Parasites Lesson PowerPoint
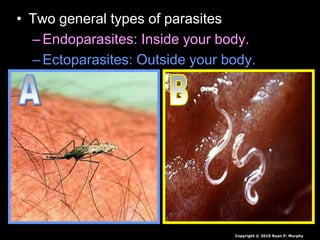
- 1. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 3. • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 4. • RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. • BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects as described and answer required questions neatly. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 5. • Keep an eye out for “The-Owl” and raise your hand as soon as you see him. – He will be hiding somewhere in the slideshow “Hoot, Hoot” “Good Luck!” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 12. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 13. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 14. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 15. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 16. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 17. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 18. • What is the most deadly animal on the planet?
- 19. • and the answer is…
- 20. • And the most dangerous animal on the planet is… The Mosquito
- 21. • Between 1 and 1.5 million people die each year from just Malaria which is carried by the mosquito.
- 24. • The mosquito injects an anticoagulant to keep the blood from clotting. This anticoagulant holds many pathogens. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 25. • Malaria, West Nile Virus, Yellow Fever, EEE, Many other types of Encephalitis, Dengue Fever, Rift Valley Fever. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 26. • West Nile Virus – Optional Video.
- 27. • To avoid some mosquito borne illnesses, wear protective clothes, repellant, avoid mosquito areas, and avoid times when they are most active, dawn and dusk. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 28. • To limit mosquitoes near your home, eliminate places for the larvae to develop in standing water. Where can stagnant water can be found near your house? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 30. New Area of Focus: Parasitism
- 31. Parasitism: One organism benefits while the other is harmed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 32. “I’m sick of studying dumb stuff” “Why should I care about studying parasites?”
- 33. • 1 in 3 American suffers in some form from a parasite. – Learn about them to help yourself. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 34. “I’m sorry that I yelled earlier.” “I didn’t know that.”
- 35. • Caution! Disgusting parasites ahead. – Be prepared to be grossed out. Close your eyes if needed.
- 36. • Parasites are one on the most numerous and successful groups of organisms on the planet. – For every species on earth, they may host a handful of unique parasites. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 37. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 38. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 39. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 40. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 41. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 42. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 43. • Most parasites have very complicated life cycles, often going through a number of different species before finding a host. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 44. • Video (Optional) Zombie Snail and the complicated life cycles of many parasites. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EWB_COS UXMw (1:22) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 45. • Parasites damage their host by consuming tissues, and releasing toxins. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 46. Two general types of parasites Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 47. Two general types of parasites Endoparasites: Inside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 48. Two general types of parasites Endoparasites: Inside your body. Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 49. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 50. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 51. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 52. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 53. • Two general types of parasites –Endoparasites: Inside your body. –Ectoparasites: Outside your body. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 54. • Worms make up some of the common parasites that affects humans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 55. • Worms make up some of the common parasites that affects humans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 56. • Worms make up some of the common parasites that affects humans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 57. • Worms make up some of the common parasites that affects humans. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 59. • A few endoparasites that affect humans. – Tape worms
- 60. • If a child frequently itches their butt, you should check to see if they have contracted pinworm.
- 61. • Pinworm
- 62. • Pinworm: Medication works, but a flashlight and small spoon is also required.
- 63. • Pinworm: Medication works, but a flashlight and small spoon is also required. Pinworms
- 64. • Pinworm: Medication works, but a flashlight and small spoon is also required. Pinworms Anus
- 65. “Yummy!” “These Pinworm eggs taste great when I bite my nails.”
- 66. • Hookworm
- 67. • Roundworms
- 68. • Guinea worms
- 69. • Guinea worms can be very large. – Video! (Optional) Caution Graphic! – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qwk- THcjmlI
- 71. • Loa loa, eyeworms
- 72. • Loa loa, eyeworms
- 73. • Brain Worm – Affects Moose. Slime from snail passes the parasite between species.
- 74. • Heartworms – Dogs – Common parasite Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 75. • Some common ectoparasites. – Fleas
- 76. • Louse
- 77. • Chiggers
- 78. • Ticks
- 80. • Crabs (louse)
- 81. • Crabs (louse)
- 82. • Crab (louse) legs and claws are highly adapted to cling to pubic hairs on the human body.
