the maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve. THE FIFTH MUSCLE OF MASTICATION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 41 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 42. They are paired muscles. Anterior digastric Mylohyoid Geniohyoid Buccinator ACCESSORY MUSCLES OF MASTICATION 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 42 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 43. Two bellies united by an intermediate tendon ORIGIN : Anterior belly – Digastric fossa of mandible Posterior belly - mastoid notch on the medial side of the base of the mastoid process FIBRES : Anterior belly runs downwards & backwards Posterior belly runs downwards & forwards INSERTION : Both the heads meet at the intermediate tendon which perforates stylohyoid muscle & is held by a fibrous pulley to the hyoid bone. DIGASTRIC MUSCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 43 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 44. NERVE SUPPLY : ANTERIOR BELLY: Mylohyoid nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve POSTERIO BELLY: Nerve from posterior auricular branch of facial nerve ACTIONS : Depress and retract the mandible, so assisting the lateral pterygoid muscle in opening the mouth elevation of the hyoid bone, utilized during swallowing and speech DIGASTRICMUSCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 44 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 45. RELATIONS – Superficial -platysma, sternocleidomastoid, splenius capitis, longissimus capitis, stylohyoid, mastoid process, the retromandibular vein, the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. DIGASTRICMUSCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 45 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 46. RELATIONS – DIGASTRICMUSCLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 46 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 Medial to the anterior belly- Mylohyoid, hyoglossus, superior oblique, rectus capitis lateralis, the transverse process of the atlas vertebra, internal jugular vein, occipital artery, hypoglossal nerve, internal and external carotid, facial and lingual arteries- medial to posterior belly
- 47. Flat, triangular muscle. Two mylohyoids forms floor of mouth Situated just below the anterior belly of digastric muscle ORIGIN : Mylohyoid line of mandible, extends from symphysis in front to last molar tooth behind INSERTION : Posterior fibres :Body of hyoid bone Middle & anterior fibres : median raphe between mandible &hyoid bone MYLOHYOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 47 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 48. Fibres Runs medially & slightly downwards NERVE SUPPLY : Mylohyoid nerve, a nerve from mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve ACTION : Elevates floor of mouth in deglutition Depress the mandible & elevates hyoid bone MYLOHYOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 48 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 49. The inferior (external) surface – platysma, anterior belly of digastric, the superficial part of the submandibular gland, the facial and submental vessels, and the mylohyoid vessels and nerve. posteriorly- the mucous membrane of the mouth. MYLOHYOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 49 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6 The superior (internal) surface- geniohyoid, part of hyoglossus and styloglossus, the hypoglossal and lingual nerves, the submandibular ganglion, the sublingual gland, the deep part of the submandibular gland and its duct, the lingual and sublingual vessels
- 50. Thin quadrilateral muscle ORIGIN : Upper fibres, from maxilla, opposite molar teeth Lower fibres, from mandible, opposite molar teeth Middle fibres, from pterygomandibular raphe INSERTION : Upper fibres – Upper lip Lower fibres – Lower lip Middle fibres – Decussate before passing to lips ACTION : Flattens cheek against gums & teeth Prevents accumulation of food in the vestibule. BUCCINATOR 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 50 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 51. Anteriorly – the superficial surface of buccinator is related to zygomaticus major, risorius, levator and depressor anguli oris, and the parotid duct. It is crossed by the facial artery, facial vein and branches of the facial and buccal nerves. Posteriorly – buccinator lies in the same plane as the superior pharyngeal constrictor, which arises from the posterior margin of the pterygomandibular raphe, and is covered there by the buccopharyngeal fascia. BUCCINATOR 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 51 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 52. Superficially – the buccal pad of fat separates the posterior part of buccinator from the ramus of the mandible, masseter and part of temporalis. Deep surface – the buccal glands and mucous membrane of the mouth. The parotid duct pierces buccinator opposite the third upper molar tooth, and lies on the deep surface of the muscle before opening into the mouth opposite the maxillary second molar tooth BUCCINATOR 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 52 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 53. Short & narrow muscle Lies above medial part of mylohyoid muscle ORIGIN : Inferior mental spine FIBRES : Runs backwards & downwards GENIOHYOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 53 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 54. INSERTION : Anterior surface of body of hyoid bone NERVE SUPPLY : By fibres from 1st cervical nerve via hypoglossal nerve ACTION : Elevates hyoid bone Depress mandible GENIOHYOID 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 54 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 55. MUSCLES RESPONSIBLE FOR MOVEMENTS OF MANDIBLE 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 55 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 56. PALPATION
- 58. The anterior region is palpated above the zygomatic arch and anterior to the TMJ The middle region is palpated directly above the TMJ and superior to the zygomatic arch The posterior region is palpated above and behind the ear
- 59. Masseter Muscle
