Electrical Heating 01 - 03
•Download as PPSX, PDF•
16 likes•12,259 views
Electrical Heating Part - 01-03
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Medium-Voltage, Gas-Insulated Arc-Resistant Switchgear Types 8DA10 & 8DB10

Medium-Voltage, Gas-Insulated Arc-Resistant Switchgear Types 8DA10 & 8DB10
Switchgear and protection lecture 2 type of circuit breakers and applications

Switchgear and protection lecture 2 type of circuit breakers and applications
Practical HV and LV Switching Operations and Safety Rules

Practical HV and LV Switching Operations and Safety Rules
Similar to Electrical Heating 01 - 03
Similar to Electrical Heating 01 - 03 (20)
INDUCTION HEATING BY HIGH FREQUENCY RESONANT INVERTERS

INDUCTION HEATING BY HIGH FREQUENCY RESONANT INVERTERS
More from Vijay Raskar
More from Vijay Raskar (16)
Recently uploaded
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Recently uploaded (20)
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx

Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Electrical Heating 01 - 03
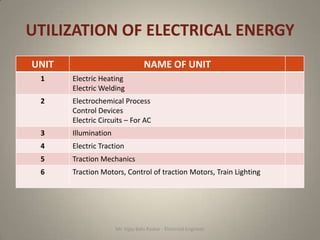
- 1. UTILIZATION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY UNIT NAME OF UNIT 1 Electric Heating Electric Welding 2 Electrochemical Process Control Devices Electric Circuits – For AC 3 Illumination 4 Electric Traction 5 Traction Mechanics 6 Traction Motors, Control of traction Motors, Train Lighting Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 2. Introduction utilization of electrical energy Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 3. WHAT IS ELECTRIC HEATING ? WHAT IS THE PRINCIPLE BEHIND IT ? Electric heating is any process in which ELECTRICAL ENERGY is converted to “HEAT ENERGY”. Electric heating works on the principle of ”JOULE HEATING” (an electric current through a resistor converts electrical energy into heat energy.) Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 4. INTRODUCTION Electrical heating is based on the principle of that when electric current passes through a medium heat is produced. Let us take the case of solid material which as resistance ‘R’ ohms and current flowing through it is I amps for ‘t’ seconds than heat produced in the material will be H=I²Rt Joules. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 5. DOMESTIC APPLICATION OF ELECTRICAL HEATING Room heater for heating the building Immersion heater for water heating Hot plates for cooking Geysers Electric kettles Electric Iron Electric oven for baking products Electric toasters etc… Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 6. INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION Melting of metals Electric welding Mouldling of glass for making glass appliances Baking of insulator Mould ling of plastic components Heat treatment of pointed surpasses Making of plywood. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 7. ADVANTAGES OF ELECTRICAL HEATING OVER OTHER METHOD OF HEATING • Clean and atmosphere / Free from dirt. • No pollution / No flue gas is produced • Response quickly • Accurate Controlled temperature can made easily • Comparatively safe • Localized application • Overall efficiency is much higher • Uniform heating • Highest efficiency of utilization • Cheap furnaces • Mobility of job Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 8. TRANSFER OF HEAT Conduction:- This phenomenon takes place in solid, liquid and gas. Heat transfer is proportional to the difference of temperatures between two faces. No actual motion of molecules. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 9. Convection This phenomenon takes place in liquid and gas. Heat is transferred due to actual motion of molecules Radiation This phenomenon is confined to surfaces. Radiant energy emitted or absorbed is dependent on the nature of the surface. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 10. CLASSIFICATION OF ELECTRICAL HEATING Power Frequency heating High Frequency heating 1. Resistance heating 1. Induction heating a. Direct Resistance heating a. Direct Core type Induction heating b. Indirect Resistance heating b. Core less type induction heating 2. Arc heating 2. Dielectric heating a. Direct Arc heating b. Indirect Arc heating Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 11. Classification of Heating Method:- Low Temperature Heating ± up to 400°C Medium Temperature Heating ± from 400°C to 1150 °C High Temperature Heating ± above 1150 °C Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 12. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 13. RESISTANCE HEATING (Example – Electric Water Heater) This method is based upon the I²R loss. Whenever current is passed through a resistor material heat is produced because of I²R losses. The generation of heat is done by electric resistor carrying current. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 14. Characteristic Features of Heating Elements 1) high resistivity 2) able to withstand high temperatures without deterioration 3) low temperature coefficient of resistance 4) positive temperature coefficient of resistance 5)free from oxidation at high temperatures Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 15. RESISTANCE HEATING DIRECT HEATING INDIRECT HEATING • Electric current is passed • Electric current is passed through highly resistive through the body (charge) material(heating element) to be heated. placed inside an oven. • High efficiency • Heat produced due to I2R loss • Example- in the element is transmitted to the body 1) Electrode boiler for • Mode of heat transfer is heating water Conduction &/or Convection 2)Resistance Welding &/or Radiation • Example- 1) Room Heaters 2) Domestic & commercial cooking 3) Heat treatment of metals Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 16. 1. DIREDCT RESISTANCE HEATING Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 17. 2. INDIRECT RESISTANCE HEATING Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 18. CAUSES OF FAILURE OF HEATING ELEMENTS Formation of hot spots. Oxidation Corrosion Mechanical failure Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 19. DIELECTRIC HEATING Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 20. Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, RF heating, high-frequency heating and diathermy. Dielectric heating is a special way of transforming electric current into heat. By the method of dielectric heating, generally, foils, plates and profiles with a thickness of 0,1- 2,0 mm is are welded. We understand dielectric heating as the generation of thermal energy (heat) in a non- conducting material by the application of an electromagnetic force or field t it. This is the Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
- 21. Mr. Vijay Balu Raskar - Electrical Engineer