- 83. “Ahhh, good job little baby crab.”
- 84. “Your almost there.” “Just keep climbing up the pubic hair.”
- 85. • Bed bugs
- 86. • This strange louse is a tongue eating parasite that lives in a fishes mouth.
- 87. • This strange louse is a tongue eating parasite that lives in a fishes mouth.
- 88. • Biting flies
- 90. • Human Bot Fly.
- 91. • Human Bot Fly
- 92. • Human Bot Fly
- 97. • Filariasis
- 98. • Filariasis
- 100. • Zombie Snail – Parasitic flatworm – Eggs exist in bird droppings, and when snail eats droppings, the parasite crawls into eyestalk and pulse. – A bird comes by and eats eye stalk / parasite and snail loses eye.
- 101. • Zombie Snail – Caused by parasitic flatworm – Eggs exist in bird droppings, and when snail eats droppings, the parasite crawls into eyestalk and begins to pulse. (Caterpillar?) – A bird comes by and eats eye stalk / parasite and snail loses eye.
- 102. • Zombie Snail – Caused by parasitic flatworm – Eggs exist in bird droppings, and when snail eats droppings, the parasite crawls into eyestalk and begins to pulse. (Caterpillar?) – A bird comes by and eats eye stalk / parasite and snail loses eye.
- 103. • Video Link! Optional, Zombie Snail – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Go_LIz7kTok
- 104. • Video – Wasp parasite and aphids – Are all parasites bad to humans? – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rLtUk- W5Gpk
- 105. • Mosquito – A parasite that carries the malaria parasite.
- 106. • Leeches
- 107. • Vampire Bat.
- 108. • The Candiru or toothpick fish…
- 109. • Video Link! The Candiru – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QQWgUht- ObI
- 110. • The Candiru or toothpick fish sucks blood and can enter any open human orifice.
- 111. • The Candiru or toothpick fish sucks blood and can enter any open human orifice.
- 112. • The Candiru or toothpick fish sucks blood and can enter any open human orifice.
- 113. • The Candiru or toothpick fish sucks blood and can enter any open human orifice.
- 114. • Some PowerPoint advice! – Involve people. I need two volunteers, one boy and one girl to read the next slide. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 116. PowerPoint advice: You should…
- 117. PowerPoint advice: You should…
- 118. PowerPoint advice: You should… KISS -or read the next slide.
- 119. • PowerPoint advice: “KISS” –Keep –It –Simple –Silly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 120. • PowerPoint advice: “KISS” –Keep –It –Simple –Silly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 121. • PowerPoint advice: “KISS” –Keep –It –Simple –Silly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 122. • PowerPoint advice: “KISS” –Keep –It –Simple –Silly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 123. • PowerPoint advice: “KISS” –Keep –It –Simple –Silly Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 124. • PowerPoint Advice: – Cheesy Effects do not help your presentation. – Waiting for information is a waste of time. – Animations can take away from your presentation. – Wait! I‟m not finished reading this. Where is it going? I‟m not ready yet! “Arrrgh, I hate animations!” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 125. • Sound effects combined with effects is even worse.
- 126. How is this color combination? Do you want to sit through 25 slides of Twinkie Yellow? Be smart about your color choice. “Keep it Simple” Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 127. I really enjoy this background color and font style. I also wanted to make a pretty font. Black and white is so boring! Is this font to small? Is this Font to Big? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 128. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 129. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Some PowerPoint advice!
- 130. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Some PowerPoint advice! Only a few words per slide.
- 131. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Some PowerPoint advice! Only a few words per slide. NO Paragraphs! NO Reading!
- 132. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Some PowerPoint advice! Only a few words per slide. NO Paragraphs! NO Reading! NO Copy and Paste.