- 60. The patient is asked to clench their teeth and, using both hands, the practitioner palpates the masseter muscles on both sides extraorally , making sure that the patient continues to clench during the procedure. Palpate the origin of the masseter bilaterally along the zygomatic arch and continue to palpate down the body of the mandible where the masseter is attached
- 61. LATERAL PTERYGOID Placing the forefinger, or the little finger, over the buccal area of the maxillary third molar region and exerting pressure in a posterior, superior, and medial direction behind the maxillary tuberosity
- 63. gently palpate them on the medial aspect of the jaw, simultaneously from both inside and outside the mouth
- 64. In case of uni or bilateral condylar fractures due to the pull of lateral pterygoid, the fractured condylar heads displaces anteromedially, thus reducing the height of the ramus of mandible, there by causing posterior gag & anterior open bite. APPLIED ASPECTS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 64 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 65. In case of unfavorable angle fractures, medial pterygoid & masseter pulls the fragment upwards causing difficulty in fracture reduction. APPLIEDASPECTS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 65 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 66. In case of bilateral para symphysis fractures, due to the pull of digastric, geniohyoid & genioglossus, the fractured segment is pulled posteriorly & inferiorly, there by causing fall back of tongue and compromising the airway. This usually happens in unconscious patients. APPLIEDASPECTS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 66 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 67. Beginning at about 30 Years of age these is a progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass that is largely replaced by fat. Due to loss of muscle mass, there is a decrease in maximal strength and a diminishing of muscle reflexes Muscle spasm of the masseter and lateral pterygoid associated with excessively wide opening of mouth results in lock jaw in dislocated position. AGEING 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 67 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 68. A lesion at foramen ovale results in parenthesis along the mandible, the mandibular teeth and the side of face, as well of paralysis of muscles of mastication. An injury to nerve supply to muscles of mastication causes the chin to be drawn to the paralyzed side on protraction. This is due to lack of contraction of medial and lateral pterygoid muscle on paralyzed side. APPLIEDANATOMY 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 68 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 69. Acute inflammation of masseter muscle with pain, swelling, tenderness restriction. This may be caused due to cellulitis, trauma, and irritation of the muscle. This can be treated by anti inflammatory analgesics, gentle range of motion exercise. MYOSITIS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 69 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 70. Inflammatory lesions about the mandibular joint may produce a chronic masseter myositis with subsequent fibrosis which may restrict the play of muscles & limit the movements of the jaw. APPLIEDASPECTS 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 70 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 71. Intensive bruxism of long duration, may result in masseter muscle hypertrophy. This may cause muscle pain, tender on palpation. It may also be associated with temporalis muscle hypertrophy. MASSETER HYPERTROPHY 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 71 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 72. MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Acquired autoimmune disorder of neuromuscular transmission characterized by muscle weakness ETIOLOGY Antibodies to acetylcholine receptor on skeletal muscle fiber CLINICAL FEATURES Diplopia, ptosis, drooping of the face, And a very sorrowful appearance to the patient. Patient rapidly exhausted, lose weight, death frequently occurs from respiratory failure.
- 73. TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS Physostigmine administered intramuscularly improves the strength of the affected muscle in a matter of minutes No cure is known even though the prognosis is good in the relapsing type.
- 74. TETANUS(LOCK JAW) Caused by exotoxins of gram positive bacillus Clostridium tetani. Disease of the nervous system characterized by intense activity of motor neuron and resulting in severe muscle spasm CLINICAL FEATURES Pain and stiffness in the jaws and neck muscles ,with muscle rigidity producing trismus and dysphagia Risus sardonicus Opisthotonous
- 75. TREATMENT All patients should receive antimicrobial drugs Active and passive immunization. Surgical wound care Anticonvulsant if indicated
- 76. BRUXISM Bruxism : Jaw clenching, with or without forcible excursive movements, where the intensity of the clenching dictates the severity (or lack of) grinding . Clenching- It can occur as a brief rhythmic strong contractions of the jaw muscles during eccentric lateral jaw movements, or in maximum intercuspation, Causes 1) Associated with stressful events 2)Non stress related or hereditary
- 77. Bruxism may lead to -tooth wear -fracture of the teeth or restoratrion -uncosmetic muscle hypertrophy Treatment -coronoplasty -maxillary stabalization appliance
- 78. MYOPATHIES Myopathy is a neuromuscular disease in which the dysfunction of muscle fibers leads to muscular weakness. The diseases may or may not involve the nervous system. The common diseases are:- 1 -Muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy Backers muscular dystrophy
- 79. 2 – Diseases involving muscle tone Hypertonia Hypotonia Myotonia 3 – Fibrillation and denervation hypersensitivity 4 – Myasthenia gravis 5 – Lambert-Eaton syndrome 6 – McARDLES syndrome 7 – Mitochondrial hypopathy 8 – Nemaline myopathy
- 80. MUSCLE HYPERTROPHY, ATROPHY, HYPERPLASIA HYPERTROPHY: when total mass of muscle enlarges., increase in actin and myosin filament in response to maximal force causing enlargement of muscle fiber. HYPERPLASIA: Under rare condition of extreme muscle force generation actual number of muscle fiber have been observed to increase. ATROPHY: When total mass of muscle decreases.
