Vijay Balu Raskar-final-ssc-science-notes
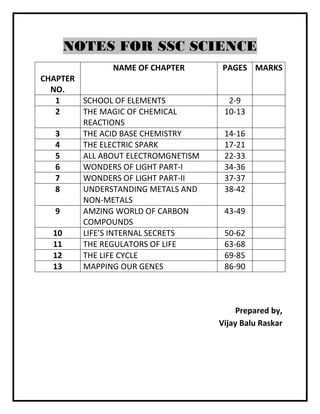
- 1. NOTES FOR SSC SCIENCE NAME OF CHAPTER PAGES MARKS CHAPTER NO. 1 SCHOOL OF ELEMENTS 2-9 2 THE MAGIC OF CHEMICAL 10-13 REACTIONS 3 THE ACID BASE CHEMISTRY 14-16 4 THE ELECTRIC SPARK 17-21 5 ALL ABOUT ELECTROMGNETISM 22-33 6 WONDERS OF LIGHT PART-I 34-36 7 WONDERS OF LIGHT PART-II 37-37 8 UNDERSTANDING METALS AND 38-42 NON-METALS 9 AMZING WORLD OF CARBON 43-49 COMPOUNDS 10 LIFE’S INTERNAL SECRETS 50-62 11 THE REGULATORS OF LIFE 63-68 12 THE LIFE CYCLE 69-85 13 MAPPING OUR GENES 86-90 Prepared by, Vijay Balu Raskar
- 2. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 1. SCHOOL OF ELEMENTS DOBEREINER’S TRIADS:- Group of elements shows similar properties. These groups were called as Triads. In triads, atomic mass of the middle element was approximately the mean of the atomic masses of other two elements. Element Atomic Mass Lithium (Li) 6.9 Sodium (Na) 23 Potasium (K) 39 Calcium (Ca) 40.1 Strontium (Sr) 87.6 Barium (Ba) 137.3 Chlorine (Cl) 35.5 Bromine (Br) 79.9 Iodine (I) 126.9 2
- 3. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Sulphur (S) 32 Selenium (Se) 79 Tellurium (Te) 128 From above table, mean value of atomic masses Lithium and Potassium is Sodium. i.e. (6.9 + 39) / 2 = 23 Similarly for other atomic masses from the other triads. The triads were known as Dobernier’s triads. DRAWBACK OF DOBEREINER’S TRIADS:- Only known some triads elements are identify from Dobereiner’s triads. Other triads did not obey Dobereiner’s rule. Hence, it is not useful. NEWLAND’S OCTAVES:- After failure of Dobereiner’s triads, newland’s octaves classification was done. 56 elements were discovered. Elements are arranged in an increasing order of their atomic masses. Every eight element had similar property with first. They compared with octaves which are found in music. Therefore, this classification is known as “Newland’s Octaves”. 3
- 4. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) STATEMENT OF LAW:- It states that, when the elements are arranged in an increasing order of their atomic masses, the properties of the eighth element are similar to the first. FEATURES OF NEWLAND’S RULE:- From 56 elements, they can be arrange only up to calcium. After calcium, every eighth element did not possess properties similar to that of the first. Only 56 elements were known but later several elements were known. It not includes inert gases because they were not discovered. MENDELEEV’S PERODIC TABLE:- The physical and chemical properties of element are a periodic function of their atomic masses. The tabular arrangement of the element based on the periodic law is called Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. FEATURES OF MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE:- The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called as periods. Periods are seven in numbers. These are numbered from 1 to 7. Properties of element in a particular period show regular gradation from left to right. Vertical column in the periodic table are called group. There are eight groups numbered from I to VIII. Groups I to VII are further divided into A and B subgroups. MERITS OF MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE:- 4
- 5. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 1st successful classified all known elements. He kept some blank places in his periodic table for new elements that were yet to be discovered. He predicted properties of these elements even before they were discovered. Later they were found to be correct. When noble gases were discovered later. They placed in periodic table without distributing table DEMERITS OF MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE:- No fixed position for Hydrogen in the periodic table. Hydrogen resembles alkali as well as halogens. Isotopes are similar elements have different atomic masses. They are placed in different position. Isotopes are chemically similar, they had same position. Element of higher atomic masses has been placed before an lower atomic mass. E.g. cobalt (Co=58.93) is placed before nickel (Ni = 58.71). Some elements placed in the same sub group had different properties. E.g. Manganese is placed with halogens which totally differ in the properties. . MODERN PERIODIC TABLE:- The chemical and physical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. The periodic table based on modern periodic law is called as Modern Periodic Table. 5
- 6. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) EXPLAINATION / POSITION OF ELEMENTS IN THE MODERN PERIODIC TABLE:- Horizontal rows in the table are called as periods. Vertical column in the table are called as groups. Table consists of seven periods and eighteen groups. Periods are numbered from 1 to 7. Elements are present in the same period have same number of shells which is equal to the period number. In each period a new shell starts filling up. The first period is shortest period containing only 2 elements. Second and third are called as short periods. They contain 8 elements each. Fourth and fifth are long periods. They contain 18 elements each. Sixth period is the longest periods. It contains 32 elements. Seventh period is incomplete period. Groups are numbered from 1 to 18. Elements having same number of valence electrons or having same outer electronics configuration are present in the same group. Elements present in the same group show same chemical properties. Group1 contain alkali metals. Group2 contains alkaline earth metals. Group17 contains halogens. Group18 contains inert gases. 6
- 7. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Metals are present on the left hand side of the periodic table. Non-metals are present on right hand side of the periodic table. Group 1 and group2 are on left side. Group13 to froup17 are on right side of the periodic table. Such groups are called as normal elements. Their one outermost is incomplete. Group3 to group12 in the middle of the periodic table are called as transition elements. Their two outermost is incomplete. Group18 is on right hand side which contains inert gases. Their outermost shell contains eight electrons. Bottom elements are called as inner transition elements. Bottom elements contain two series of elements lanthanides and actinides. Elements are classified on the basis of their electronic configuration. Elements are divided into four blocks. S-block, p-block, d- block and f-block. Group1 and group2 are included in s-block. s-block elements are metals and contain 1 or 2 electrons. Group 13 to group 17 and 0 group are included in p-block. p-block elements are metals, non-metals and metalloids. And contain 3 or 8 electrons. s-block and p-block elements are called as normal elements. Outermost shell incomplete except 0 group. 7
- 8. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 0 group elements have complete outermost shell. They are called as inert or noble elements. Group3 to group12 are included in d-block. d-block elements are known as transition elements. d-block elements are metals. In the d-block Outermost shells incomplete. MERITS OF MODERN PERIODIC TABLE OVER MENDELEEV’S PERIODIC TABLE:- All isotopes of the same elements have different masses but same atomic number. Therefore they occupy the same position in the modern periodic table. When elements are arranged according to atomic numbers the anomaly regarding certain pairs of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table disappears. Elements are classified according to their electronic configuration. Into different blocks. PERIODIC PROPERTIES:- The properties which shows gradual variation in a group and in a period. They are repeat themselves after a certain interval of time. VALENCY:- It is determined by number of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. All elements of a group have same number of valence electrons. 8
- 9. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) They have same valency. Valency increases from 1 to 4 second for 2nd and 3rd period. Valency decreases from 4 to 0 when we go from left to right in the table. ATOMIC SIZE:- It is determined by atomic radius. For an isolated atom, atomic radius is the distance between the center of atom and outermost shell. Atomic radius decreases from left to right. Atomic radius increases from top to bottom. Increase and decrease is happen because of adding electrons. 9