- 133. Tornado Formation – A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with and extending between a cloud (often a thunderstorm cloud) and the surface of the earth. Winds in most tornadoes blow at 100 mph or less, but in the most violent, and least frequent, wind speeds can exceed 250 mph. – Tornadoes, often nicknamed "twisters," typically track along the ground for a few miles or less and are less than 100 yards wide, though some monsters can remain in contact with the earth for well over fifty miles and exceed one mile in width. – Several conditions are required for the development of tornadoes and the thunderstorm clouds with which most tornadoes are associated. Abundant low level moisture is necessary to contribute to the development of a thunderstorm, and a "trigger" (perhaps a cold front or other low level zone of converging winds) is needed to lift the moist air aloft. – Once the air begins to rise and becomes saturated it will continue rising to great heights and produce a thunderstorm cloud, if the atmosphere is unstable. An unstable atmosphere is one where the temperature decreases rapidly with height. – Atmospheric instability can also occur when dry air overlays moist air near the earth's surface. Finally, tornadoes usually form in areas where winds at all levels of the atmosphere are not only strong, but also turn with height in a clockwise, or veering, direction. – Tornadoes can appear as a traditional funnel shape, or in a slender rope-like form. Some have a churning, smoky look to them, and others contain "multiple vortices" - small, individual tornadoes rotating around a common center. Even others may be nearly invisible, with only swirling dust or debris at ground level as the only indication of the tornado's presence. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Some PowerPoint advice! Only a few words per slide. NO Paragraphs! NO Reading! NO Copy and Paste. It’s cheating and boring.
- 134. • Some PowerPoint advice – Visuals are more important than words. – This is a picture of a tornado forming. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 135. • Some PowerPoint advice – Visuals are more important than words. – This is a picture of a tornado forming. Note – Cyclonic formation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 136. • Some PowerPoint advice – Visuals are more important than words. – This is a picture of a tornado forming. Note – Cyclonic formation Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 137. • The requirements of this project in in 10 seconds. – Don‟t make your presentation PowerPointless. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 138. • Activity! Creating a PowerPoint Presentation on parasites. • Fact sheet in activities folder – Visit the cdc website to find A-Z list of parasites and choose one of interest (10 minutes) • http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ – 1 Slide Title Page: Common and science name of parasite. – 2/3 slides: Pictures of parasite / host – 2/3 slides: How do you get it / transmitted? – 3 slides: How it effects it‟s host (health effects)? – 1 slide: How do you treat this parasite? – 1 Slide: What‟s the life cycle of this parasite? – Works cited page optional but encouraged, use APA format. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 139. Activity Sheet! Parasite Research Sheet - Found in activities folder.
- 141. • Scabies (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 143. • Scabies is spread from person to person contact Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 144. • People don‟t usually have symptoms during the first 2 to 6 weeks they are infested (CDC, 2010). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 145. • The scabies mite can be spread during this time. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 146. • The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 147. • The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin. (CDC, 2010). Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy Lays Eggs in Skin
- 148. • Picture of rash caused by the burrowing scabies mite. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 149. • The rashes and infections can be minor, • Or the they can very serious. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 150. • The rashes and infections can be minor, • Or the they can very serious. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 152. • Scabies occurs worldwide and can infect anyone. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 153. • Picture of scabies mite infecting homeless in Norway. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 154. • Scabies life cycle goes from egg to nymph to adult. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 155. • Scabicides are used to kill scabies and eggs. – Doctor‟s prescription is needed. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 156. • Learn more at…http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/
- 157. • Works Cited • Centers For Disease Control. (2010, November 2). Parasites - scabies. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/in dex.html
- 158. • Information to complete works cited page can be found at… • http://citationmachine.net/index2.php