- 81. TRISMUS
- 82. CAUSES Pericoronitis Masticatory space infection Inferior alveolar nerve block Post surgical trismus Tetanus Hypocalcemic tetani
- 87. MPDS Defined as – pain is constant, dull in nature, in contrast to the sudden sharp, shooting, intermittent pain of neuralgia [chronic pain ]. But the pain may range from mild to intolerable. The condition is ch/by unilateral facial pain secondary to the TMJ disorder, which is often associated with periarticular muscle spasm and pain with dysfunction of the spastic muscle
- 88. ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS The factors are:- 1- Intra-capsular causes: Internal derangements like- I. Anterior disc dislocation with reduction and without reduction II. Disc perforation III. Disc adhesions
- 89. 2 Extra-capsular causes- Occlusal disharmony Psychosis Muscular imbalance Hypermobility, subluxation Muscular over extension due to restoration or prosthesis Muscle overecontraction- loss of posterior teeth Para-functions- bruxism, clenching, grinding etc
- 90. CLINICAL FEATURE Pain which is usually unilateral and aggravated on chewing, yawning , and opening. Pain in temples, vertex, occipital areas, headaches, neck and shoulder aches are common. Restricted joint excursion Pathological joint sounds – clicking sound, crepitus like sound. Muscle tenderness. Otological symptoms. Occlusal discrepancies. Altered psychosis. Subluxation or dislocation
- 91. MANAGEMENT 1 Pharmacologicle T/t. 2 Intra- articular injection. 3 Occlusal splints. 4 physiotherapeutic T/t. 5 stress management. 6 Biofeedback and relaxation therapy. 7 Psychological T/t. 8 surgical T/t:- a] Arthrocentesis
- 92. B] capsule tightening procedures . C] creating mechanical obstacle. D] removal of mechanical obstacle. F] creation of new muscle balance .
- 93. 1. Gray’s Anatomy - Churchill Livingstone. 2. Human anatomy - B. D. Chaurasia. 3. Grant’s Atlas of Anatomy - Anne M. R. Agur , Arthur F.Dalley. 4. Text book of Anatomy with Colour Atlas - Inderbir Singh. 5. Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma - Fonseca. 6. Text book of Histology - Hiatt & Garner 7. Text Book of Medical Physiology - Arthur C. Guyton REFERENCES 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 93 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
- 94. THANK YOU 7 / 5 / 2 0 1 7 1 : 4 6 P M 94 R T 2 / M U S C L E S O F M A S T I C A T I O N / 7 6
Editor's Notes
- Skeletal- Elongated and tubular, multiple nuclei located in periphery. Striated muscle has alternating light and dark bands Cardiac- not long as skeletal & are branched cells. Mono or bi nucleated located in center, striated, intercalated. Smooth- Spindle shaped, wide in middle & narrow at both ends, Single centrally located nucleus. No visible striation, but has same contractile protein
- In embryonic development each skeletal muscle fiber arises from the fusion of a million mesodermal cells called as myoblasts.of which few cells called satellite cells which persists later in life fuse and cause regeneration Hyperplasia-Abnormal increase in number of cells Hypertrophy- Abnormal enlargement of a body part or organ
- FH - Frankfort horizontal - line connecting the points porion (po) and orbitale (or) Po - porion - the most superior point of the external auditory meatus Or - orbitale - the most inferior point of the orbit
- This results in inability to close the jaw. (This dislocation can be reduced by downward pressure on the posterior teeth forcing the condyle downward and upward pressure on the chin slipping the condyle backward into place)
- Treatment is done by providing rest to the muscle and stoppage of bruxism.