- 10. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 2. THE MAGIC OF CHEMICAL REACTION COMBINATION REACTION: When two or more substances combine to form single product. It is said to be combine reaction. E.g. By combining Iron and Sulphur. We will get Iron sulphide ENDOTHERMIC REACTION: Reaction accompanied by absorption of eat are called Endothermic reaction. The reactants require heat to form products. Temperature of the solution falls. 10
- 11. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) EXOTHERMIC REACTION: It is the reaction in which heat evolved. Tis is known as exotermic reaction. Heat is evolved. DISPLACEMENT REACTION: When a more reactive element removes another element, having less reactivity, from its compound, these reactions are known as displacement reaction. DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION: Te reactions where a precipitate is formed by exchange of ions between the reactants are known as double displacement reactions. 11
- 12. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) OXIDATION REACTION: The chemical reaction in which reactants gain oxygen to form corresponding oxide is known as oxidation reaction. REDOX REACTION: When oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously in a given chemical reaction. It is known as redox reaction. CORROSION: The slow process f decay or destruction of metal due to the effect of air, moisture and acids on it is known as corrosion. Prevention of corrosion is always necessary. It will not only save the money but also prevent from accidents, damages etc 12
- 13. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It can be prevented by using solution, coating surface by paint, galvanizing and electroplating with other metals. RANCIDITY: When left over edible oil is heated, it starts frothing up and its smell turns foul. If food is cooked in this oil. Due to oxidation of oil, its taste changes. When oil and facts are oxidized or even allowed to stand for a long time, they become rancid. Antioxidants are used to prevent oxidation of food containing fats and oils. NEUTRALIZATION: Acid + alkali = salt +water This is neutralization. The yellow oily left over stains turns red / orange because of neutralization. Edible oils are compounds of alcohols and organic acids. Neutralization reaction is indicated by yellow (turmeric) turns into red. 13
- 14. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 3. THE ACID BASE CHEMISTRY INDICATORS:- The acidic and basic nature of the compound can be indicate by some natural as well as chemical substances. They are known as indicators. NATURAL INDICATORS:- Natural substances such as rose petals, turmeric, beet root, etc are known as natural indicators. SYNTHETIC INDICATOR:- some chemical substances like methyl orange, eosin, phenolphthalein are called as synthetic indicator. UNIVERSAL INDICATOR:- Mixture of several indicator is known as universal indicator. pH SCALE:- DIAGRAM:- pH scale helps to measure hydrogen ion concentration in solutions. 14
- 15. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) p stand for potenz (Means strength) and H stand for Hydrogen. pH scale start from 0 to 14. O (Most acidic) to 14 (most basic) The value of pH indicates acidic or basic nature of a solution. The strength of base is represented by pOH. When the pH value is in between 0 to 7 then solution is acidic in nature. When the pH value is in between 7 to 14 then solution is basic in nature. When pH value is exact 7 then solution is neutral in nature. When acids in aqueous gives more number of H+ ions then they termed as strong acids. The human body works within pH range of 7.35 to 7.45 NEUTRALIZATION: The reaction between acid and base to form salt and water is called as neutralization. Acid + Base = Salt + Water IONIZATION:-Separation of HCL into H+ and Cl- ions will be possible in presence of water. The process is termed as ionization. WATER OF CRYSTALLIZATION:- The droplets of water you observe on sides of the test tube are known as “water of crystallization”. 15
- 16. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Fixed number of water molecules present in the crystal structure. On heating or on exposure to air, salts lose water of crystallization and turn into substance which is termed as anhydrous substance. Water of crystallization is necessary for the maintenance of crystalline properties, but capable of being removed by sufficient heat. A salt with associated water of crystallization is known as a hydrate. SOAP AS A SALT:- When oils or fats are boiled with aqueous solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide, then sodium or potassium salt of carboxylic acids are obtained. These salts are called as soap. The process of alkaline hydrolysis of oil or fats is known as saponification. 16
- 17. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 4. THE ELECTRIC SPARK ELECTRIC CURRENT(I):- It is the flow of electrons through the conductor OR It is the amount of charge flowing through a particular cross sectional area in unit time. Unit of Current is ampere. ONE AMPERE: If one coulomb of charge is passing through any cross section of a conductor in one second. Then the amount of current flowing through the conductor is said to be one ampere. ELECTRIC CIRCUIT: A continuous path consisting of conducting wires, resistance and battery along with electric current flows. It is called as circuit. Diagram: 17
- 18. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: It is a diagram which shows the connection of different components in a circuit. It is called as circuit diagram. Diagram: Current is flows from positive to negative terminal. Diagram: POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE: It is the electrical difference between the two points. It is the ratio of work done to the quantity of charge transferred. Its unit is volt and denoted by “V” 18
- 19. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) ONE VOLT: if one joule of work is done in moving one coulomb of electric charge from one point to another. It is said to be one volt. OHM’S LAW: Diagram: “The ohm’s law states that, a current flowing through the conductor is directly proportional to voltage or potential difference and inversely proportional to the resistance. All physical conditions are constant like length, area of cross-sectional, temperature and material.” Where, V = Voltage or Potential difference = Unit: Volt I = Current = Unit: Ampere 19
- 20. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) R = Resistance =Unit:- Ohm ONE OHM RESISTANCE: If one ampere current flows through the conductor and one volt potential difference is applied across it. Ten it is said to be resistance one ohm. RESISTANCE: it is the property of conductor which opposes the flow of current. RESISTIVITY: JOULE’S LAW: The quantity of heat (H) generated in a conductor of Resistance (R), when a current (I) flows through it for a time (t), is directly proportional to: 1) The square of the current. 2) The resistance of the conductor and 3) The time for which the current flows. APPLICATION OF HEATING EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT: In an electric circuit, the unavoidable heating can increase the temperature of the components and alter their properties. Heating effect has many application like iron, toaster, oven, kettle, heater etc 20
- 21. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) An electric bulb consists of a filament. Filament becomes hot and emits light. Te bulbs are filled with chemically inactive nitrogen and argon gases to prolong the life of filament. An electric iron consists of a coil of high resistance by mica sheets. Mica sheet is bad conductor of electricity and good conductor of heat. Coil is placed in the block which is preventing from shock to the living. Fuse is used in electric circuit to prevent from excess flow of current. Fuse element melts when excess current is flowing through the circuit. In industry, soldering, welding, cutting, drilling and working of electric furnaces. In surgery a fine heated platinum wire is used for cutting tissues much more efficiently than a knife. ELECTRIC POWER: Electric power is rate of doing work per time. SI unit is Watt. It is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. ONE WATT POWER: If one joule of work is done per second then the electric power is one watt. RESISTANCE IN SERIES / PARALLEL:- See note book……. 21