- 159. • Activity! Creating a PowerPoint Presentation on parasites. • Fact sheet in activities folder – Visit the cdc website to find A-Z list of parasites and choose one of interest (10 minutes) • http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ – 1 Slide Title Page: Common and science name of parasite. – 2/3 slides: Pictures of parasite / host – 2/3 slides: How do you get it / transmitted? – 3 slides: How it effects it‟s host (health effects)? – 1 slide: How do you treat this parasite? – 1 Slide: What‟s the life cycle of this parasite? – Works cited page optional but encouraged, use APA format. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 160. • Video Link! How to make a PowerPoint. – Note: This video is also a good example of an extremely boring and ineffective PowerPoint. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VUqIDs5MZxM Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 161. • Parasite Presentations. – Each person should set-up their presentation area so it‟s nice and neat. – Students should record information about parasites directly to their homework bundle. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 162. • The Parasite Zone. Creepy music to play during the presentations. – Twilight Zone Intro: 30 Sec. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cxf_Dvy0VLs – Dark Ambient: 7 minutes. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n1vjTJTRn48 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LJyiTDAWzDA&feat ure=related Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 163. • Video Link (Optional) Parasites with Hank. • Please preview for language. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ABeBqbBy2Lo
- 164. Diseases can be spread by… - - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 165. Insects Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 166. • Lyme disease is carried by the deer tick / black legged tick, not the wood / dog tick. – Optional Video on Lyme Disease. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 167. • Which tick below is a deer tick, and which is dog tick? The deer tick carries Lyme Disease. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 168. • Dog Tick (No Lyme) Deer Tick / Black Legged Tick (Lyme)
- 169. • Dog Tick (No Lyme) Deer Tick / Black Legged Tick (Lyme)
- 170. • Which is a deer tick (Lyme Disease) and which is a dog tick? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 171. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 172. Dog Tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 173. Dog Tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 174. Dog Tick Deer tick (Lyme Disease) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 175. • Which is a dog / wood tick, and which is a deer / black legged tick (Lyme Disease)?
- 176. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 177. • Answer! Dog Tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 178. • Answer! Dog Tick Deer Tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 179. • Ticks can be very small in their nymph stages so you must search very well. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 180. • Male dog tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 181. • Male dog tick Female dog tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 182. • Which dog tick is male, and which is female? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 183. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 184. Female dog tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 185. Female dog tick Male dog tick Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 187. • Which is the male dog tick and which is the female? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 188. • Answer: They are both male. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 189. • Which of the four is a female tick? A B CD
- 190. • Which of the four is a female tick? A B CD
- 192. • Which of the four is a deer tick? A B CD
- 193. • Which of the four is a deer tick? None A B CD
- 195. • Which of the four is a deer tick? A B D C
- 196. • Which of the four is a deer tick? Letter C A B D C
- 199. • Ticks climb to a spot, sometimes along a well traveled path and “quest” for a host to walk by and grab on. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 200. • Which is a deer tick questing? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 201. • Which is a deer tick questing? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 202. • The deer tick spreads a bacterium when it bites a human and fills with blood.
- 203. • Tick Removal. What should you do?
- 204. •Tick Removal. –1) Use fine-point tweezers to grasp the tick at the place of attachment, as close to the skin as possible.
- 205. •Tick Removal. –2) Gently pull the tick straight out.
- 206. •Tick Removal. –3) Place the tick in a small vial labeled with the victim's name, address and the date.
- 207. •Tick Removal. –4) Wash your hands, disinfect the tweezers and bite site.
- 208. •Tick Removal. –5) Mark your calendar with the victim's name, place of tick attachment on the body, and general health at the time.
- 209. •Tick Removal. –6) Call your doctor to determine if treatment is warranted.
- 210. •Tick Removal. –7) Watch the tick-bite site and your general health for signs or symptoms of a tick-borne illness. Make sure you mark any changes in your health status on your calendar.
- 211. •Tick Removal. –8) If possible, have the tick identified / tested by a lab, your local health department, or veterinarian.
- 212. – Which is not a step you should take when removing a tick? – 1) Use fine-point tweezers to grasp the tick at the place of attachment, as close to the skin as possible. – 2) Squeeze the tick and twist before pulling it out. – 3) Place the tick in a small vial labeled with the victim's name, address and the date. – 4) Wash your hands, disinfect the tweezers and bite site. – 5) Mark your calendar with the victim's name, place of tick attachment on the body, and general health at the time. – 6) Call your doctor to determine if treatment is warranted. – 7) Watch the tick-bite site and your general health for signs or symptoms of a tick-borne illness. Make sure you mark any changes in your health status on your calendar. – 8) If possible, have the tick identified/tested by a lab, your local health department, or veterinarian.