- 22. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 5. ALL ABOUT ELECTROMAGNETISM MAGNETIC LINES OF FORCE: Diagram: It is the path along which the unit North Pole moves in a magnetic field is called magnetic lines of force. PROPERTIES OF MAGNETIC LINES OF FORCE: 1) They are closed continuous curve. 2) They start from North Pole and end on South Pole. 3) The tangent at any point on the magnetic lines of force gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point. 4) No two magnetic lines of force can intersect each other. 22
- 23. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 5) They are crowded at strong magnetic field. 6) They are weak at far from each other. RIGHT HAND THUMB RULE: “By holding a current carrying straight conductor in your right hand then thumb points towards the direction of current and curled fingers around the conductor will give the direction of magnetic field.” Diagram: SOLENOID: A coil of many turns of insulated copper wire wrapped in the shaped of cylinder is called a solenoid. Diagram: The magnetic field lines in a solenoid through which current is passed. These lines are similar to bar magnet. 23
- 24. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Properties are same as bar magnet. One end of the South Pole and other end of North Pole. If the rod is hard steel and magnetic field is strong then permanent magnet can be produced. Permanent magnets are made up of carbon steel, chromium steel, cobalt, tungsten steel and some alloy. FLEMING’S LEFT HAND RULE: “Stretch the forefinger, the central finger and thumb of your left hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger shows the direction of the field and central finger shows the direction of the current then the thumb will point towards the direction of the motion of the conductor.” Diagram: ELECTRIC MOTOR: Electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Diagram: 24
- 25. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) PRINCIPAL: A current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force. CONSTRUCTION: It includes armature coil, Strong magnet, Split ring commutator, Brushes and battery. 1) Armature coil: In the figure, ABCD is an armature coil. It is a large number of turns of a insulated copper wire. It is wound on iron core in rectangular shape. Armature coil placed in between two poles. 2) Strong magnet: There are two poles i.e. South and North Pole This magnet provides a strong magnetic field. 3) Split ring commutator: In the figure, There are two metallic rings R1 and R2 . Ends of the armature coils are connected to the rings. Commutator reverses the direction of current in the armature coil. 4) Brushes: In the figure, there are two brushes i.e. B1 and B2 25
- 26. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) They are used to press the commutator. 5) Battery: It is the source of energy. Battery supplies the current to the armature coil. WORKING: When current is passing through the coil ABCD. Side AB and CD experience the force by fleming’s left hand rule. Both the forces are equal and opposite. Force rotates the coil in clockwise direction until the coil is vertical. Contact between brush and commutator brakes. At this condition, coil supply is cut-off. No force is acts on the coil. But, coil does not stop due to inertia. It rotating until the commutator again comes in contact with the brushes. Again the current starts passing through coil. Thus, the coil rotates with the help of electrical energy. USES OF DC MOTOR: 1) They are used for domestic appliances and industries like Mixers. Blenders. Refrigerator. 26
- 27. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Washing machines. Electric fans. Hair dryers. Record players. Tape recorders. Blowers. Electric cars. Rolling mills. Electric cranes. Electric lifts. Electric trains. FLEMING’S RIGHT HAND RULE: “Stretch the thumb, forefingers and middle finger of the right hand so that they are perpendicular to each others. If the forefingers indicates the direction of the magnetic field and thumb shows the direction of motion of the conductor. The middle finger shows the direction of induced current.” DC VS AC:- Direct current Alternating current The magnitude and direction The magnitude and direction of current is constant. of current is reverses periodically. DC is not used for large scale. AC is used for large scale. 27
- 28. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Frequency of DC is Zero. Frequency of AC is about 50 Hz in India. It is not raised or decreases by It is possible to raised or using transformer. decreases by using transformer. ELECTRIC GENERATOR: It is an electric device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Diagram: 28
- 29. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) PRINCIPAL: it is work on the principal of electromagnetic induction. EXPLAINATION: When the coil of generator rotates in a magnetic field. Then magnetic field induces a current in this coil. This induced current is flows into the circuit connected to the coil. There are two types of Generator: 1) A.C. Generator 2) D.C. Generator A.C. Generator: It is an electric device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current. CONSTRUCTION: The main components are, 1) Armature coil 2) Strong Magnet 3) Split rings 4) Brushes 1) Armature coil: In the figure, ABCD is an armature coil. It is a large number of turns of a insulated copper wire. 29
- 30. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It is wound on iron core in rectangular shape. Armature coil placed in between two poles. 2) Strong magnet: There are two poles i.e. South and North Pole This magnet provides a strong magnetic field. 3) Split ring commutator: In the figure, there are two brass slit rings R1 and R2 . Ends of the armature coils are connected to the rings. Rings are rotates along with the armature coil. 4) Brushes: In the figure, there are two brushes i.e. B1 and B2 They are used to press the commutator. WORKING: Magnetic field is provided by strong magnets. When the armature coil rotates in the magnetic field. It cuts magnetic lines of forces. Changing magnetic field produces induced current in the coil. Direction of current is determined by Fleming’s Right Hand Rule. Current is flowing through brushes for half cycles for brush 1 to 2 Reverse direction is repeated. Induced current is alternating. This is called as alternating current. 30
- 31. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) D.C. Generator: It is an electric device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of direct current. It is also called as Dynamo. CONSTRUCTION: The main components are, 1) Armature coil 2) Strong Magnet 3) Split rings or commutator 4) Brushes 5) Bulb 1) Armature coil: In the figure, ABCD is an armature coil. It is a large number of turns of a insulated copper wire. It is wound on iron core in rectangular shape. Armature coil placed in between two poles. 2) Strong magnet: There are two poles i.e. South and North Pole This magnet provides a strong magnetic field. 3) Split ring commutator: In the figure, there are two metallic slit rings R1 and R2 . Ends of the armature coils are connected to the rings. Rings are rotates along with the armature coil. 31
- 32. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 4) Brushes: In the figure, there are two brushes i.e. B1 and B2 . They are used to press the commutator. 5) Bulb: Bulb is connected across carbon brushes. The output is shown by glowing bulb. WORKING: When coil of DC generator rotates in the magnetic field. Then potential difference is induced in the coil. This gives the rise to the flow of current. Current flows in the same direction of rotating magnetic field. Brushes are always contact with the arm of the armature coil. SAFETY MEASURE IN USING ELECTRICITY: 1. We can use fuse to protect from excess flow of current like short circuit. 2. We have to wear gloves to protect from shocks. Gloves are made up of insulated materials. 3. We have to wear rubber soled shoes to protect from shocks. 4. The insulation of wires must be checked periodically. 5. Earthing is very essential for appliances for stability and to protect from shocks. 32
- 33. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 6. Electric circuits should be switched off during lightining. To protect from burning. SHORT CIRCUIT: If the live wire and neutral wire touch each other then short circuit happens. At short circuit, resistance is very small. High current is passing during short circuit. Short circuit provides large amount of heat. Temperature will be increases and circuit catches fire. OVERLOADING: Large amount of current will flow beyond the permissible value of current. This causes the fire. At the same time, many appliances are switched ON, overloading is happened. Overloading can be avoided by not connecting many appliances at same time. 33
- 34. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 6. WONDERS OF LIFE PART-I 34
- 35. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 35
- 36. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) MIRROR FORMULA:- 1 1 1 f v u Where, f = Focal Length u = Object Distance V = Image Distance MAGNIFICATION FORMULA:- Magnification = Object((Height )) = h u M image Height h 2 v 1 SIGN COVERSIONS (Sperical mirror/):- Focal length of convex mirror is positive. Focal length of concave mirror is negative. 36
- 37. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Distance measured perpendicular to the above the principal axis are taken as positive. Distance measured perpendicular to the below the principal axis are taken as positive. Left side = positive and Right side = negative The object is always placed on the left side of the mirror. Refer table for nature of image (See note book / book). SIGN CONVERSION (Lens):- Focal length of convex lens is positive. Focal length of concave lens is negative. Distance measured perpendicular to the above the principal axis are taken as positive. Distance measured perpendicular to the below the principal axis are taken as positive. Left side = positive and Right side = negative The object is always placed on the left side of the lens. Refer table for nature of image (See note book / book). LENS FORMULA:- 1 1 1 f v u POWER OF LENS: 1 P f NOTE:- 37
- 38. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) If magnification is negative then height of image shows image is inverted and real. Used table “to find nature of image and use concept taught in the lecture. Use technique as per our lecture. 7. WONDERS OF LIFE PART-II REFRACTION:- The phenomenon of changes in the direction of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another is called as refraction. Velocity of light is different in different media. LAWS OF REFRACTION:- The incident ray and the refracted ray are on opposite sides of the normal at the point of incident and all three lie in the same plane. The ratio of angle of incidence and angle of refraction is constant. This constant is called as refractive index. Constant is denoted as sin I / sin r = constant 38
- 39. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 8. UNDERSTANDING OF METALS AND NON-METALS Physical properties of Metals: 1. Metals have lustre. 2. Metals are malleable and ductile. 3. Metals are Good conductors of heat & Electricity. 4. Metals are solids at Room temperature except Mercury & gallium. 5. Metals are not brittle. 6. Metals are strong. 7. Metals have high tensile strengths. 8. Metals have high melting and boiling points. Chemical properties of Metals: 1. Metals form electropositive ions in a reaction. 2. Metals react with air to form basic oxides. 3. Metals react with water to evolve hydrogen. 4. Metals reacts with acids to form salt and Hydrogen. 5. Metals are reducing agents as they donate electrons. 39
- 40. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Physical properties of Non-Metals: 1. Non-Metals are non-lustrous except Iodine. 2. Non-Metals are not ductile nor malleable. 3. Non-Metals are bad conductor of heat & electricity. 4. Non-Metals either solid or gaseous state. 5. Non-Metals are generally brittle. 6. Non-metals are not strong. 7. Non-Metals have low tensile strength. Chemical properties of Non-Metals: 1. Non-Metals form electronegative ions in a reaction. 2. Non-Metals react with water to form acidic oxides. 3. Non-Metals react with non-metals to form ionic compound. 4. Non-Metals reacts with acids to form salt and Hydrogen. 5. Metals are oxidizing agents as they accept electrons. Metalloids: Metalloids are the elements which possess both the properties of metal as well as non-metals. E.g. Silicon, Germanium, Antimony, etc. Lustre: Metals in their pure state have a shine and can be polished to give a highly reflective surface. Malleability: Metals have ability to withstand hammering and can be made into thin sheets. Such a property is called as Malleability. Ductility: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires is called ductility. E.g. Gold and Silver 40
- 41. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Sonorous: The metals that produce a sound on striking a hard surface are said to be Sonorous. Anodizing: It is a process of forming a thick oxide layer of aluminum. Minerals: The naturally occurring compounds of metals along with others impurities are called as Minerals. Ores: The minerals from which metals are extracted profitably and conveniently are called Ores. Gangue: Impurities like Soil, Sand, Rocky material etc are called Gangue. Metallurgy: The process used for extraction of metals in their pure from their ores is called Metallurgy. Roasting: The sulphide ores are first converted into oxides by heating strongly in excess of air. This process is known as Roasting. Calcinations: The carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air. This process is known as Calcination. Corrosion: is the disintegration of materials due to reaction with its environment. Galvanizing: It is process of giving a thin coating of zinc on iron or steel to protect them from corrosion. E.g. shiny iron nails, pins etc. Tinning: It is the process of giving a coating of tin. E.g. cooking vessels. Electroplating: In this process metal is covered with another metal using electrolysis. E.g. silver-plated spoons. 41
- 42. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Anodizing: It is process of metal coating electrically with a thin strong film of their oxides. Alloy: It is the homogeneous mixture of two or more metals pr a non metals in a definite proportion. E.g. Brass(cu +zinc), Bronze(cu + tin) , Stainless steel etc. Sodium is stored under kerosene: Sodium is a silver coloured metal reacts so violently with water that flames are produced due to formation of hydrogen gas. Sodium is potentially explosive in water and it is rapidly converted into sodium hydroxide on contact with moisture. Sodium hydroxide is corrosive substance. Gold & Silver are used to make jewellery: the following reasons are there: 1. They are not affected by air and water. 2. Silver and gold are very soft metals and can be moulded into different shapes. 3. They are very pure forms of metals so there are very little impurities. 4. They are not very reactive in open atmosphere i.e almost inert metals. 5. They have property to shin. 42
- 43. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points: Ionic compounds are basically the combination of a metal and a non-metal. High heat is usually required to break the bonds of ionic compounds. However, its high melting points and boiling points are part of the physical properties of ionic compounds. Diagram of extraction of aluminium: Methods of preventing rusting of iron: 1. Galvanizing 2. Tinning 3. Electroplating 4. Anodizing 5. Alloying Prevention of corrosion: corrosion can be prevented if contact between metal and air is cut off. There are two ways to prevent, 43
- 44. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 1. If metal is coated which does not allow moisture and oxygen. 2. Coating of metal with paint, oil, grease or varnish. 9. AMAZING WORLD OF CARBON COMPOUNDS 44
- 45. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Covalent bond: Bonds formed by sharing of electrons is called as Covalent Bond. A Single covalent bond is formed by sharing of two electrons. Organic compounds: Compounds directly or indirectly obtained from Plant and Animals. Properties of organic compounds: 1) Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points. 2) They are insoluble in water but soluble in other organic solvents. 3) They are poor conductor of heat and electricity. Inorganic compounds: Compounds obtained from minerals. Parent compounds: All organic compounds contain hydrogen along with carbon. Saturated Hydrocarbons: Carbon items are linked with other hydrogen atom by only single bonds. E.g. Alkane, Methane, etc Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Carbon items are linked with other hydrogen atom by double or triple bonds. E.g. Alkene, Alkyne etc Catenation: The remarkable property of carbon atom to form bonds with itself and give rise to a single large structure or chain is called catenation OR Catenation is the property of direct bonding between atoms of same element to form a chain. The carbon chain can be straight or branched. 45