- 213. – Which is not a step you should take when removing a tick? And the Answer is… – 1) Use fine-point tweezers to grasp the tick at the place of attachment, as close to the skin as possible. – 2) Squeeze the tick and twist before pulling it out. – 3) Place the tick in a small vial labeled with the victim's name, address and the date. – 4) Wash your hands, disinfect the tweezers and bite site. – 5) Mark your calendar with the victim's name, place of tick attachment on the body, and general health at the time. – 6) Call your doctor to determine if treatment is warranted. – 7) Watch the tick-bite site and your general health for signs or symptoms of a tick-borne illness. Make sure you mark any changes in your health status on your calendar. – 8) If possible, have the tick identified/tested by a lab, your local health department, or veterinarian.
- 214. – Which is not a step you should take when removing a tick? And the Answer is… – 1) Use fine-point tweezers to grasp the tick at the place of attachment, as close to the skin as possible. – 2) Squeeze the tick and twist before pulling it out. – 3) Place the tick in a small vial labeled with the victim's name, address and the date. – 4) Wash your hands, disinfect the tweezers and bite site. – 5) Mark your calendar with the victim's name, place of tick attachment on the body, and general health at the time. – 6) Call your doctor to determine if treatment is warranted. – 7) Watch the tick-bite site and your general health for signs or symptoms of a tick-borne illness. Make sure you mark any changes in your health status on your calendar. – 8) If possible, have the tick identified/tested by a lab, your local health department, or veterinarian.
- 215. • Squeezing the tick may force more dangerous bacterium into your body.
- 216. • Squeezing the tick may force more dangerous bacterium into your body. – Gently pull the tick straight out.
- 217. • Squeezing the tick may force more dangerous bacterium into your body. – Gently pull the tick straight out. – Gently so you don‟t rip it in two leaving the head stuck in your skin.
- 218. • If you have been bitten by a tick and develop a “bullseye” spot, seek medical attention. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 219. Diseases can be spread by… - Insects - - - Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 220. Air Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 221. Air Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 222. Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 223. • Water Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 224. Food Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 225. Food Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 226. Person to person Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 227. Person to person Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 228. Person to person Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 229. Person to person Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 230. • Video! A Sneeze sends out millions of mucus particles at 100 mph. Back Again! – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NVXukm1lNOs Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 231. • Video! A Sneeze sends out millions of mucus particles at 100 mph. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2QAGVMlns4 – Why is it so important that we cover our mouth? Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 232. – Activity: Shake the hand of the person next to you. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 233. • Not the best way to greet when you think about disease transmission. – Activity: Shake the hand of the person next to you. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 234. • Not the best way to greet when you think about disease transmission. – Activity: Shake the hand of the person next to you. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 235. • Yum, viruses taste good! Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 236. • Yum, viruses taste good! Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 240. • Millions upon millions of native peoples died as a result of disease being brought over from Europe. (No immunity) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 241. • Video! The transportation of viruses. (5:40) – Pandemic Planning? – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VwzjU0KRm3U Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 243. Animal to Person (Contact) Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 244. • Avian Bird Flu (Possible Pandemic) – Optional Video (10 minutes – Slow) – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4nqmyIcO78 E&feature=fvst Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 246. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 247. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 248. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 249. • Hantavirus: A deadly virus found on the feces of mice. Avoid close contact (airborne as well) with these droppings. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 254. • Rabies and animals – Don‟t come in contact with animal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 255. • Rabies and animals – Don‟t come in contact with animal. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 256. • Dispose of household trash in barrels that are tamper proof. Remove often. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 257. • „Ahh”, “I found this cute wild bunny outside and I‟m going to raise it myself. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 258. • Now it has to have its head cut off to check for the rabies virus in the brain tissue or you run the risk of death. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 259. • Now it has to have its head cut off to check for the rabies virus in the brain tissue or you run the risk of death. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 260. • Guess the hidden picture beneath the boxes. – Raise your hand when you think you know. You only get one guess. Copyright © 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
- 275. Mosquito – Most Dangerous Animal on the Planet
- 276. Mosquito – Most Dangerous Animal on the Planet