- 46. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It is the property of direct bonding between atoms of same element to form a chain. Isomers: Compounds with identical (Same) molecular formula but different structure called Isomers and the property is known as isomerism. Functional Group: The atom or group of atoms present in the molecule which determine characteristics. Such a property of organic compounds is called the functional group. Homologous series: A group of organic compound containing same functional group which can be represented same general group is known as Homologous series. Characteristics of Homologous series: 1) General formula of all compounds in the series is the same. 2) They have same functional group. 3) Physical properties are changes with increase of molecular formula in the series. 4) Chemical properties are nearly same. 5) All connected members are differing from one another by – CH2 group. 6) Molecular weight differs by 14units. IUPAC: International Union Pure and Applied Chemist Alkane: Single bond of C-C in hydrocarbons. Alkene: Double bond of C=C in hydrocarbons. Alkyne: Triple bond of carbon in hydrocarbons. 46
- 47. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Functional Group: The atom or group of atoms present in the molecule which determines characteristics property of organic compounds is called as Functional Group. (-OH) group is known as alcoholic functional group. STRUCTURE OF BENZENE: C6 H 6 ISOMERS: Compounds with identical molecular formula but different structure is called Isomers. ISOMERISM: Property of isomers called as Isomerism. COMBUSTION: All hydrocarbon burn in air or oxygen to form CO2 and H 2O includes large amount of heat. 47
- 48. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) For example: ADDITION REACTION: It is the reaction in which two molecules react to form a single product is known as addition reaction. Addition reaction occurs only in unsaturated compounds. Double bond or triple bond compounds. For example: SUBSTTUTION REACTION: It is reaction in which one or more atoms are substitute in a molecule for another atom. For example: 48
- 49. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) REACTIONS WITH ETHYL ALCOHOL: (a) Action with sodium metal: When sodium metal react with ethyl alcohol. It gives hydrogen gas. Reaction: (b)Action with Phosphorous Trichloride: When ethyl alcohol react with phosphorous trichloride. It gives ethyl chloride.. Reaction: ETHANOIC ACID: Ethanoic acid is also known as acetic acid. Ethanoic acid = C2 H 4O2 It is a weak acid. 49
- 50. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It is colorless and corrosive liquid. It has pungent smell at ordinary temperature. Below 290 K, it solidilies to an ice. This ice is called as mass or glacial acetic acid. REACTION WITH ETHANOIC ACID: (a) Action with halogens: When acetic acid reacts with chlorine gives monochloroacetic acid. Reaction: (b) Action with metals: When acetic acid reacts with sodium or zinc. It gives sodium acetate with liberation of hydrogen gas. Reaction: (c) Action with Alcohol: 50
- 51. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) When acetic acid reacts with ethyl alcohol in presence of anhydrous ZnCl2 It gives ethyl acetate. Reaction: 10. LIFE’S INTERNAL SECRETS LIFE PROCESS: Nutrition, respiration, excretion, transportation, reproduction, sensitivity and growth are process which is common to all living beings are called as life process. NUTRIENTS: We get energy from food which contains several components called nutrients. On the basis of chemical nature: 1) Inorganic and 2) Organic Nutrients Inorganic Nutrients: Plant gets their nutrients from environments like soil. They convert into organic compounds by photosynthesis. Organic Nutrients: From animals but originate from plants. 51
- 52. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) AUTOTROPIC NUTRITION: The process of intake of nutrients by synthesizes their own organic food are called as Autotropic Nutrients. Such organisms are called as Autotrophs. Most of the plants are autotrophs. Heterotrophic Nutrition: The process of intake of nutrients by other organisms are known as Heterotrophic Nutrients. Such a organisms are called as Heterotrophs. HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM: Diagrams: Vertical section of human heart and others: Refer book NUTRITION IN HUMAN BEINGS: All the processes involved in nutrition in human beings take place by association of digestive organs called digestive system. 52
- 53. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Digestive system includes alimentary canel and digestive glands. Alimentary canel is long and extends from mouth to anus. The salivary glands, liver, pancreas and gastric glands are associated with alimentary canel. MOUTH: Alimentary canel starts with mouth. We eat different types of food from mouth. Mouth generates particles small in size. By enzymes, complex food converted into simpler molecules. Enzymes break down starch into a simple sugar maltose. Digestion starts from mouth. STOMACH: Stomach is present left side of the abdomen. 53
- 54. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) The partly digested food goes down into oesophagus into “J” shaped stomach. Food is pushed forward in the canal due to contraction and relaxation of the muscles. The gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach. It contains three gastric juices. They are hydrochloric acid, enzyme pepsin and mucus. The muscular walls of the stomach churn the food. The exit of the food from the stomach by sphincter muscle. Small amount of digested food pass through small intestine. SMALL INTESTINE: It is the longest part of the alimentary canal. It is about 5 to 6 meter. Its diameter is small. The length of small intestine is different for every animal. Carbohydrate, fats and proteins are digested in the small intestine. Food is made alkaline nature. The largest gland in the body secretes bile juice which is stored in the gall bladder. Bile makes the food alkaline. Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice. The bile and the pancreatic juice enter the small intestine through a common duct. 54
- 55. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Digested food is absorbed by small intestine having numerous fingers like projections called villi. Villi absorb the food are richly supplied with blood vessels. Absorbed food is supplied to entire body for an energy. LARGE INTESTINE: Unabsorbed food and the residue are sent to large intestine. It does not have any digestive function. It wall have villi to absorb salt and water. Rest of the material is removed from the body through the anus. PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Green plants synthesize their food during the process of photosynthesis. They taken in carbon dioxide and water then converted into carbohydrates (Glucose) in the sunlight, chlorophyll. The carbohydrates are provides energy. Carbohydrates are stored in the starch. 55
- 56. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Carbon dioxide enters into the leaves through stomata. Water is taken from soil. Chlorophyll present in the chloroplasts absorbs the radiant energy from the sunlight. Sunlight splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. They release the energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate) Energy produced is used to reduce carbon dioxide to carbohydrates. 56
- 57. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) All the steps are depends on conditions like time The photosynthesis is takes place in green plants only. Photosynthesis is takes place only in the presence of chlorophyll. Without carbon dioxide photosynthesis cannot take place. Raw materials of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. Sunlight, water, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll are required. Also require nitrogen, iron, phosphorus, magnesium for regulation, body building. Nitrogen is essential for synthesis of proteins. RESPIRATION: It is the process of release of energy from the assimilated food is called Respiration. RESPIRATION PROCESS: It is the complex process. An aquatic animal living in water uses oxygen dissolved in water. 57
- 58. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Amount of oxygen is less in water than air. Breathing is so fast in water than air. Terrestrial animals take up oxygen from the air. Respiratory organs are different for different animals. There is two phases. Breathing and cellular 1) Breathing or external respiration: Exchange of gaseous takes place. Air goes to lungs and expels the air containing more of carbon dioxide from the lungs to the outer environment. 2) Cellular or internal respiration: It is takes place in the mitochondria of the cells to release energy in the form of ATP. INHALATION: When the muscular diaphragm of the body relaxes then volume of the thoracic cavity increases. When volume of the thoracic cavity increases ten air pressure inside the cavity decreases. The outside air enters in the lungs through the nostrils. EXHALATION: When the diaphragm contracts or become covex the thoracic cavity decreases in volume. Lungs come to their original size. Forcing the air outside the lungs trough the same path but opposite direction. 58
- 59. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) HEART: Diagram: It is a muscular organ. Heart pumps blood. Heart is covered by pericardial membrane. Its weight is nearly 360gm. Heart have two chambers, left and right chamber. Chambers are used to prevent mixing of bloods. Separation of blood is essential for high energy. It is used to maintain body temperature. Each chamber is divided into two chambers. Upper and lower Upper chamber is called atrium. Lower chamber is called as ventricle. Human heart has four chambers. CIRCULATION OF BLOOD WITHIN THE HEART: 1) The muscles of the atria are relaxed. 2) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different organs via large veins. 59
- 60. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 3) Te left atrium receives oxygen rich blood from lungs. 4) The atria contract and pour the blood into respective ventricles which expand to receive the blood. 5) Left ventricle gets filled with oxygenrated blood right gets deoxygenarated blood. 6) The thick walled ventricles contract resulting in pumping out oxygenarated blood to the body through aorta. 7) Deoxygenarated blood from the right ventricle enters the lungs through the pulmonary artery for oxygenation. 8) The valve between the atria and ventricles does not allows to flow backwards. 9) Deoxygenarated blood enters the right part of the heart and again after oxygenation it enters the left part of the heart. So, blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle. This is known as double circulation. HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM: Diagram: 60
- 61. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It includes a pair of kidneys, pair of ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Kidneys remove the waste products from the blood and urine. Kidneys are two bean shaped structures located at the back of the abdomen and one on either side of the vertebral column. The main filtration unit in the kidney is a cluster of thin walled blood capillaries called as a Nephron. Each nephron has a cup shaped thin walled upper end called Bowman’s capsule. Bowman’s capsule contains a bundle of blood capillaries called glomerulus. Urea formed in the liver enters the blood. Blood containing filters through glomerular capillaries. The blood free from materials is taken to the heart through the renal vein. Nephron tubule reabsorbs water and useful molecules. The remaining fluid waste goes out from ureter. It is further stored in the urinary bladder. Kidneys are the major excretory organs in human being. Skin and the lungs also help in the process of excretion. A NEPHRON: Diagram: 61
- 62. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) The main filtration unit in the kidney is a cluster of thin walled blood capillaries called as a Nephron. Each nephron has a cup shaped thin walled upper end called Bowman’s capsule. Nephron tubule reabsorbs water and useful molecules. VERTICAL SECTION OF A KIDNEY: Diagram: Kidneys remove the waste products from the blood and urine. 62
- 63. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Kidneys are two bean shaped structures located at the back of the abdomen and one on either side of the vertebral column. Kidneys are the major excretory organs in human being. 63
- 64. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 11. THE REGULATORS OF LIFE Co-ordination:- All multi-cellular organisms have various tissue system and organ system. There should be perfect co-ordination between systems or organs. Co-ordination means orderly execution of the activities. This is for proper growth and development of an organism. Plants absorb water in which minerals are dissolved from the soil with the help of roots. There is loss of water for this process. This loss of water is known as transpiring. Transpiring is done by transpiring organs. Co-ordination in plants:- Plants are without nervous system or muscular system. The movements of plants are different than animals. The movements exhibited by plants in response to the stimulus. This response to stimulus is called as seismonastic movement. There is no growth. The movement of a seeding is because of growth. 64
- 65. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) If growth is prevented then seeding does not exhibit any movement. There are two types of movement.1) Dependent and 2) Independent Movement Dependent Movement:- Do result in their growth. In response to an external stimulus called as tropism or tropic movement. It grows in direction of source of light. The movement towards light from dark to light is called as phototropic movement. When light falls on a part of the plant, a hormone called auxin. Chemotropism is the movement of plant part in response to certain chemicals. Independent Movement:- Do not result in their growth. Movement depends on surroundings. Movements happens place different from place to place of touch. The electrical or chemical means to transfer information from one cell to another. Plant cells change their shape by entering water in them. The cells either swell or shrink. Co-ordination in human beings:- 65
- 66. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Different activities are taking place simultaneously. They need efficient and effective co-ordination. Co-ordination controlled by two mechanisms, (a) Nervous Control and (b) Chemical Control. The components of human nerves system are brain, spiral cord and the nerves. The nervous system divided into three systems. They are (1) CNS (Central Nervous System (2) PNS (Peripheral Nervous System and (3) ANS (Autonomic System) CNS consists of spinal cord and brain. CNS regulates all body activities. PNS includes nerves. Nerves form a network and spread throughout the body. As per the function of nerves, they are categorized as afferent and efferent nerves. Afferent carries impulses from sensory organs to brain. Efferent carries impulses from brain to sensory. The nerves are composed of neurons and neuroglia. Neurons cells are capable of creating and transmitting electrochemical impulses. During movements, muscles tissues doing best job. Muscle posses special kind of proteins. Muscles are capable to change their shape. 66
- 67. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Nervous tissue classified as 1) sensory neurons 2) motor neurons and 3) association neurons. Sensory neurons conduct impulses from the sense organs to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons conduct impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors organs like muscles and glands. Association neurons perform integrative functions of the nervous system. RELEX ACTION:- Any sudden action in response to some happening in the environment is called as reflex action. Without getting any sense or feelings we react. Sensation of pains. Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord, although the massages reach the brain. Nervous from all over the body meeting in a bundle such connection is called as spinal cord. Reflex arcs are evolved in animals. Thinking process is bit slows. Reflex arcs to more efficient for quick responses. CNS (Central Nervous System) It is composed of brain and spinal cord. It is delicate organ. The brain is protected organ called cranium or skull. 67
- 68. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Spinal cord is protected by vertebral column or back bone. Protective membranes called meanings. Meanings are present in the space between the soft CNS and the bone. Cavities are present in the brain known as ventricles. Long cavity of the spinal cord is called as central canal. The ventricles, central canal and space between the meanings are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CFS protects from mechanical shocks. Thinking process and others movements are done with the help of brain and muscles. The fore brain or cerebrum is the main thinking part of the brain. The brain is the complex organ. There are different areas for thinking, sensation, memory etc. Hind brain is responsible for coordinating the voluntary movements and maintaining the balance of the body. The chemical control:- The chemical control is brought about by chemical substances called hormones. Hormones are secreted by the endocrine glands also known as ductless glands. Ductless glands are without duct to transport their secretions. 68
- 69. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Hormones are directly released into the blood stream. Hormones reach everywhere in the body. The endocrine system shares its responsibility of control and co-ordination with the nervous system. Hormonal action is much slower and long lasting. Hormones are secreted according to the requirement. Hormones required mechanism for secretions. Sugar level of the blood falls, the secretion of insulin is reduced. DRAW :- NEURON 69
- 70. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 12. THE LIFE CYCLE Reproduction:- All living organisms produce individual (new single organism) of same species, new generation of the species from an existing individual. This fundamental characteristic of living things is known as reproduction. Reproduction is important to maintain number of individuals of a species. Reproduction is also important to prevent their extinction. Basic of reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions for creating copies of DNA. DNA copies are similar but not identical to the original. Types of Reproduction / Modes of Reproduction: 1) Asexual and 2) Sexual Explanation: 1) Asexual:- It involves one parent. One parent may be Unicellular and Multicellular. Cells divide mitotically (It is a type of cell division leading to growth and development). There is no fission of two different cells. The daughter cells produced by asexual reproduction. These cells are generally identical to the parent cells. Advantages: - Rapid reproduction. 70
- 71. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Disadvantages: - Lack of genetic variations. UNICELLULAR:- Unicellular reproduce by (1) Binary Fission (2) Multiple Fission and (3) Budding 1) Binary Fission:- Diagram of Binary fission in amoeba It is a method of asexual reproduction. It employed by most prokaryotes, some protozoa and some organelles within eukaryotic cells. Living cells divided into two equal or nearly equal parts. Both have potential to grow to the size of the original one. The plane of cytoplasmic division is through any plane in amoebae. Cytoplasmic division is simple binary fission. Some organisms fission occurs through a specific axes (Transverse or Longitudinal axis) 2) Multiple fission:- Diagram of multiple fission in Amoeba 71
- 72. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) During unfavorable condition, amoeba withdraws its pseudopodia. Psuedopodia almost round and secretes a hard covering called cyst. Inside the cyst nucleus divides into many nuclei by repeated division. Repeated division followed by division of cytoplasm. The cyst bursts to release daughter cells during favorable condition. 3) Budding:- Diagram of Budding in Yeast A form of asexual reproduction in living organisms in which new individuals form from outgrowths (buds) on the bodies of mature organisms. Yeast produce by budding. 72
- 73. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Yeast produce in which a small outgrowth is formed on the parental cell. The nucleus of the parental cell divides and one daughter nucleus migrates into the bud. The bud increases in size, separates and grows further. In unicellular, life process occurs in a single cell. In multicellular, life process occurs in different cell. Multicellular organisms have special organs and placed at definite place in the body. Complexity in reproduction increases with complexity in structure of organisms. MULTICELLULAR:- Multicellular reproduce by (1) Fragmentation (2) Regeneration (3) Budding (4) Vegetative Propagation and (5) Spore Formation 1) Fragmentation:- Diagram of Fragmentation in Spirogyra 73
- 74. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) When water and nutrients are available then Spirogyra grows and multiplies rapidly. The filament of spirogyra undergoes fragmentation resulting in numerous filaments. Cell enlargement and subsequent mitosis, each fragment grows and develops into a mature filament. 2) Regeneration:- Diagram of Regeneration in Planaria The capacity to regenerate is very high among some animals. They can reconstruct entire body from the isolated body cells. Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells. These cells proliferate and make large number of cells. Regeneration is not same as reproduction. 3) Budding:- Diagram of Budding in hydra When hydra matured then it will be fed. 74
- 75. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Its bodywalls begins to form a rounded growth from the stalk of the adult. This growth is called as bud. Bud is develop in time into a miniature hydra. The body layer, body cavity and digestive cavity of young hydra are continuous with that of the parent. After development of hydra, base of new hydra seal off. 4) Vegetative Propagation Diagram of Vegetative Propagation When new plants are produced from the Vegetative parts called as Vegetative Propagation. Vegetative parts like roots, stems, leaves and buds) All plants produced by Vegetative Propagation are similar to the parent. They are produced from a single parent. 75
- 76. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Plant produced by Vegetative Propagation takes less time to grow and bear flower, fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. 5) Spore formation:- Diagram of Spore formation The hyphae of bread mucor (mould) are thread like structures. The mucor forms spores inside a sporangium. When spores are ready to leave the sporangium, it breaks open. If they land in moist place, they germinate to form new mucor or mould. 2) Sexual:- 76
- 77. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It involves two parents. Parents are male and female. There are two main processes (1) Meiosis and (2) Fertilization. There is fusion of two germ cells. Offspring’s produced by sexual reproduction are different from parents. Variations give rise to variety and diversity. Variation enables organisms to adapt and survive in the changing environment. (1) Meiosis:- It is a process in which having number of chromosomes takes place resulting in the formation of haploid gametes. It has chromosomes (2n to n). (2) Fertilization:- It is the process in which male gamete fuses with female gamete. Resulting in the formation of diploid zygote. It restores the number of chromosomes (2n). MALE / MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM:- 77
- 78. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Testes and penis are main organs of male reproductive system. Male produces Sperms or Male germ cell. Male germ cell and egg is combining to develop into new individuals. TESTIS:- It produces sperms or male germ cell. Sperms can be form at low temperature. Testes are located outside abdominal cavity in the scrotum. Testes secrete the hormone testesteron. Epididymus:- Immature sperms travel for development and storage. 78
- 79. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Vas Deferens:- It is the passage for sperms towards urethra. Seminal vesicle and Prostate glands:- They produce ejaculatory fluid which helps the sperm in transport and provides nutriention. Penis:- It delivers the sperms for fertilization. Sperms:- It consists of one head, one mitochondria and one tail. Head is upper part. Head carries genetic information. Mitochondria is middle part. Mitochondria for energy production. Tail is lower part. Tail helps for movements towards female germ cells. FEMALE / FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM:- 79
- 80. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Vagina, uterus, oviduct and ovaries are the main organs of female reproductive system. Female produces Egg. Male germ cell and egg is combining to develop into new individuals. VAGINA:- It is the muscular tube. It is extends from vaginal opening to uterus. It provides route for the menstrual blood to leave the body during menstruation. It is the path for sperms. It is the path for childbirth. UTERUS:- It is the muscular organ. 80
- 81. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) It has strong muscles. It has ability to expand and contract. It can push the baby during labour. OVIDUCTUS:- It connects uterus to the ovary. OVARIES:- Two oval shaped organs lie to the upper left and right of the uterus. They develop and release eggs into the oviduct. They secrete hormone estrogen which brings about changes in Girls during puberty. After baby born, there are thousands of immature eggs which remain inactive till maturity. MENSTRUATION:- Some time egg is not fertilized. Unfertilized egg along with blood and mucous comes out from uterus. This is called as menstruation. Menstruation is lasts from three to five days. The importance of variations: Variation changes in ecological system Ecological system means varying system, varying water level etc. Ecological system is beyond our control. 81
- 82. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Water level can wipe out a species. Variation is suitable for some individuals. Some individuals can survive because of variation for new environment. DIAGRAMS (Theory from book / note book) LONGITUDINAL SECTION OF TYPICAL FLOWER:- GERMINATION OF POLLEN ON STIGMA:- 82
- 83. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) NEEDS FOR AND METHOD OF FAMILY PLANNING:- LARGE FAMILY There are many disadvantages. Finance problems. As the population increases, decreases the per capita income and natural recourses takes place. General health is going down. Economical burden increases on nation. Large family affect both individual and community life. Lack of better education. Economic pressure. Insufficient medical care and low nutrition. SMALL FAMILY 83
- 84. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) there are many advantages. Family planning saves lives. For birth control. Everything is perfect and opposite of large family. General health is going smooth. No Economical burden increases on nation. Not affects both individual and community life. Better education. No more Economic pressure. No Insufficient medical care and high nutrition. METHODS The WHO has prepared guidelines and considered reproductive health as a fundamental human right. Concentration to avoid pregnancy. Keep sexual health by condoms, oral pills, copper-T etc Organize sex education to learn AIDS dieses and protection etc POLLINATION:- There are two types of pollination. 1) Self Pollination and 2) Cross Pollination Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma. Pollination is occurs in same flowers or same flowers in same plant is called self pollination. 84
- 85. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Pollen is transfer from one flower to another plan flower is called as cross pollination. The agents of cross pollinations are wind, water or animals. FERTILIZATION:- It is the process in which male gamete fuses with female gamete. Resulting in the formation of diploid zygote. It restores the number of chromosomes (2n). After the pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates. The pollen tube grows tube out from a pollen grain. Pollen grain travels through style to reach ovary. 85
- 86. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Each pollen tube contains two male gametes and releases them near the egg. One male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form zygote. The second male gamete fuses with secondary nucleus in the embryo sac to form endosperm. This is called double fertilization. The zygote develops into embryo and endosperm serves as nutritive tissue for the growing embryo. This embryo is capable of growing into a new plant. GERMINATION: After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops into seeds. The ovary develops into the fruits. The seed contains the future plant. It develops into the seeding under appropriate condition. This process is known as germination. 86
- 87. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) 13. MAPPING OUR GENES INHERITANCE:- The process of genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. Members of a generation inherit the characters from the members of the previous generation. Same basic design with minor changes in it for next generation. In asexual mode of reproduction, the individuals produced are very similar to one another and are with very minor difference. Difference is due to small inaccuracies involved in DNA copying. In sexual reproduction, greater diversities will be generated. HEREDITY:- It is the transmission of traits, physical or mental, from parents to offspring. The offspring of dogs are dogs only. The offspring of pigeons are pigeons only. The offspring of human are human only. MENDEL’S LAWS FOR INHERITANCE OF TRAITS:- 87
- 88. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) The law is based on equal contribution of both the mother and father for equal quantity of genetic material to the child. Equal contribution is required from parents. Mendel’s experiment is based on a number of visible contrasting characters of garden peas pisum sativum like tail or short plants etc. Mendel chose pea-plants with different characteristics like plant bearing red flowers and white flowers for his experiment. He calculated the percentage of plants with red and white flowers from offspring (Progeny). MENDEL’S MONOHYBRID CROSSES:- It is the only one pair of contrasting characters or traits. These crosses are termed as “Monohybrid Crosses”. Parental Generation (P1):- He obtained pea-plant with round and yellow seeds. Pea-plant bearing wrinkled and green seeds. One parent = Round shaped seed (RR) and yello coloured seed(YY) = DOMINANT Other parent = Wrinkled seed(rr) and Green coloured seed(yy) = Recessive P1 generation each pair of genes (RR or YY) segregates independently from other. RRYY plants can produce only RR or YY or RY gamets. Rryy plants can produced only rr gamets. 88
- 89. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) First Filial Generation(F1):- The F1 plants are called dihybrid. The F1 plants produce four types of gamets. They are ry, RY, rY and Ry out of RY and ry are similar to P1 gamets. RY and ry are known as parental combination. rY and Ry are called as recombination. With F1 generation plants undergo self pollination. They give rise to second filial generation (F2) Second filial Generation(F2):- The four types of male gametes and four types of female gametes give rise to 16 mating combinations. Male gametes are arranged on top of the board and female gametes on the side. Proportion of different types of the F2 individuals are represents on the Punnett square and not their actual numbers. EVOLUTION:- Varieties of organs are nearby. Organisms changes with organs with times. Every plants or organs are well adapted by environment. Organisms have some salient features to acclimatize to their environment. Organisms are dying if they are unable to adjust with surroundings. 89
- 90. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) Variations are passed from one generation to next generation. Difference in the variations, different individuals would have different advantages. Selection of variants by the environment factors forms the basis for evolutionary processes. There are more than one crore species found on earth. Life is present on all part of the earth from equator to the poles in the air, soil, sea , wood etc Till date there are many theories have been proposed to explain the origin and diversity of life. The theory of “Evolution of Life: is the most widely accepted. DRAW:- Structure of DNA 90
- 91. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) DETERMINATION OF SEX:- There is a genetic or chromosomal mechanism for determination of sex. Some animals se are depend on environment. Therefore they fertilized eggs for temperature. Sex determination in the human being is genetically. Sex can be determined by genes. In human being, there are 46 chromosomes. 23pairs out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and 1 is sex chromosomes. In male, longer “X” chromosomes and shorter “Y” chromosomes are presents. In female, two similar chromosomes are presents. Child is depends on both male or female 50% All children inherit “X” chromosomes from their mother. Sex of the offspring is determined by chromosomes inherit from father. If it is “X” then daughter and if “Y” then it will be son. Draw figure from book:- 91
- 92. SSC- Science vijayraskar2003@yahoo.co.in / vijay.raskar1986@gmail.com Prepared by Vijay Balu Raskar (MBA-Operation & B.E.Electrical) ALL THE BEST Dattadeep Classes Student 92
